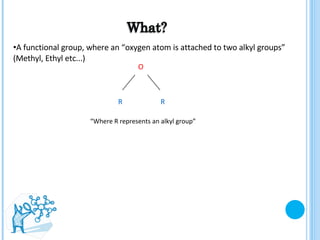
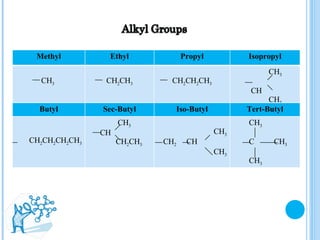
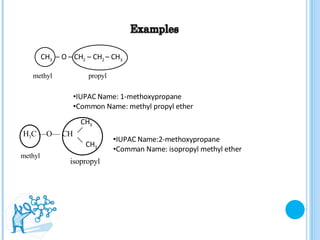
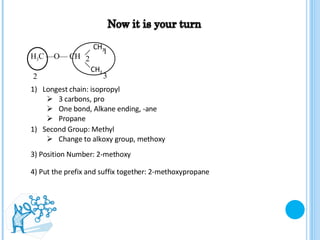
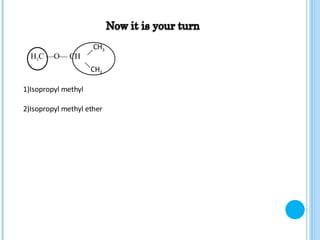
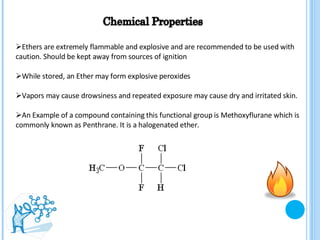
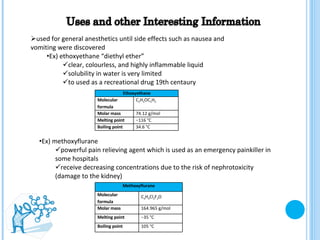
The document discusses ethers, which are organic compounds that contain an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl groups or aryl groups. It provides examples of common ethers such as diethyl ether, ethoxyethane, and methoxyflurane. It discusses the IUPAC naming conventions for ethers and their properties such as being flammable, soluble in water due to polarity, and having lower boiling points than other polar compounds. Uses of some ethers mentioned include as anesthetics, recreational drugs, lubricants, and industrial solvents.