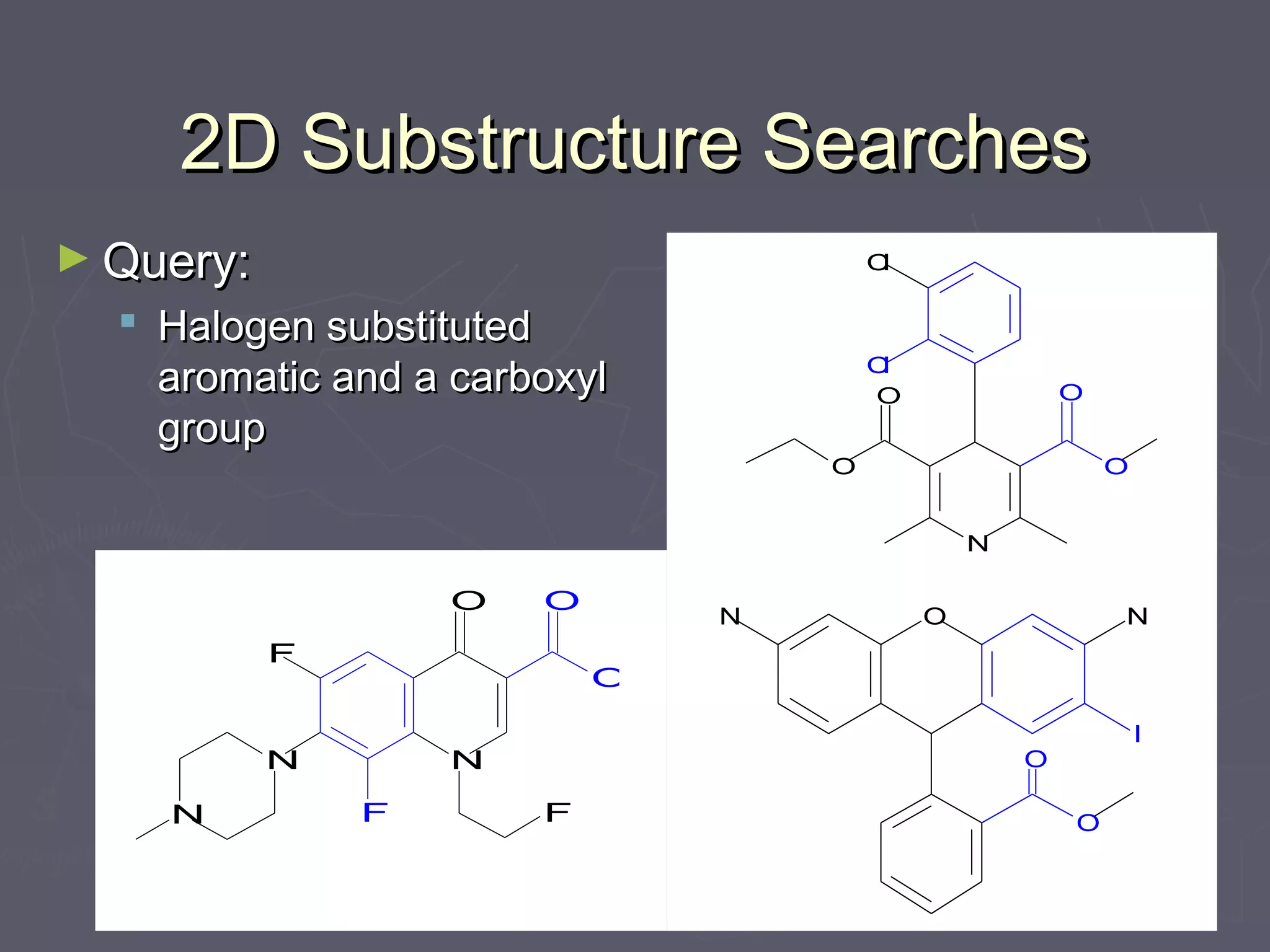
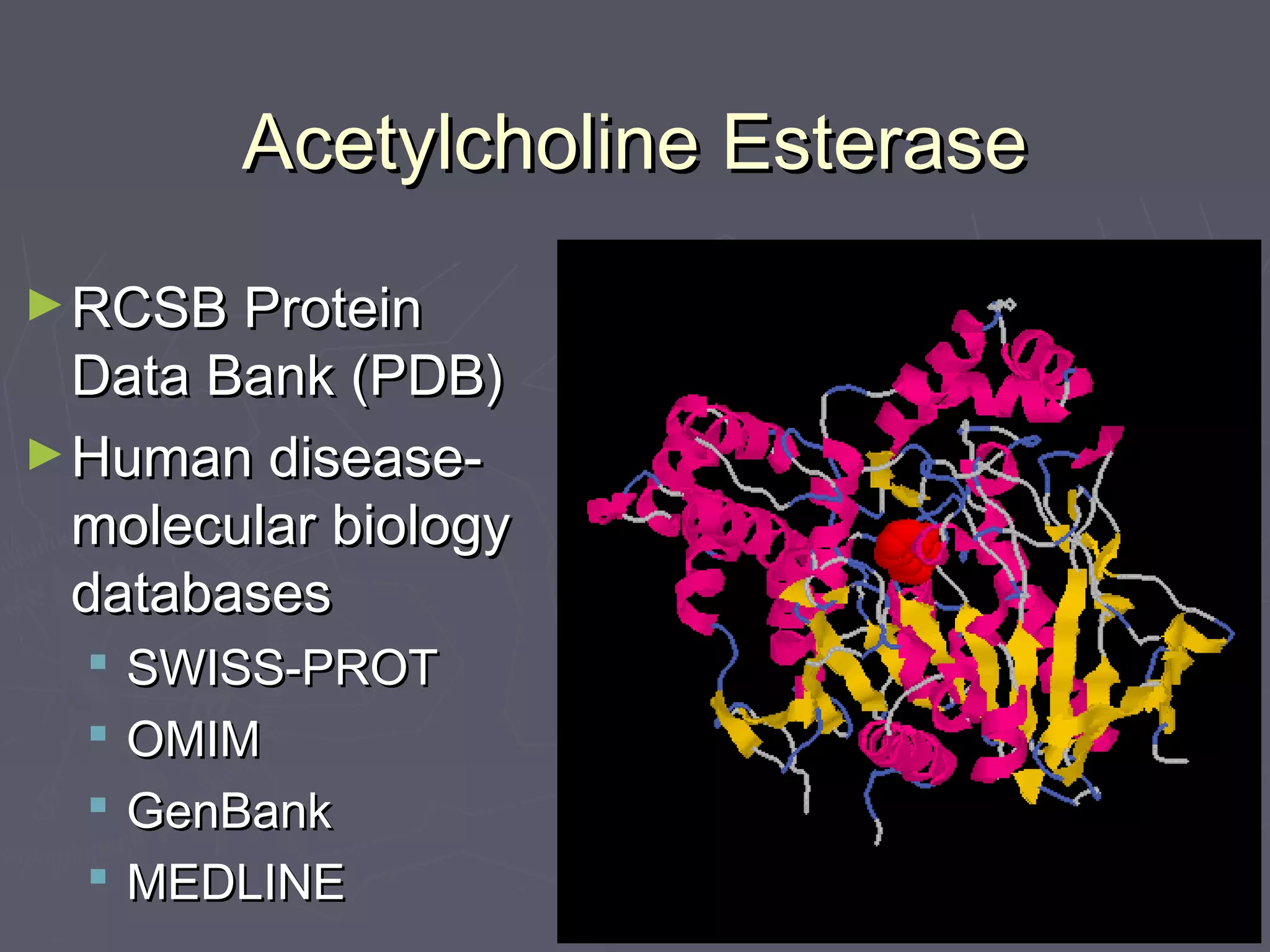
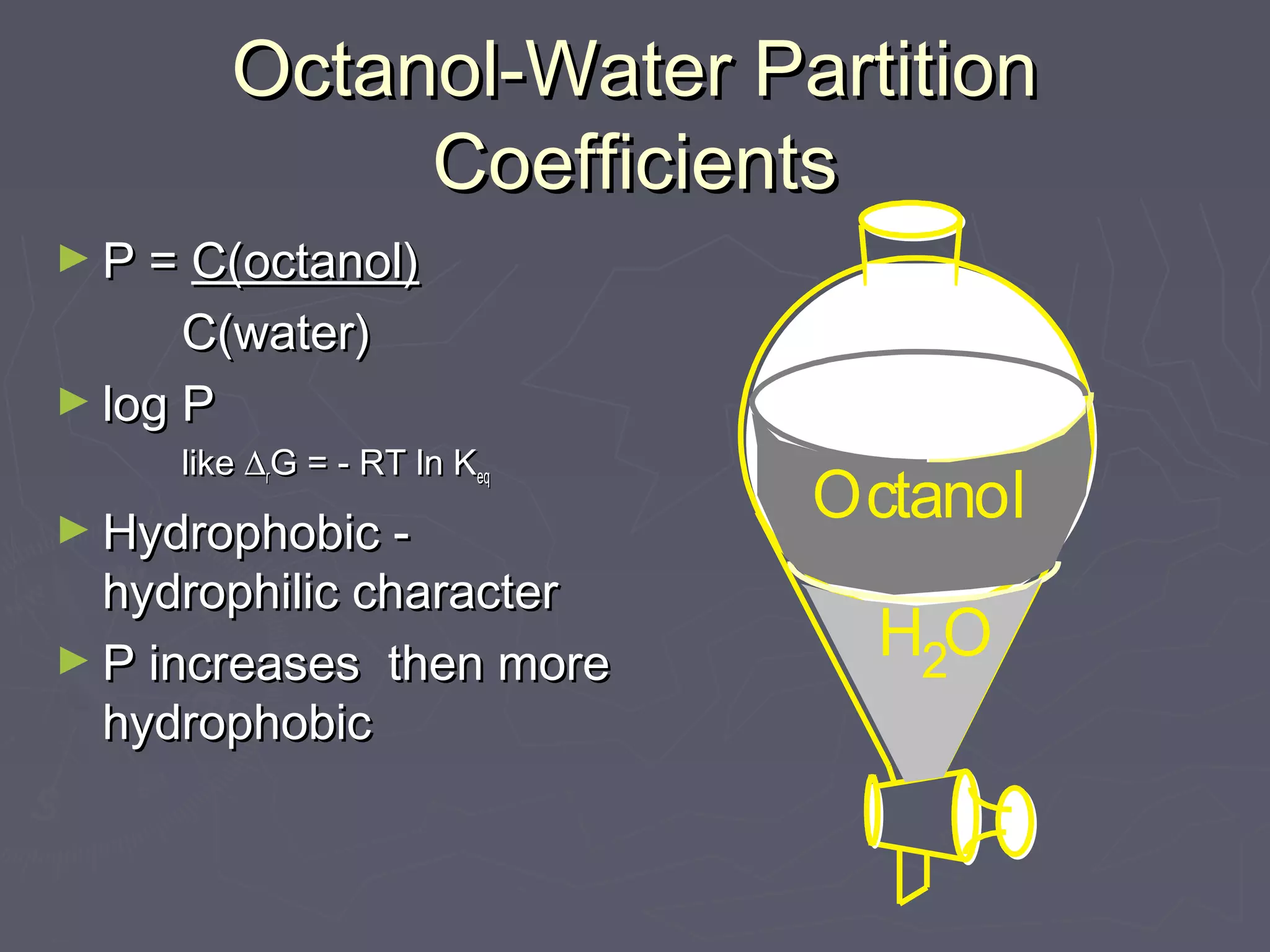
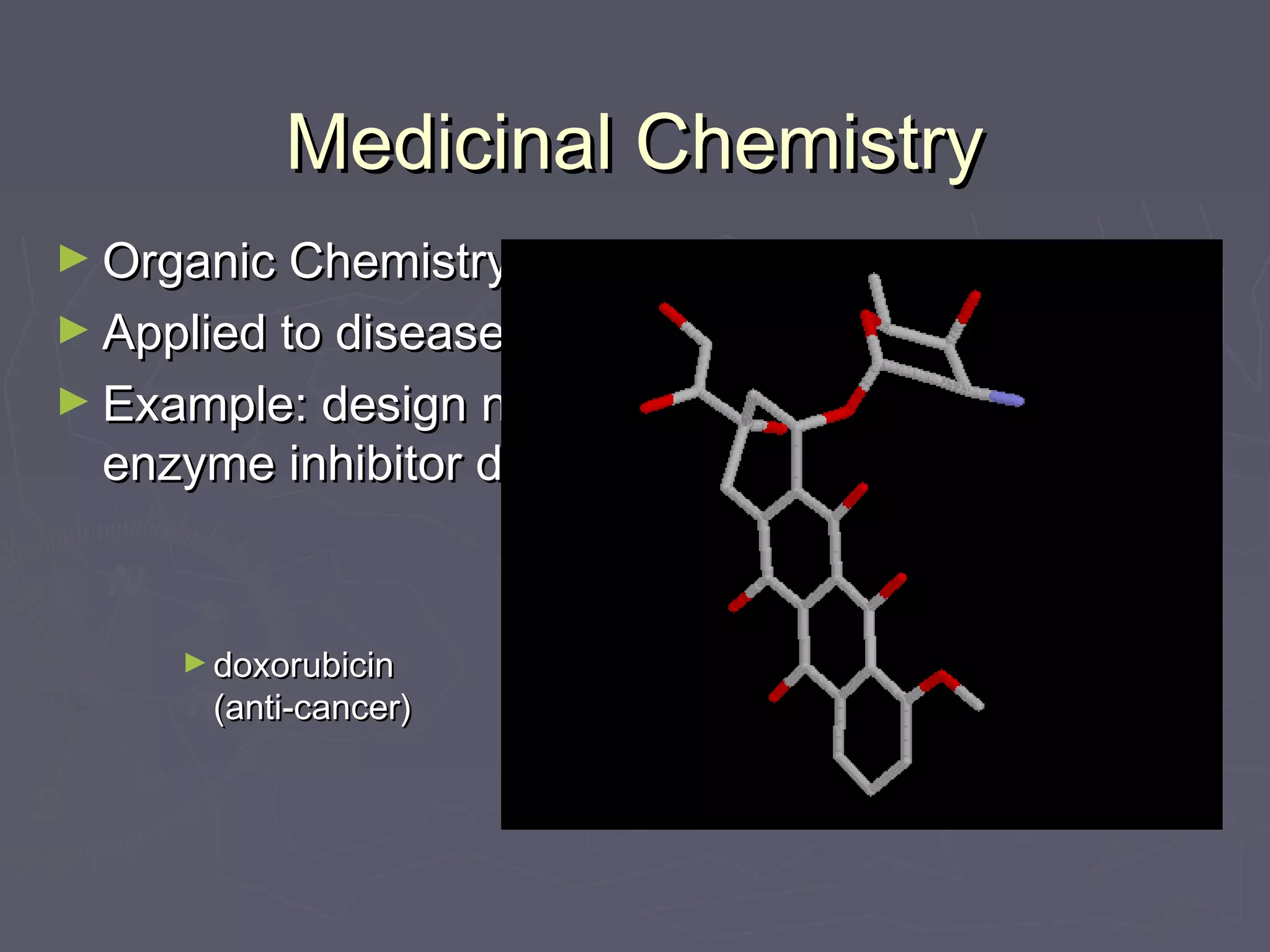
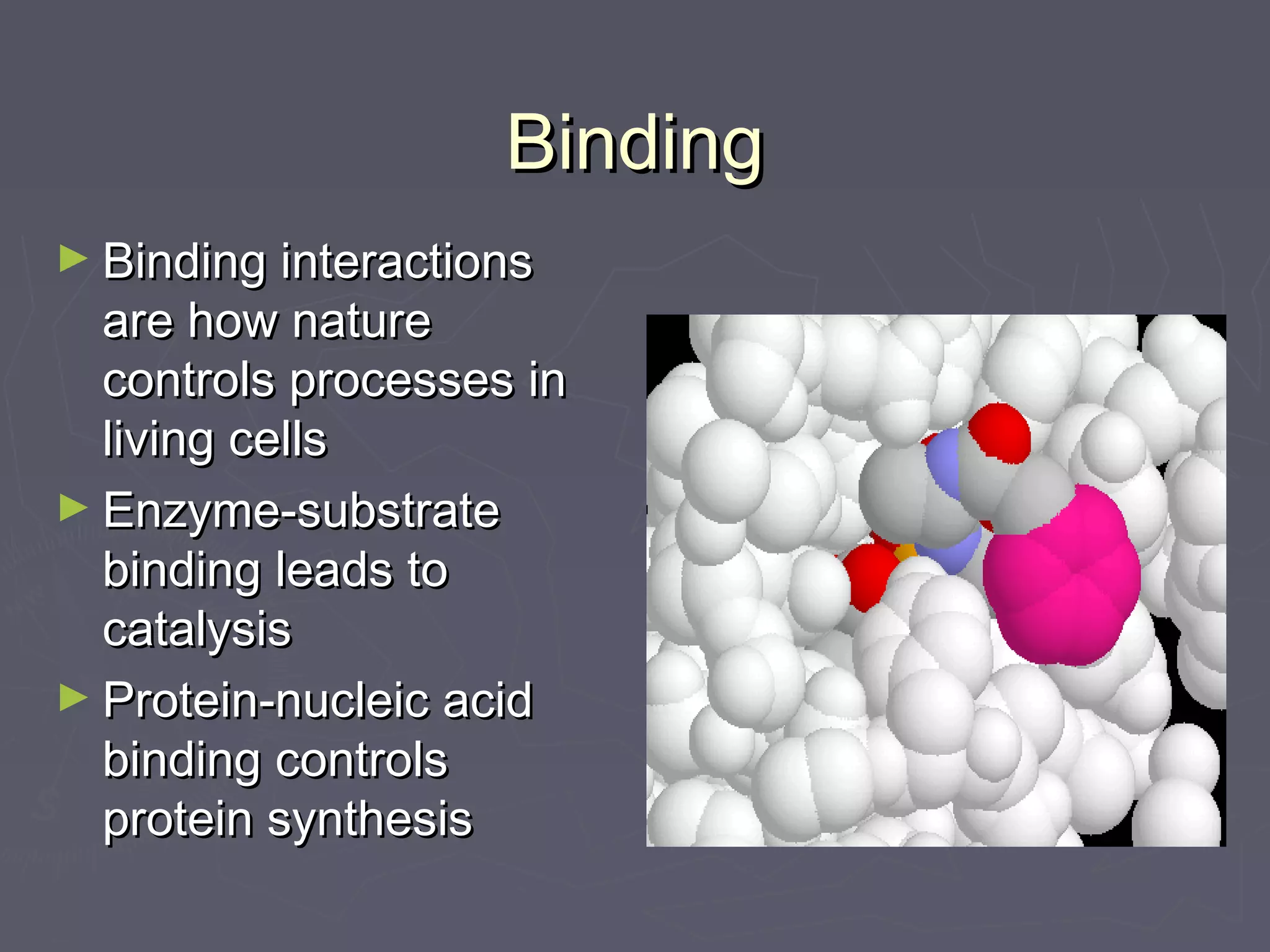
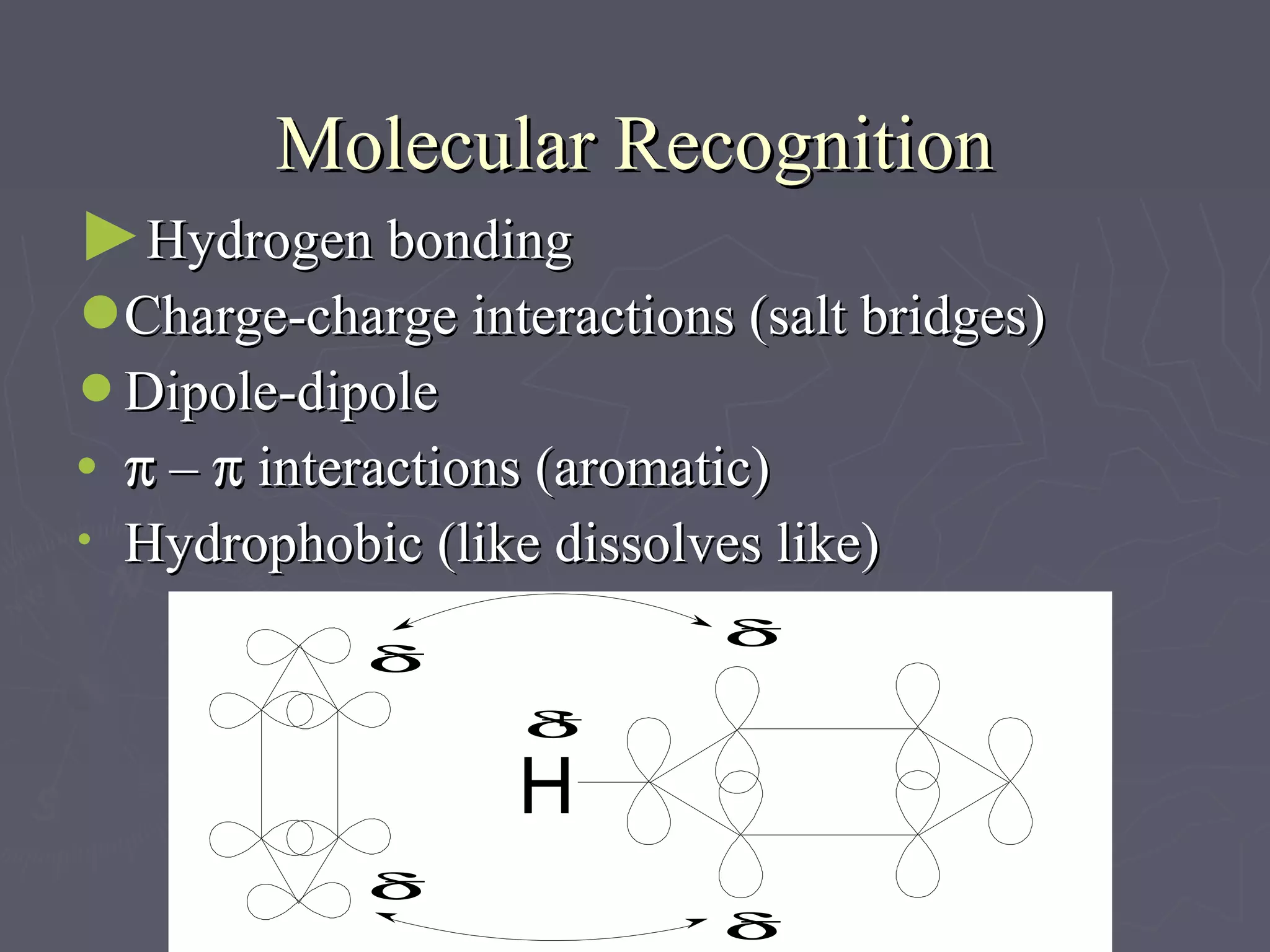
This document discusses molecular design and computer-aided molecular design. It covers topics like medicinal chemistry applied to diseases, designing new enzyme inhibitor drugs like doxorubicin. Natural products chemistry and examples like penicillin and taxol are also mentioned. Principles of molecular recognition involving hydrogen bonding, charge interactions, and hydrophobic effects are summarized. Computer-aided molecular design techniques like quantitative structure-activity relationships are also discussed. Specific examples involving acetylcholine esterase and using log P values to understand hydrophobicity are provided.





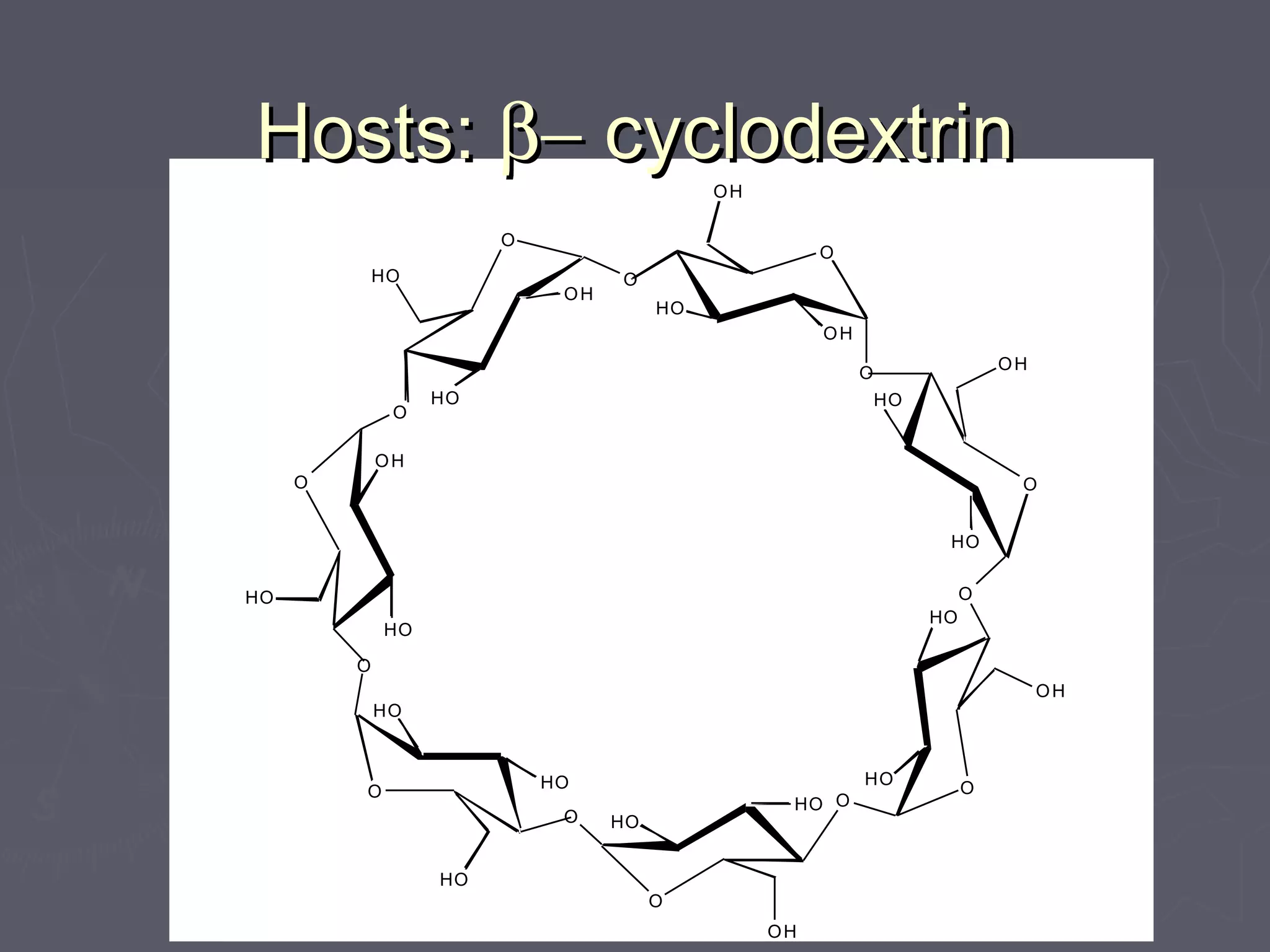
![Hexasulfo-calix[6]arenesHexasulfo-calix[6]arenes
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
OH
S
S
S
S
S
S
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
O
OO
O
O
O
O
O
O
O](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/moleculardesign-3028-150131123229-conversion-gate01/75/Molecular-design-10-2048.jpg)