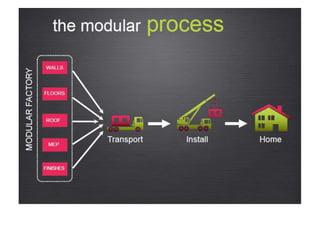
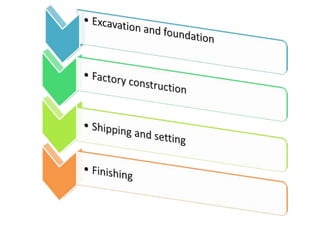
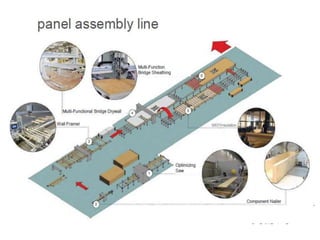
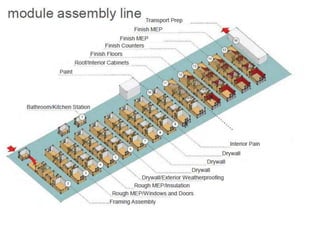
A modular home is a factory-built residence assembled on-site, differing from traditional homes in construction speed and efficiency, often completed within weeks. These homes meet specific codes that can exceed those of site-built homes and allow for personalized features while minimizing waste and environmental impact. Modular homes offer advantages such as quick assembly, reduced weather-related delays, and flexibility for future expansion.