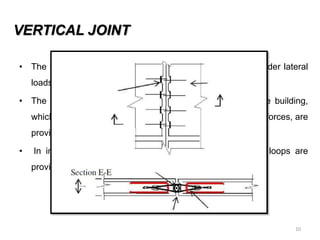
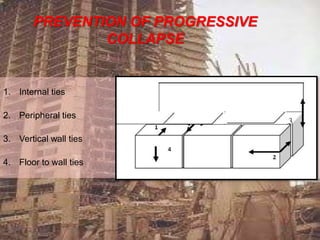
This document discusses a case study of the Pragati Towers residential building in Mumbai, India that utilized prefabricated construction. The building used precast concrete panels for the walls from the 1st to 23rd floors that were constructed in a factory and transported to the construction site. Analysis of the building found that modeling the vertical joints between precast panels as either integrated joints that allow shear transfer, or discrete gaps that do not allow shear transfer, produced different structural behavior results. Prefabricated construction provided benefits such as quality control, reduced construction time, and environmental efficiencies.