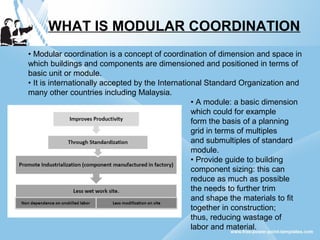
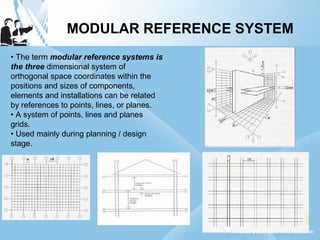
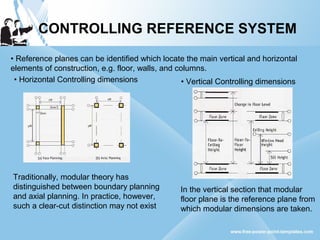
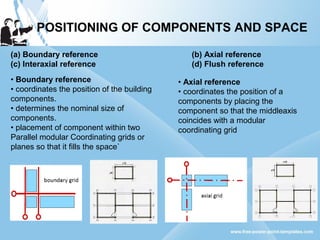
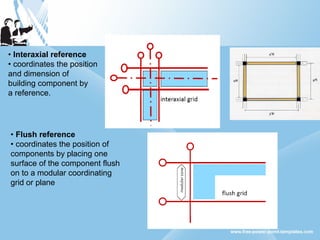
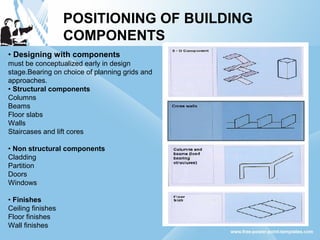
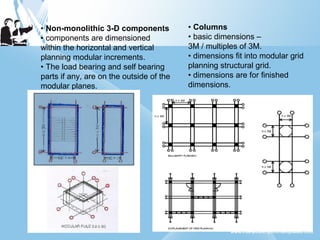
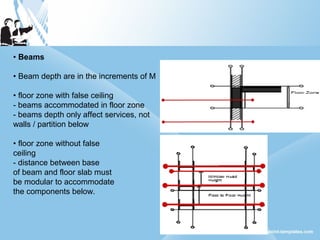
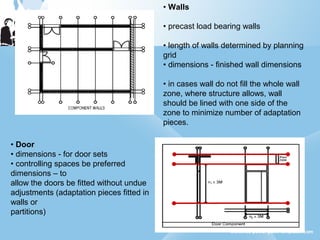
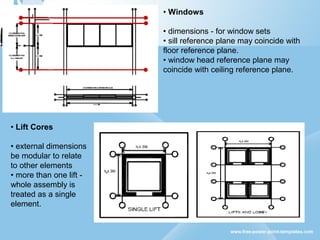
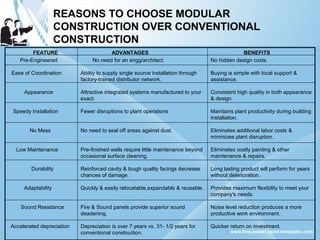
Modular construction involves prefabricating building components at a factory and transporting them to the construction site. It offers advantages over conventional construction like cost savings of up to 35%, speedier installation, less waste of materials, and reusability/relocatability of components. Modular coordination is an important concept in modular construction that standardizes dimensions and positioning of building elements in relation to basic modular units for efficiency and industrialization.