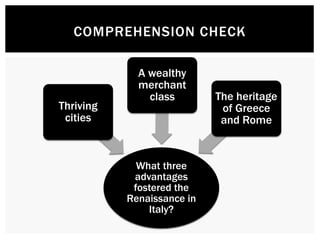
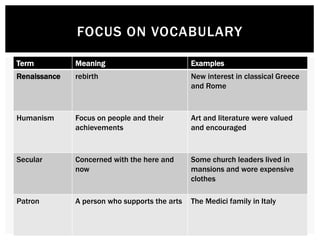
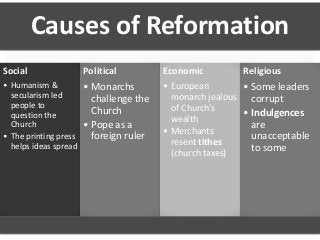
This document provides an overview of the Italian Renaissance and its spread to Northern Europe. It discusses several key factors that fostered the Renaissance in Italy, including thriving city-states, a wealthy merchant class, and Italy's classical heritage. Important Renaissance figures like Leonardo da Vinci and Raphael are mentioned. The document also notes how Renaissance ideas spread north to places like France and the Low Countries, influenced by travelers and royal patrons. Key artistic and literary developments in these northern regions are summarized as well.