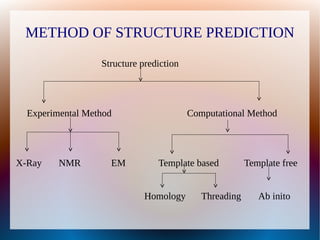
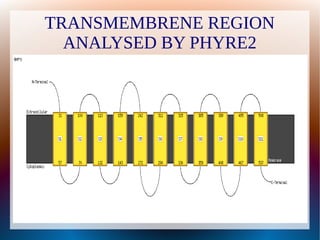
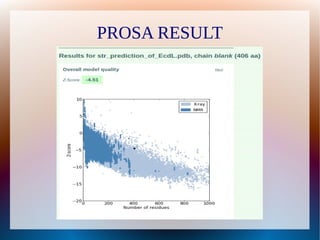
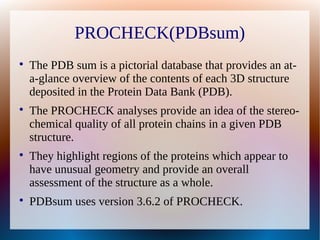
The document is a modelling assignment focused on predicting the 3D structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence using various computational methods, namely threading and ab initio modeling. It details the use of tools like Phyre2 and Robetta for structure prediction, alignment, and validation of the generated model, culminating in the identification of the protein as a multidrug-resistance transporter. Validation was performed using various servers, including Anolea and ProSA, with results indicating a successful model of the chosen amino acid sequence.


![OBJECTIVE
To build the model of given amino acid residue sequence and validate
the generated model.
>gi|407259499|gb|AFT91383.1| EcdL [Emericella rugulosa]
MDDSPWPQCDIRVQDTFGPQVSGCYEDFDFTLLFEESILYLPPLLIAASVALLRIWQL
RSTENLLKRSGLLSILKPTSTTRLSNAAIAIGFVASPIFAWLSFWEHARSLRPSTI
LNVYLLGTIPMDAARARTLFRMPGNSAIASIFATIVVCKVVLLVVEAMEKQRLLLD
RGWAPEETAGILNRSFLWWFNPLLLSGYKQALTVDKLLAVDEDIGVEKSKDEIRRR
WAQAVKQNASSLQDVLLAVYRTELWGGFLPRLCLIGVNYAQPFLVNRVVTFLGQPD
TSTSRGVASGLIAAYAIVYMGIAVATAAFHHRSYRMVMMVRGGLILLIYDHTLTLN
ALSPSKNDSYTLITADIERIVSGLRSLHETWASLIEIALSLWLLETKIRVSAVAAA
MVVLVCLLVSGALSGLLGVHQNLWLEAMQKRLNATLATIGSIKGIKATGRTNTLYE
TILQLRRTEIQKSLKFRELLVALVTLSYLSTTMAPTFAFGTYSILAKIRNMTPLLA
APAFSSLTIMTLLGQAVSGFVESLMGLRQAMASLERIRQYLVGKEAPEPSPNKPGV
ASTEGLVAWSASLDEPGLDPRVEMRRMSSLQHRFYNLGELQD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/shwetamodelling-160504060124/85/modelling-assignment-3-320.jpg)