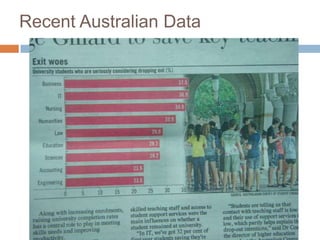
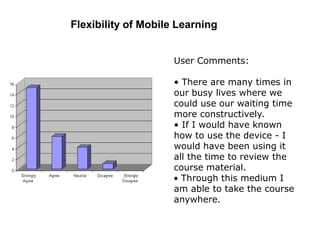
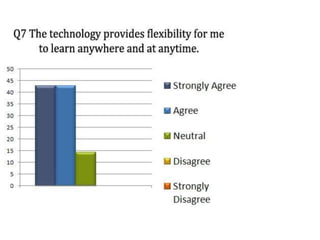
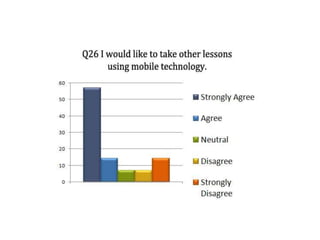
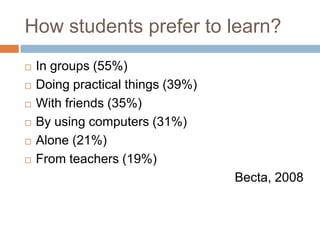
The document discusses the significance of mobile learning in higher education, addressing the current state, challenges, and potential benefits of integrating mobile technology in educational settings. It highlights the readiness of students for mobile learning compared to faculty, outlines various successful mobile learning initiatives globally, and presents future trends where mobile devices will be ubiquitous in education. The conclusion emphasizes the need for mobile technology to promote educational access and social justice among underserved populations.