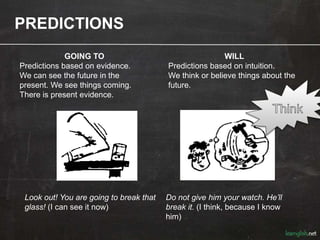
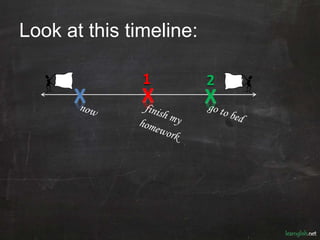
The document discusses various ways to talk about the future in English using future forms. It explains the uses of "going to" for predictions based on evidence and decisions already made. "Will" is used for predictions based on intuition and instant decisions. Plans can be expressed using "going to" or the present continuous. Future time clauses with words like "after", "before", and "until" take the present simple verb form. The future continuous expresses an action in progress at a specific future time. The future perfect indicates an action will be completed before another specified future time.