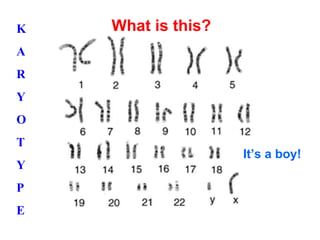
The document discusses chromosomes, karyotypes, mitosis, and the cell cycle. It explains that chromosomes contain genes and pair up in complex organisms. Karyotypes show the total number of chromosomes. Mitosis is cell division that produces two identical cells and has phases of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The cell cycle includes growth, DNA replication, and cell division phases. Uncontrolled cell division can cause cancer.