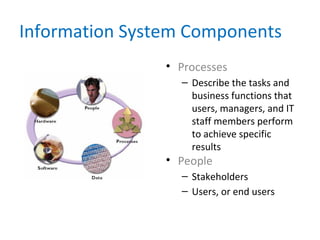
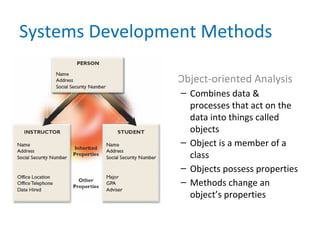
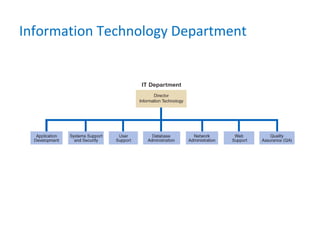
This chapter introduces systems analysis and design and information systems. It discusses how information technology impacts business strategy and defines the components of an information system. It also explains different types of information systems and development methods like structured analysis, object-oriented analysis, and agile development. The role of systems analysts and how they help develop high-quality information systems is also covered.