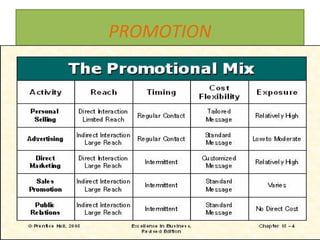
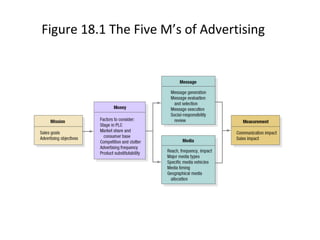
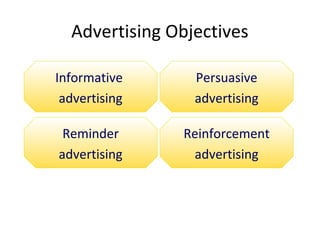
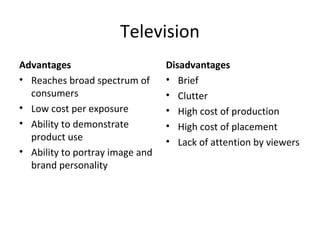
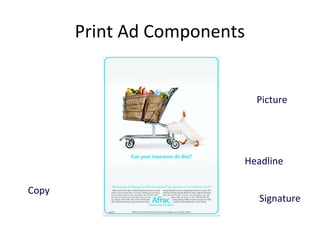
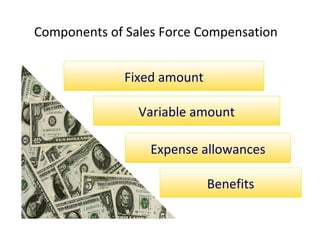
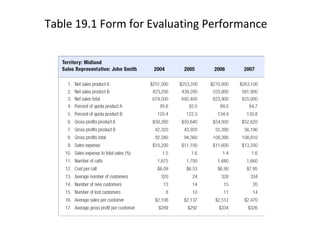
The document discusses various aspects of promotion including developing advertising campaigns, sales promotion tactics, using sponsored events for brand building, the roles and tools of public relations, the key elements of direct marketing campaigns, and managing a sales force including determining size, compensation, recruiting, and evaluating performance. It provides information on different promotion methods and considerations for each in a structured way with headings, figures, and tables.