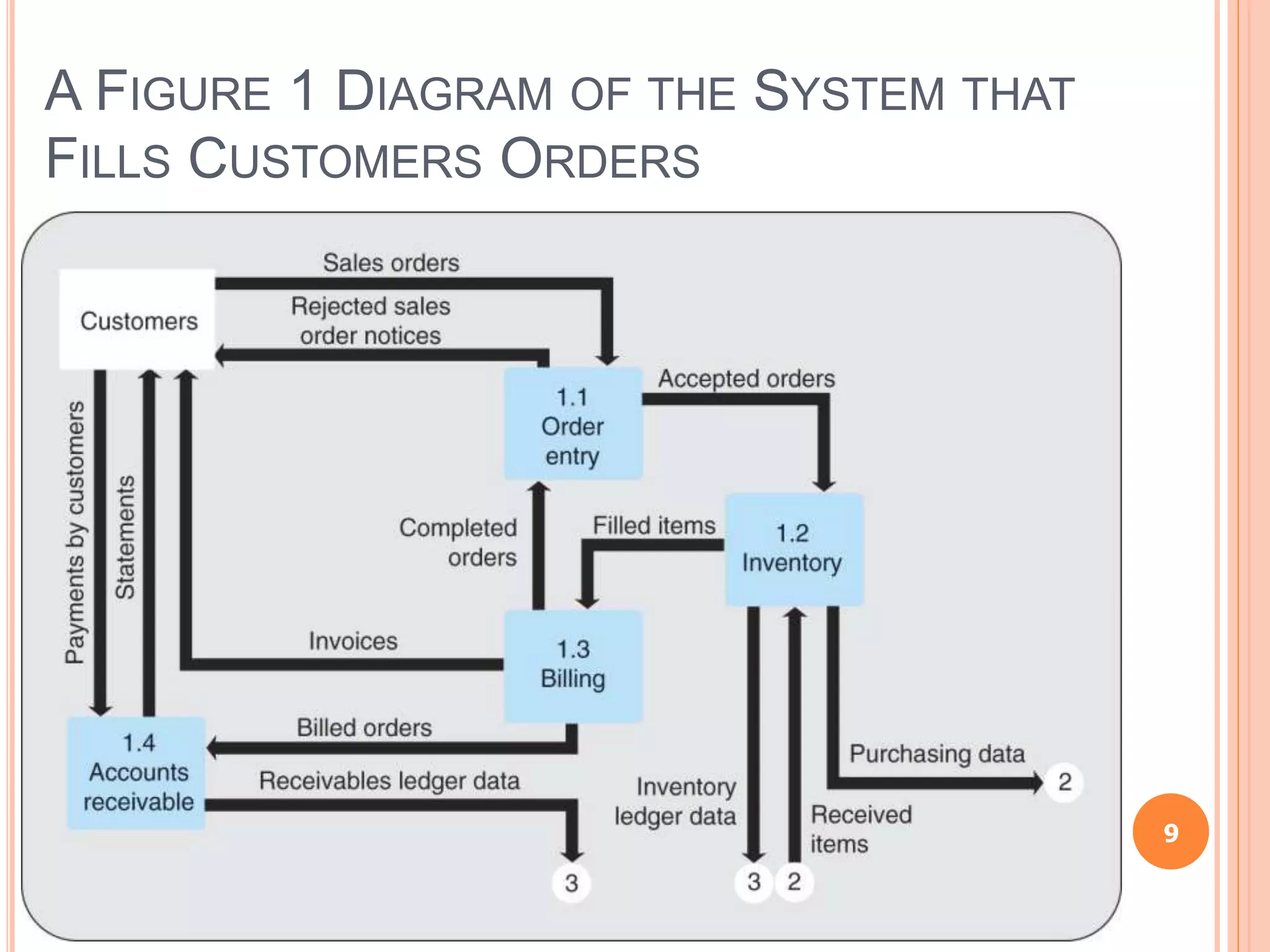
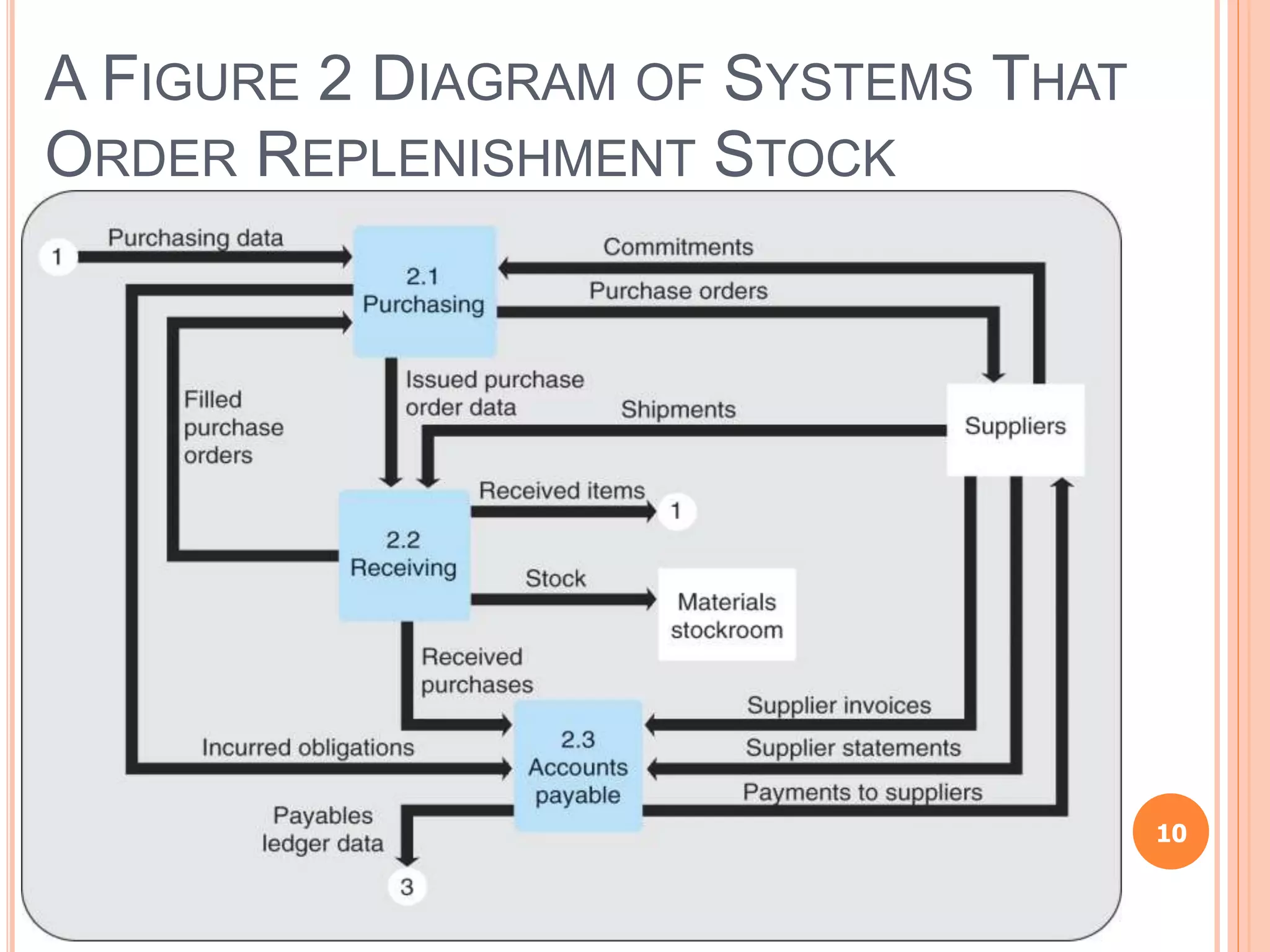
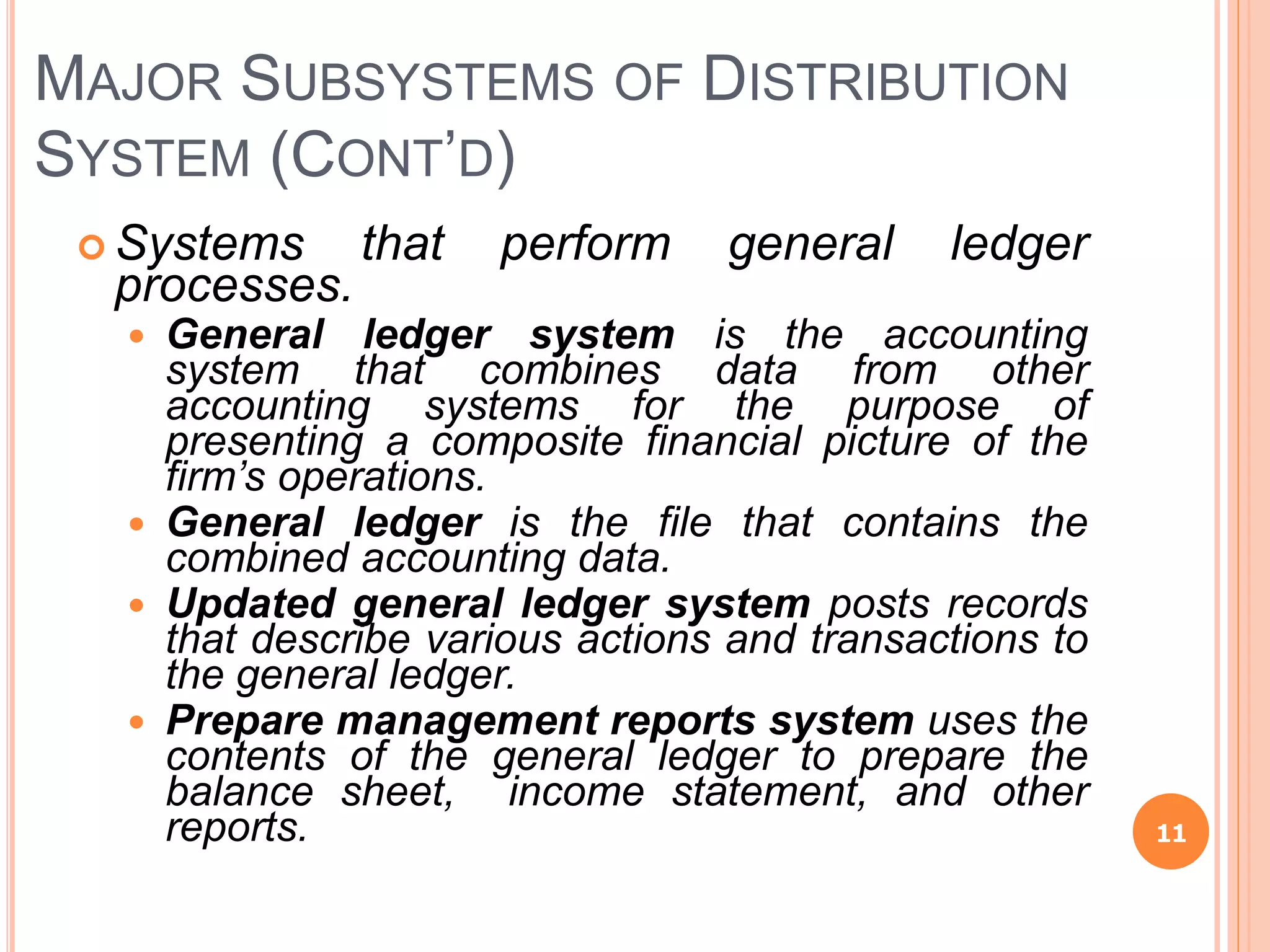
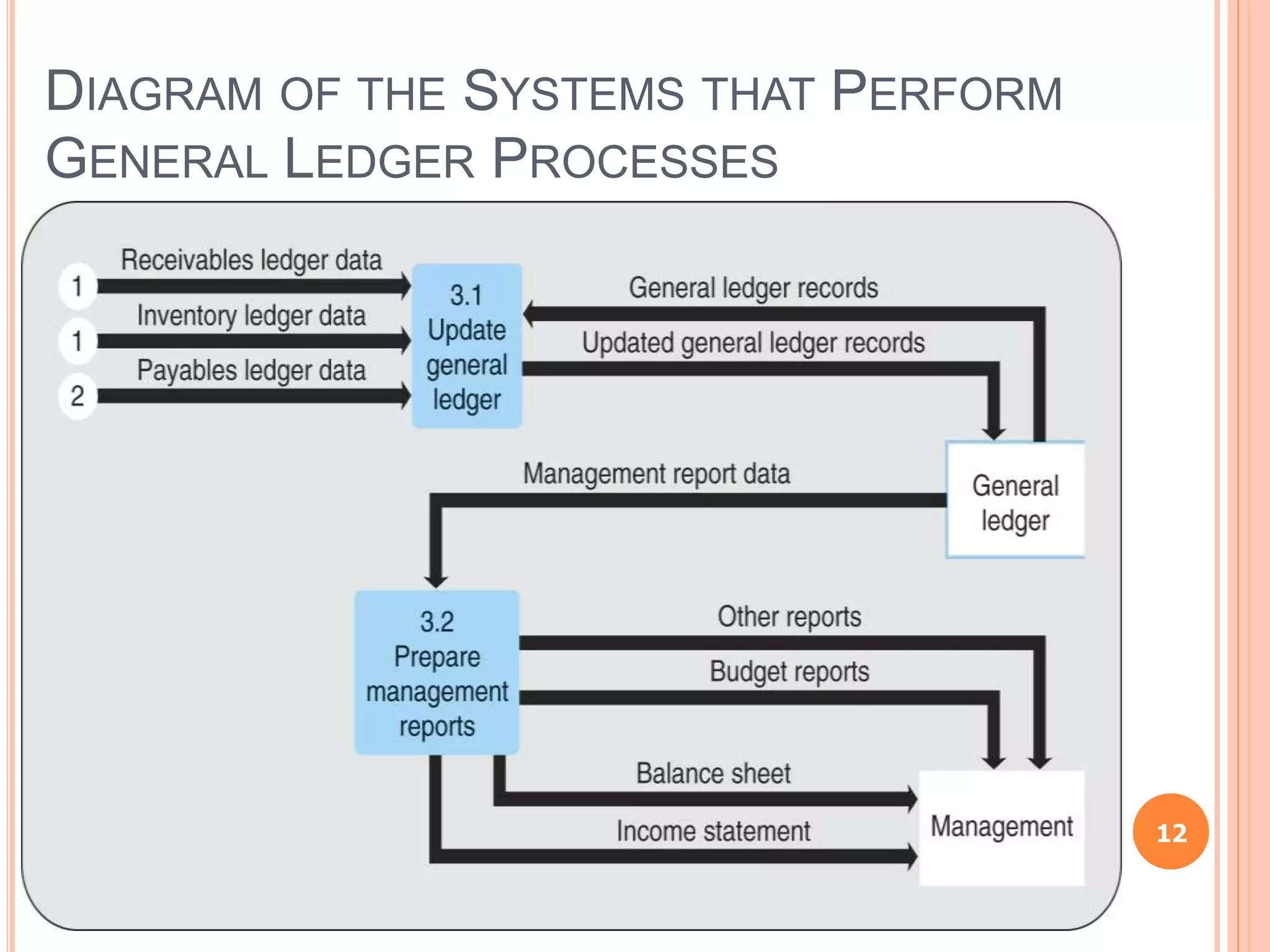
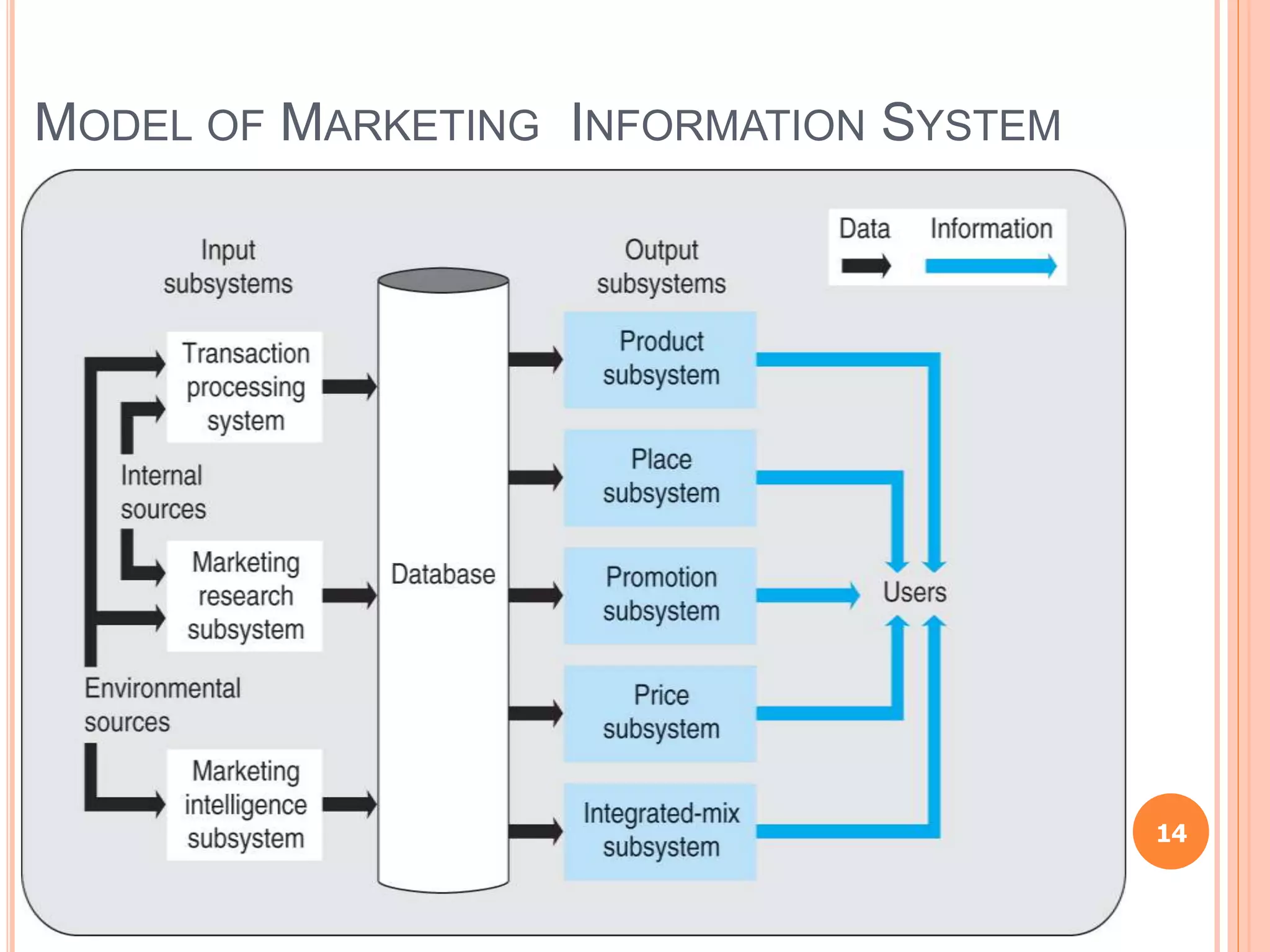
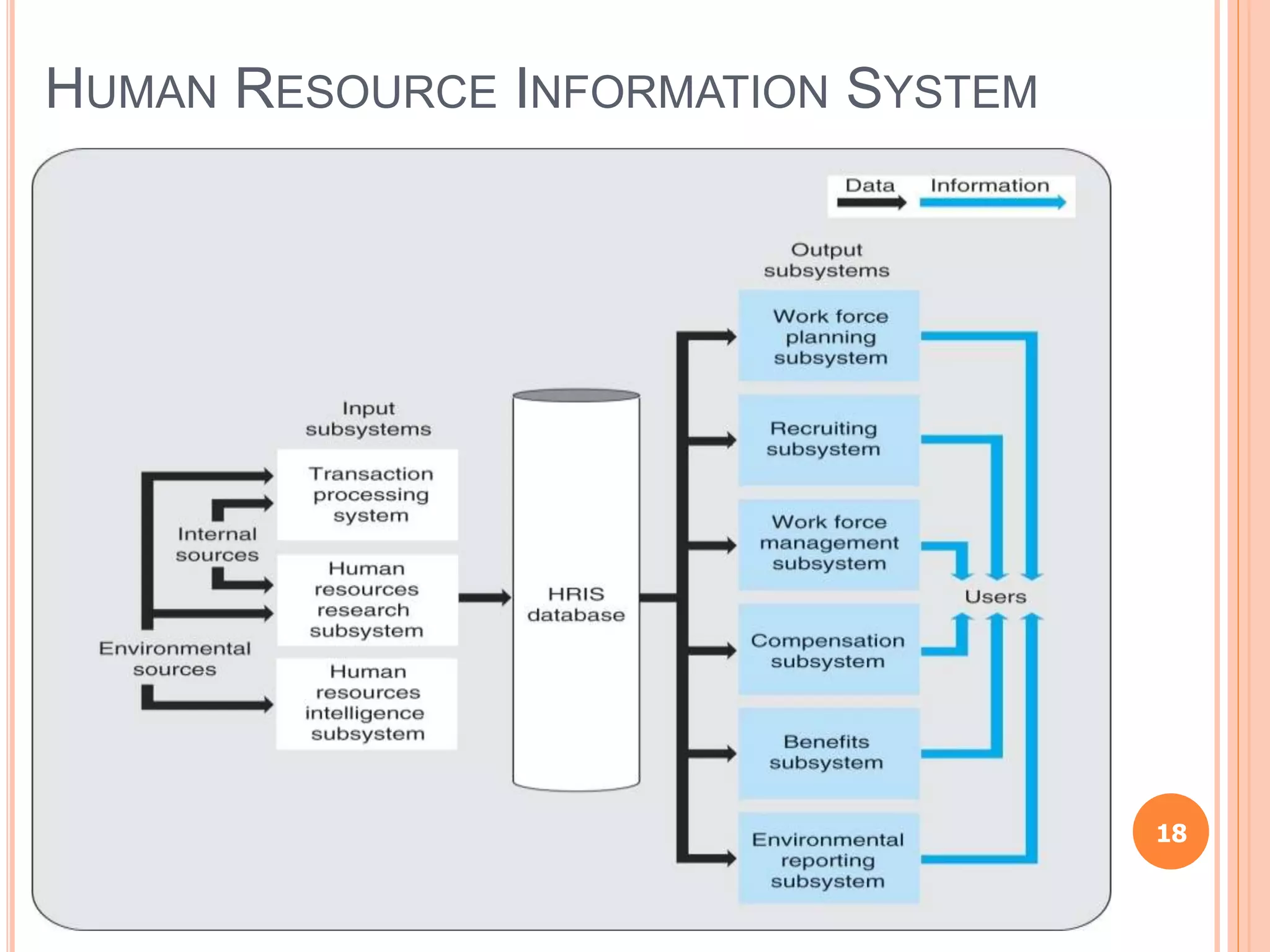
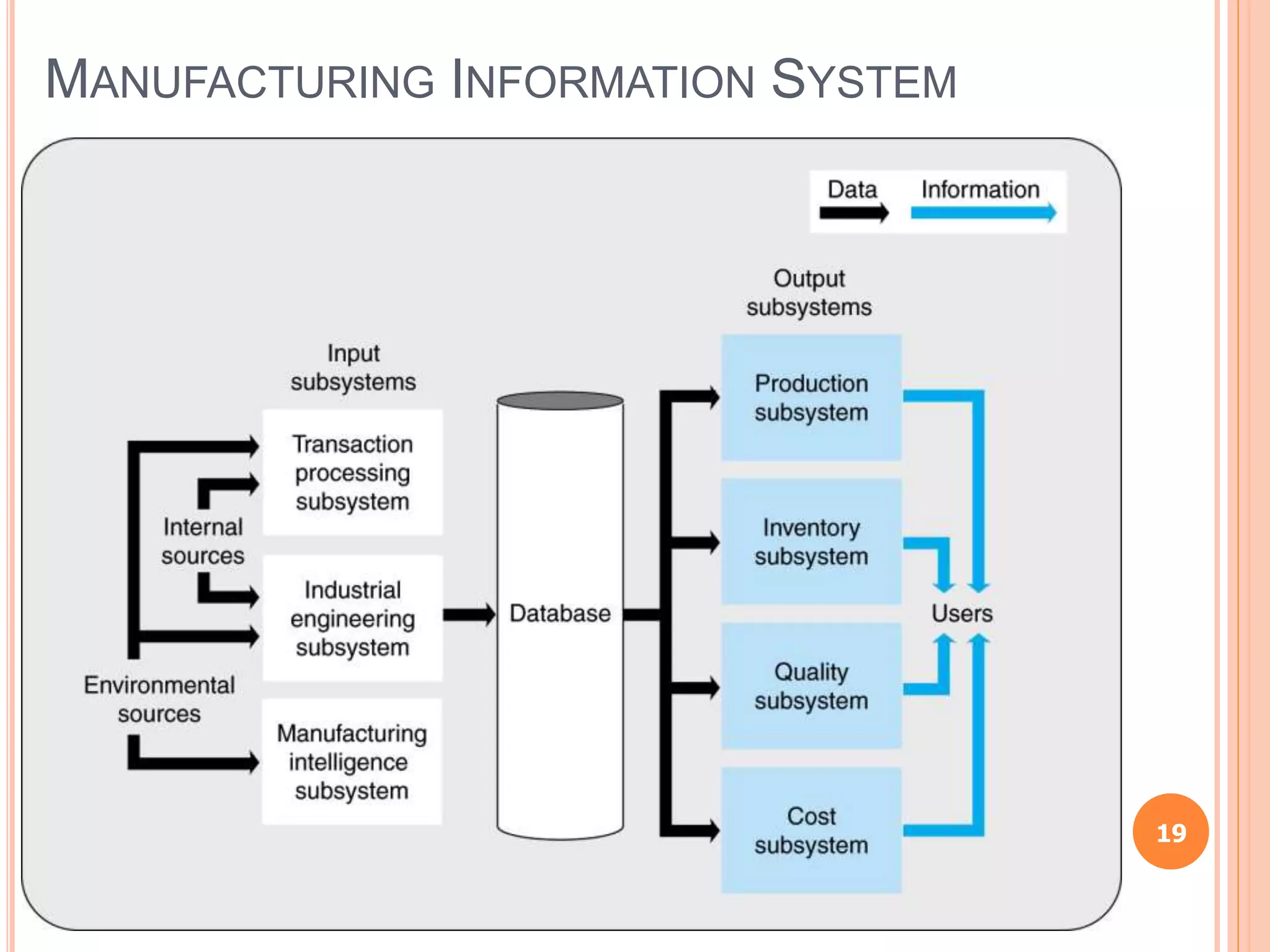
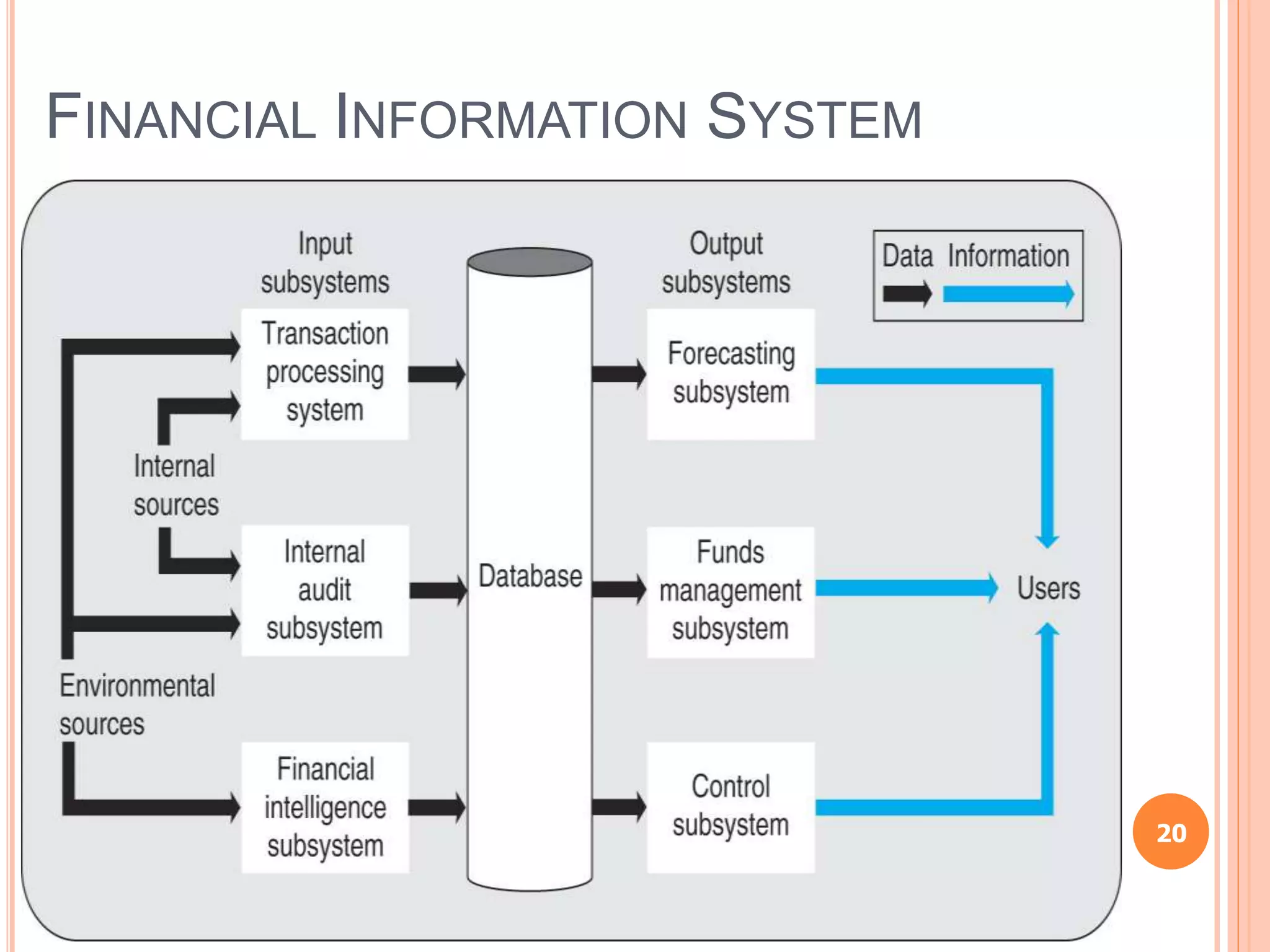
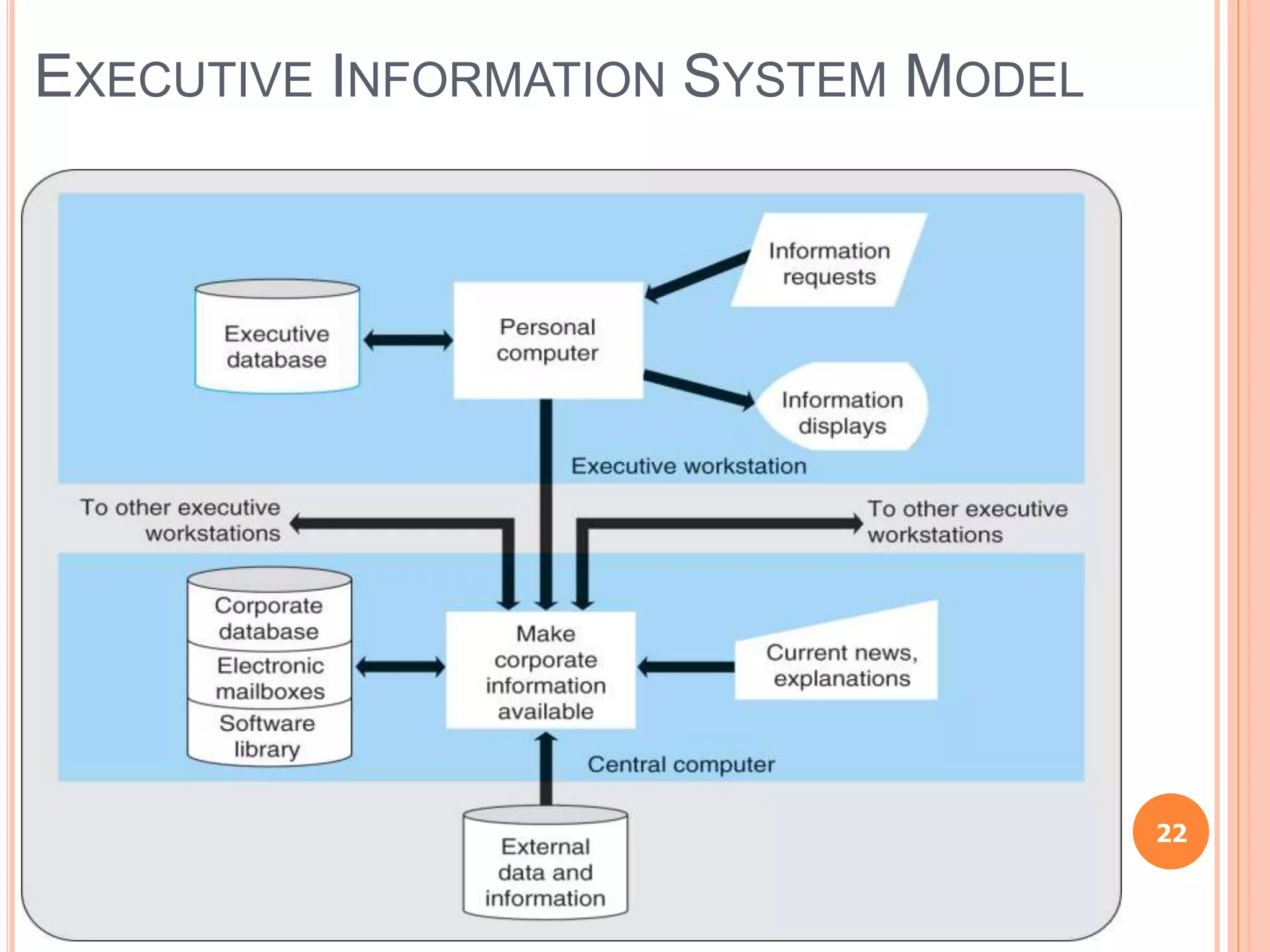
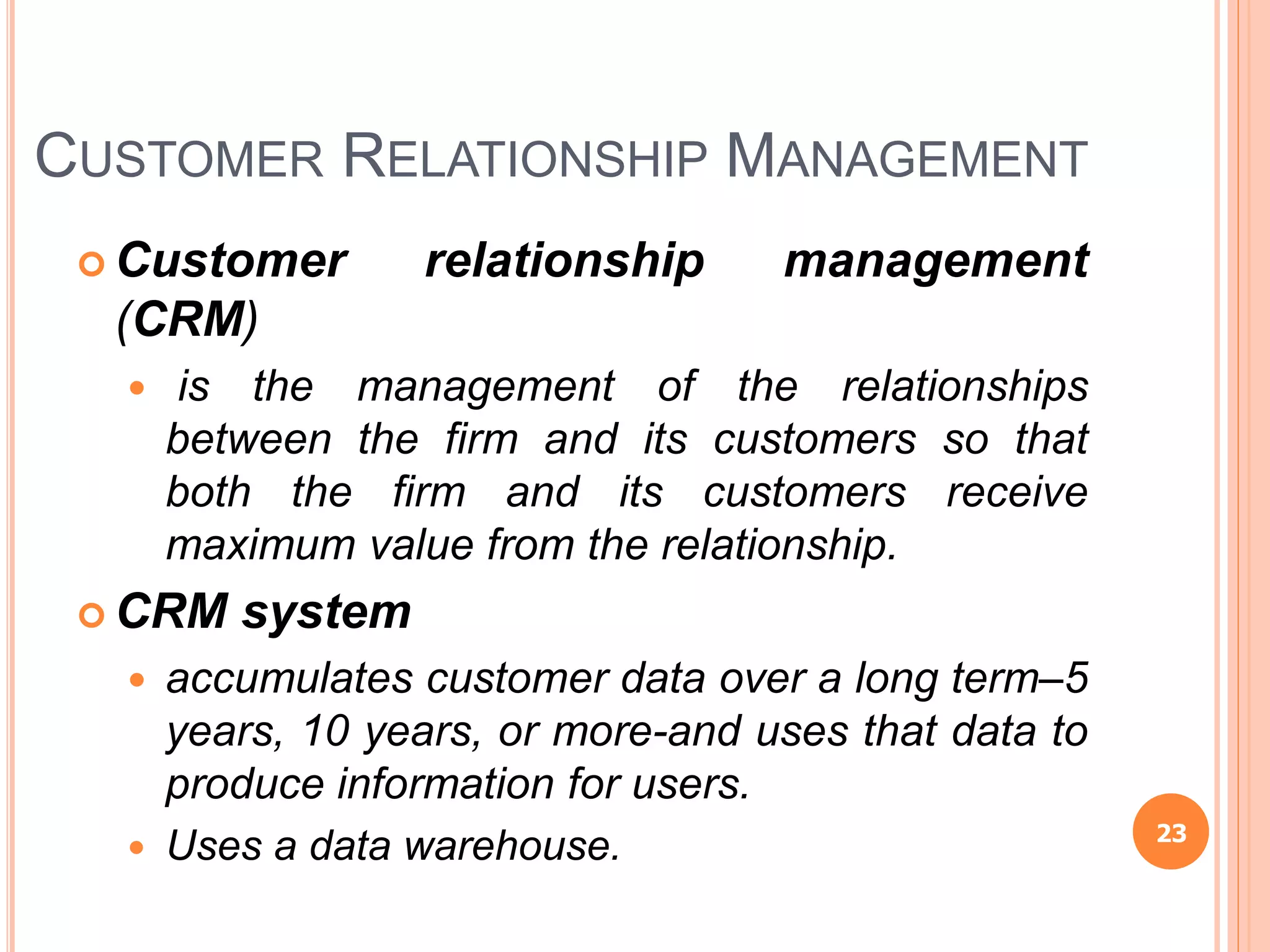
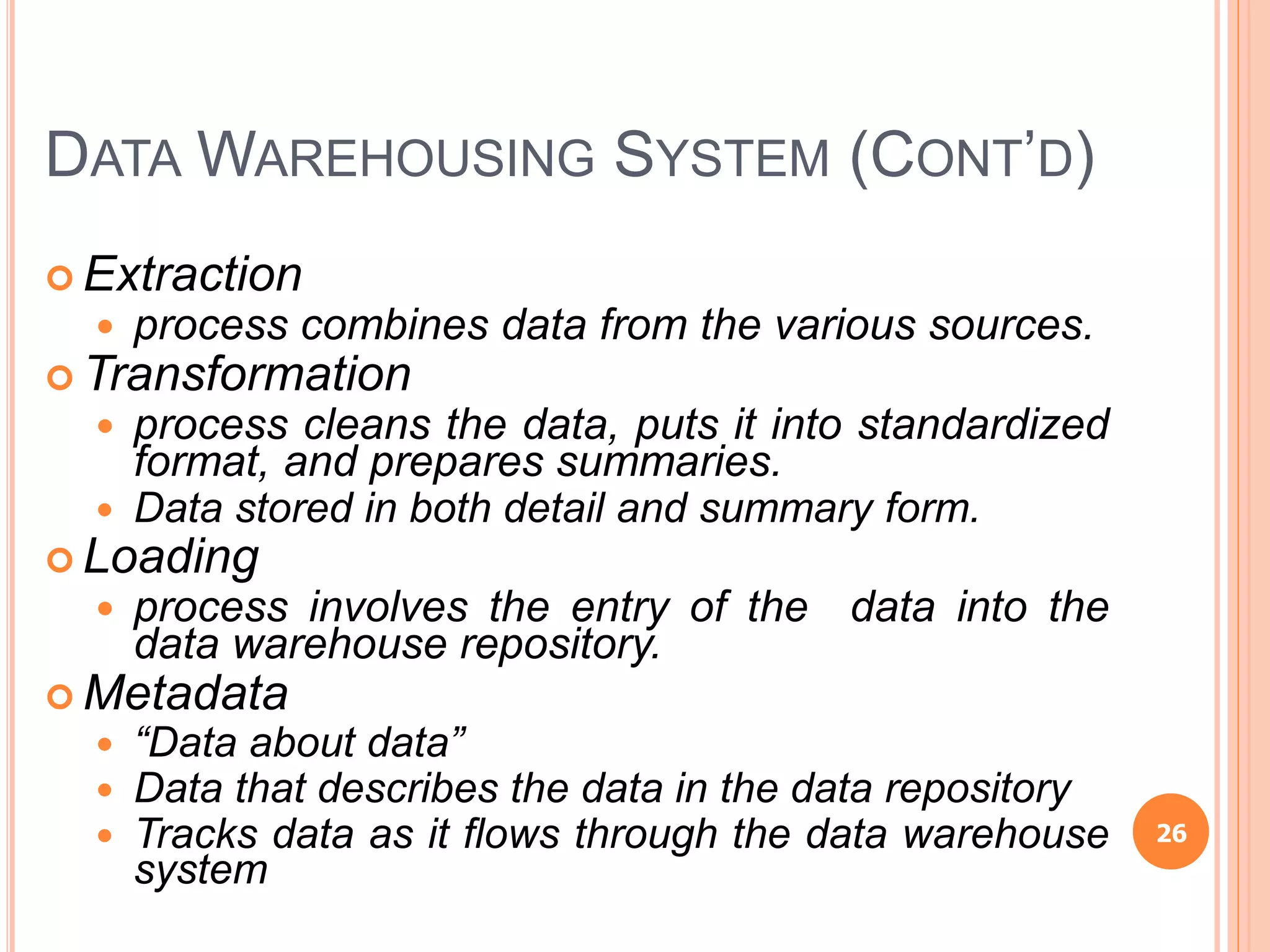
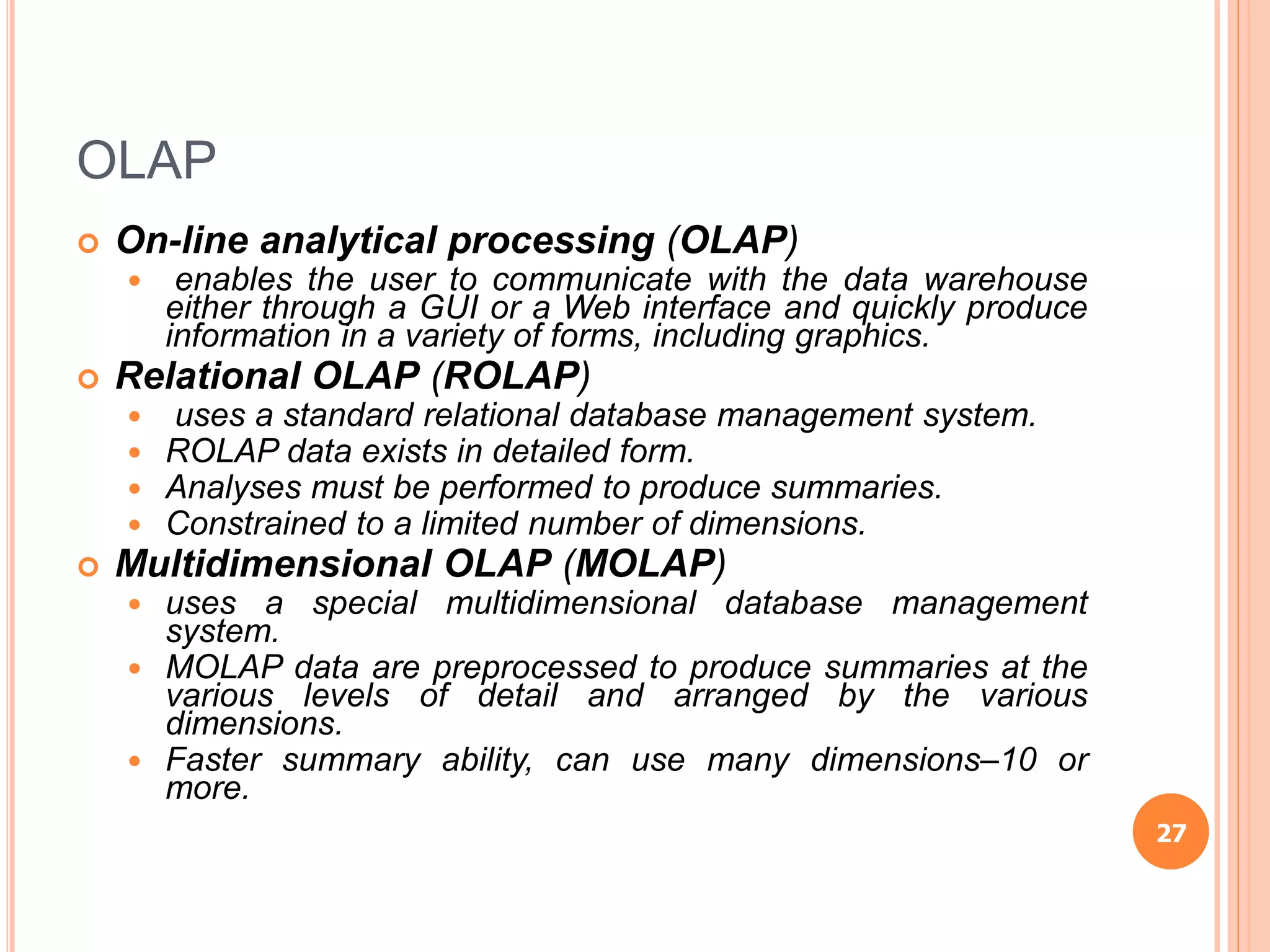
Chapter 8 of the document discusses the significance of information systems in organizational success, covering transaction processing systems, and various organizational information systems like marketing, human resources, and financial systems. It describes how data warehousing and on-line analytical processing (OLAP) facilitate effective decision-making by managing vast amounts of data for analysis and reporting. Additionally, it explains data mining techniques used to discover hidden relationships within the data.