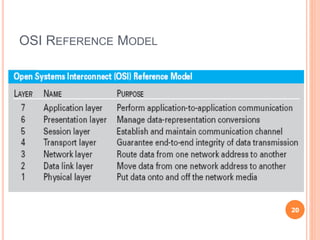
Chapter 5 of the document discusses management information systems with a focus on computing and communication resources, covering various hardware components, memory, storage devices, input/output devices, personal computing, and home network security. It highlights the importance of software, including system and application software, and outlines different communication protocols and types of networks such as LANs, MANs, and WANs. Additionally, the chapter touches on issues related to computing security and the integration of computing and communications technologies.