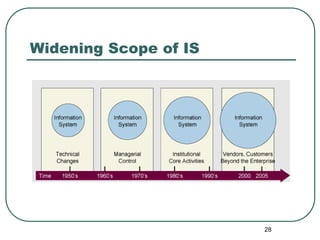
This document provides an overview of management information systems (MIS). It defines MIS as using technology to create business value by identifying information needs for decision making and developing systems to meet those needs. The document describes the components, characteristics, aims, outputs and benefits of MIS. It also discusses MIS careers and opportunities, noting that MIS helps increase productivity, enhance decision making, and support corporate strategy while facing challenges like information overload and rapidly changing technology.