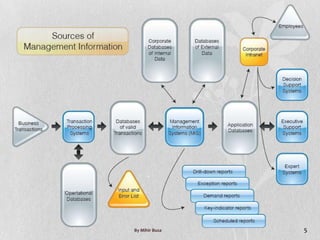
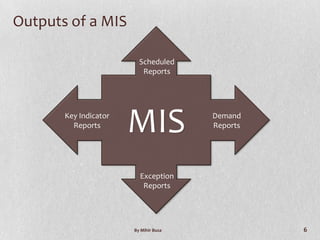
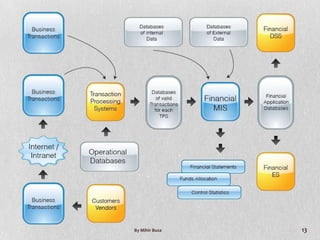
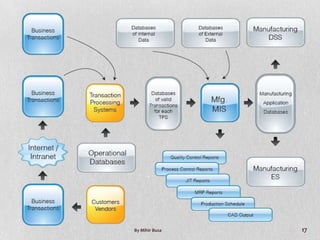
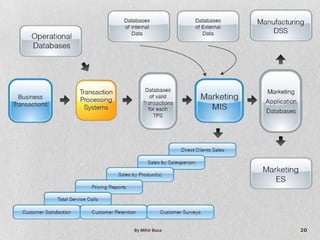
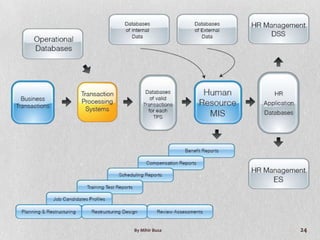
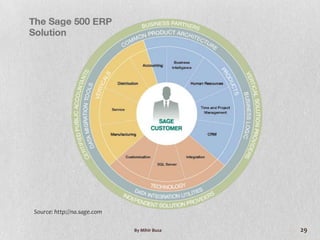
Management Information Systems (MIS) provide managers with information to support effective decision making and feedback on daily operations. MIS outputs are generated from accumulated transaction data and integrated across functional subsystems. MIS investments can boost production processes, leverage IT investments, expand businesses, and improve commerce. A well-planned MIS provides timely, accurate, consistent, complete, and relevant reports through scheduled, indicator, demand, and exception reports. An example of a current MIS is SageOne, which integrates accounting, payroll, billing, and other functions.