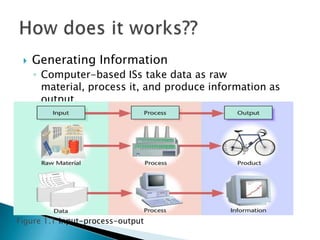
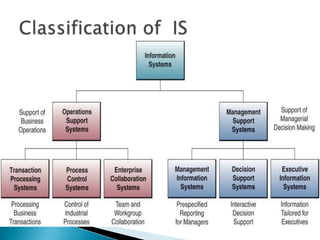
Management information systems (MIS) collect, process, store, and distribute data to support decision-making and control in organizations. Decision support systems (DSS) are a type of information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities. DSS provide analysis of information to help decision makers choose among alternative solutions. There are different types of DSS, including communication-driven, data-driven, document-driven, knowledge-driven, model-driven, spreadsheet-based, and web-based systems. DSS use analytical tools like what-if analysis, sensitivity analysis, goal-seeking analysis, and optimization analysis to help decision makers evaluate alternatives.