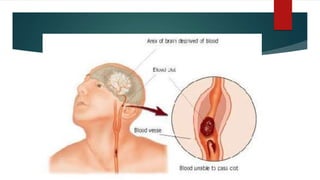
A minor stroke, often termed a 'mini stroke', is characterized by mild and non-disabling symptoms, although no consensus definition exists. It results from temporary disruptions in blood supply to the brain, commonly due to blood clots and associated risk factors like hypertension and diabetes. Treatment typically involves medications to reduce clot risk and managing other risk factors, with additional interventions considered if necessary.