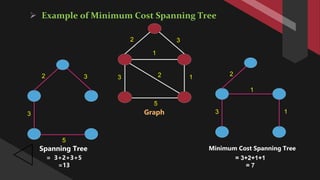
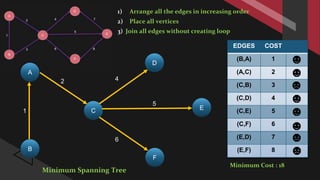
The document outlines Kruskal's algorithm, a greedy method for finding the minimum spanning tree in a connected weighted graph. It describes the necessary properties of spanning trees, the definition of minimum cost spanning trees, and provides a step-by-step algorithm along with its time complexity analysis. The algorithm's performance is characterized as O(e log v) or O(e log e), where e represents the number of edges and v the number of vertices.