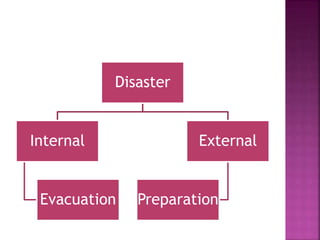
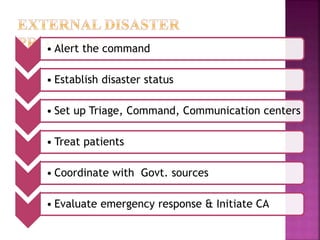
This document discusses hospital disaster preparedness in India. It notes that hospitals play an important role in disaster response but most Indian hospitals have little knowledge of or preparation for disasters. It outlines some common internal and external disaster scenarios hospitals may face. The document then provides details on forming a disaster management team, preparing an emergency manual, establishing communication codes, staff roles and responsibilities, and conducting drills to evaluate response and identify areas for improvement. The goal is to better prepare healthcare organizations to effectively respond to disasters.