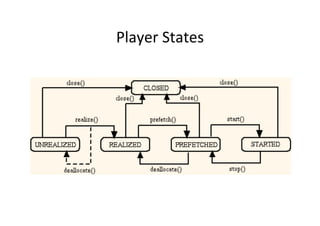
The document discusses the basics of sound and music capabilities in MIDP 2.0, including the Media API subset called the Audio Building Block. It describes playing audio files of different content types like WAV, MP3, and MIDI. The relationship between classes like Manager, DataSource and Player for controlling audio playback is also covered at a high level.




![Audio
Data
Path
For
example:
Handles
Interface
in
applause.wa transporEng
the
javax.microediEon.
data
to
the
v
media
player
Audio
DataSource
Player
Data
[
speaker
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musicsounds-1223284466949260-9/85/MIDP-Music-and-Sound-5-320.jpg)


![Supported
Protocols
and
Content
types
• To
find
out
at
runEme
what
content
types
and
protocols
are
supported:
– Manager-‐class
• public static String[]
getSupportedContentTypes(String protocol)!
• public static String[]
getSupportedProtocols(String content_type)!
• See
example:
MediaInformaEonMIDlet.java](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/musicsounds-1223284466949260-9/85/MIDP-Music-and-Sound-9-320.jpg)