This document provides an overview of the key features and tools in Microsoft Word, including:
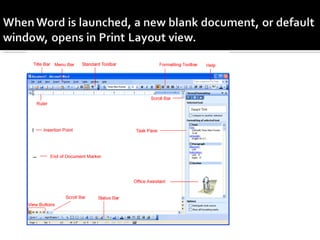
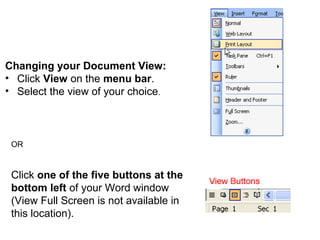
1) It describes the various parts of the Word interface such as the title bar, menu bar, toolbars, rulers, and status bar.
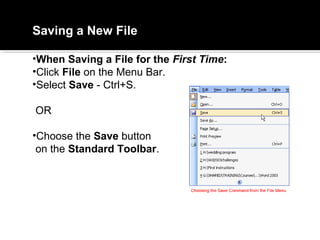
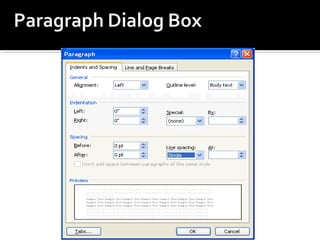
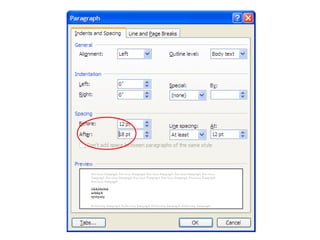
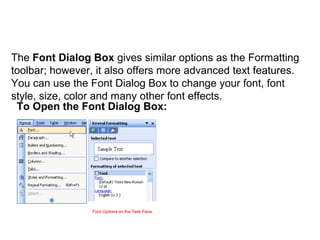
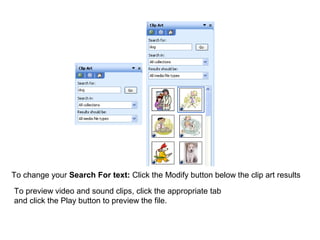
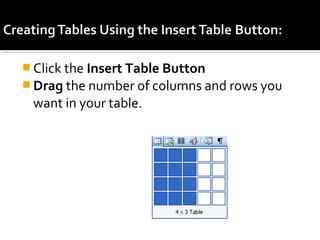
2) It explains how to perform common tasks like opening and saving documents, cutting/copying/pasting text, formatting text styles and paragraphs, adding tables and pictures, and working with headers and footers.
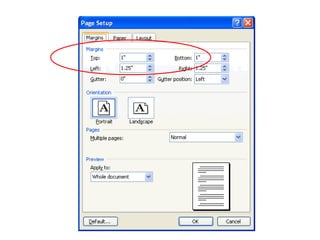
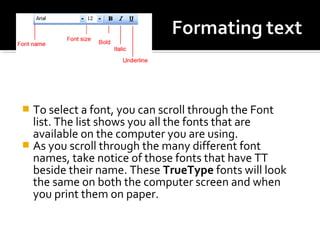
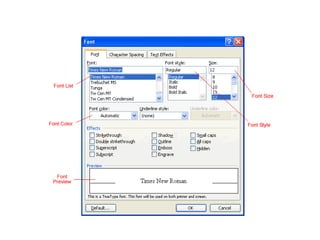
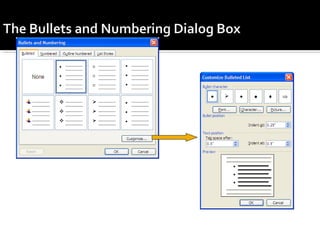
3) It provides instructions for using many of the formatting and layout tools in Word for adjusting fonts, colors, alignments, margins, columns, and more.