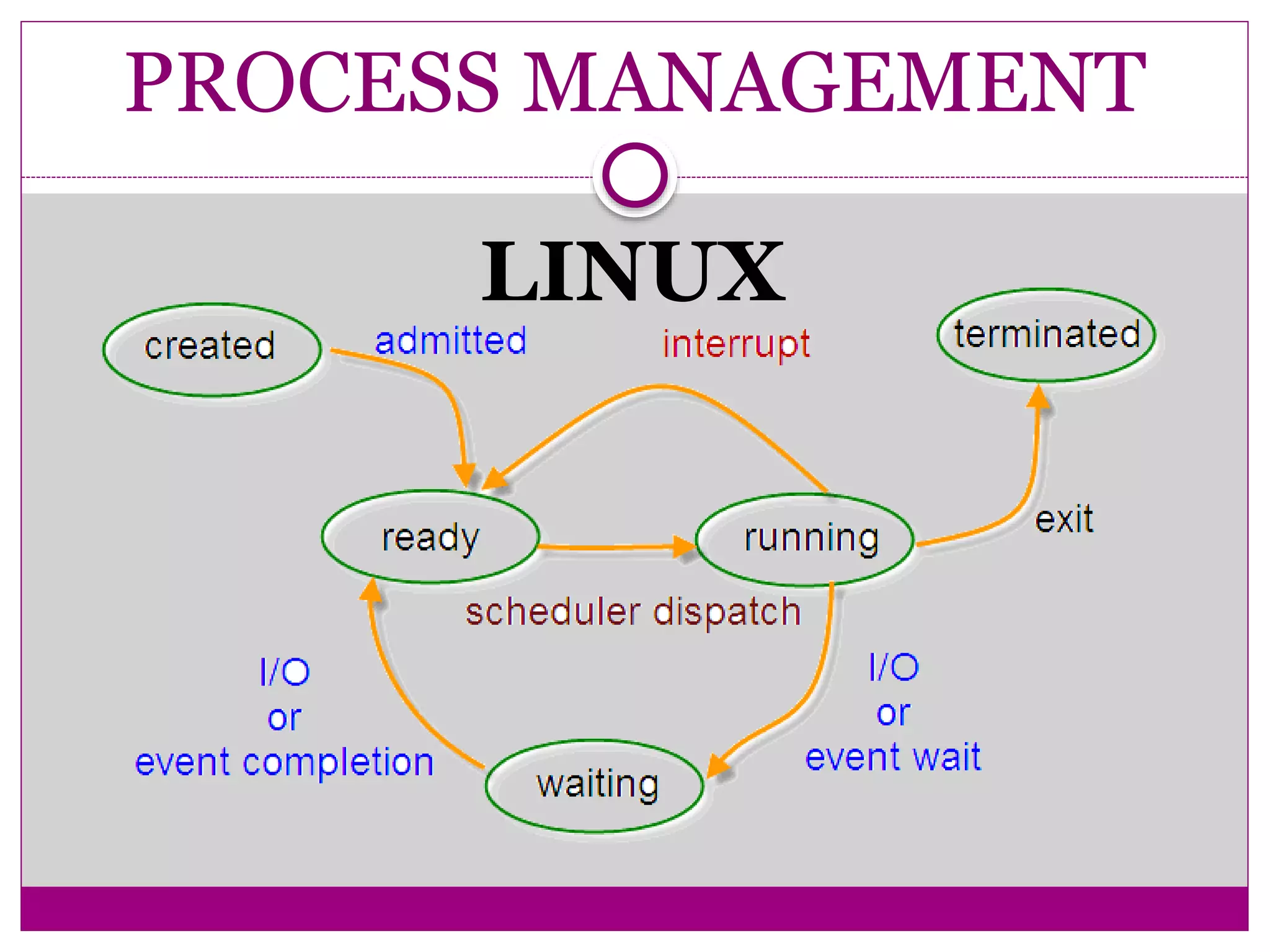
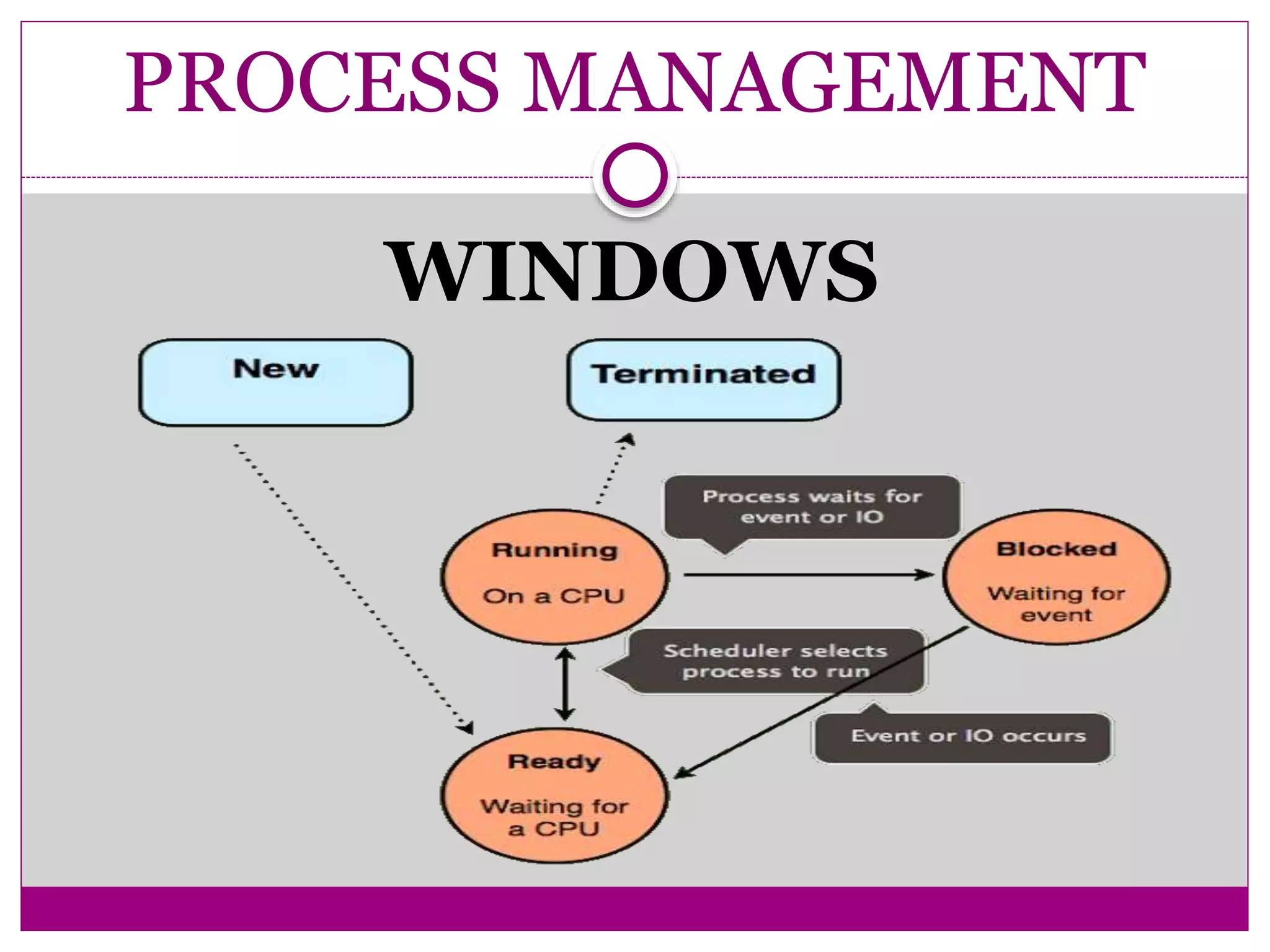
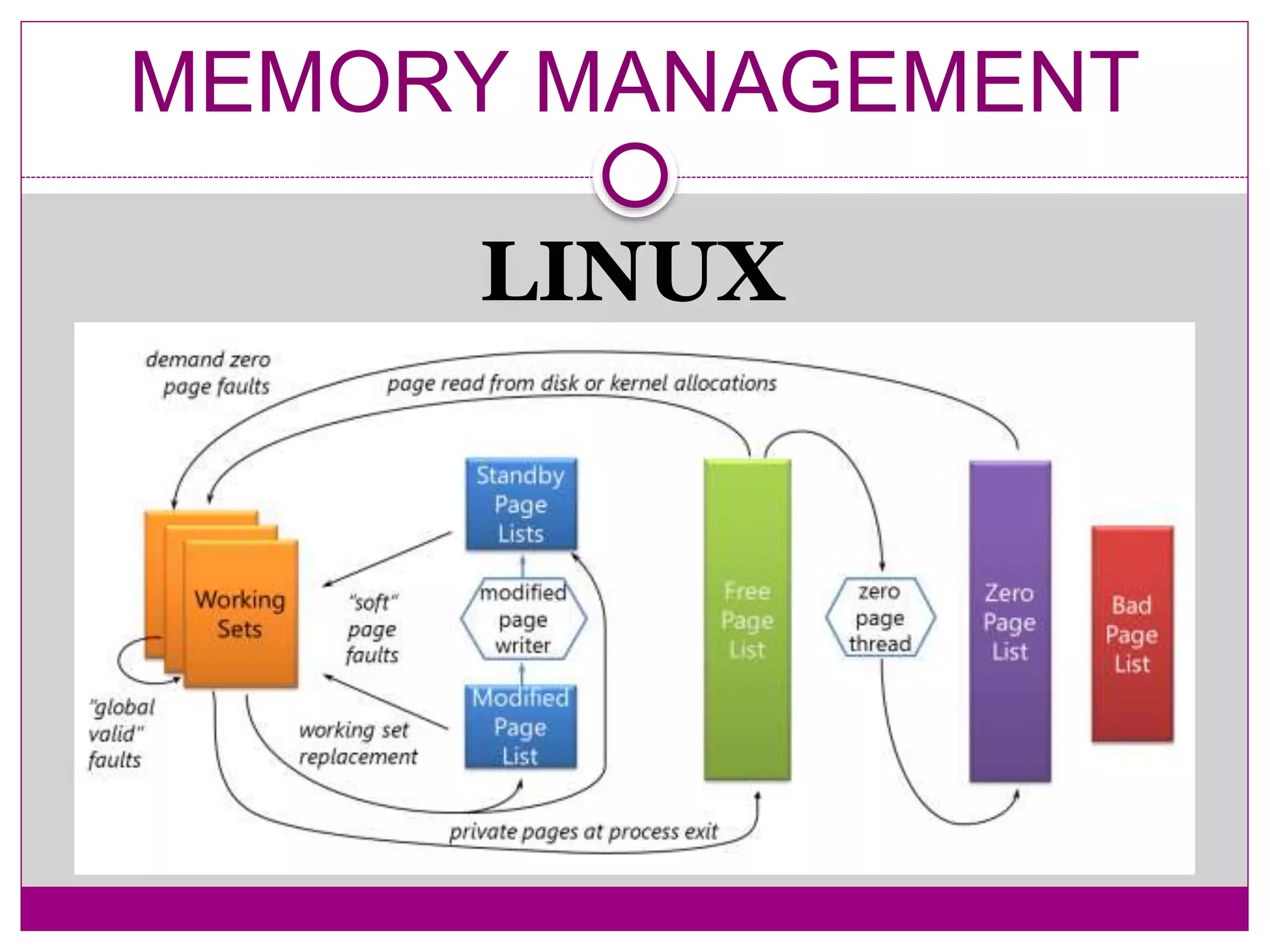
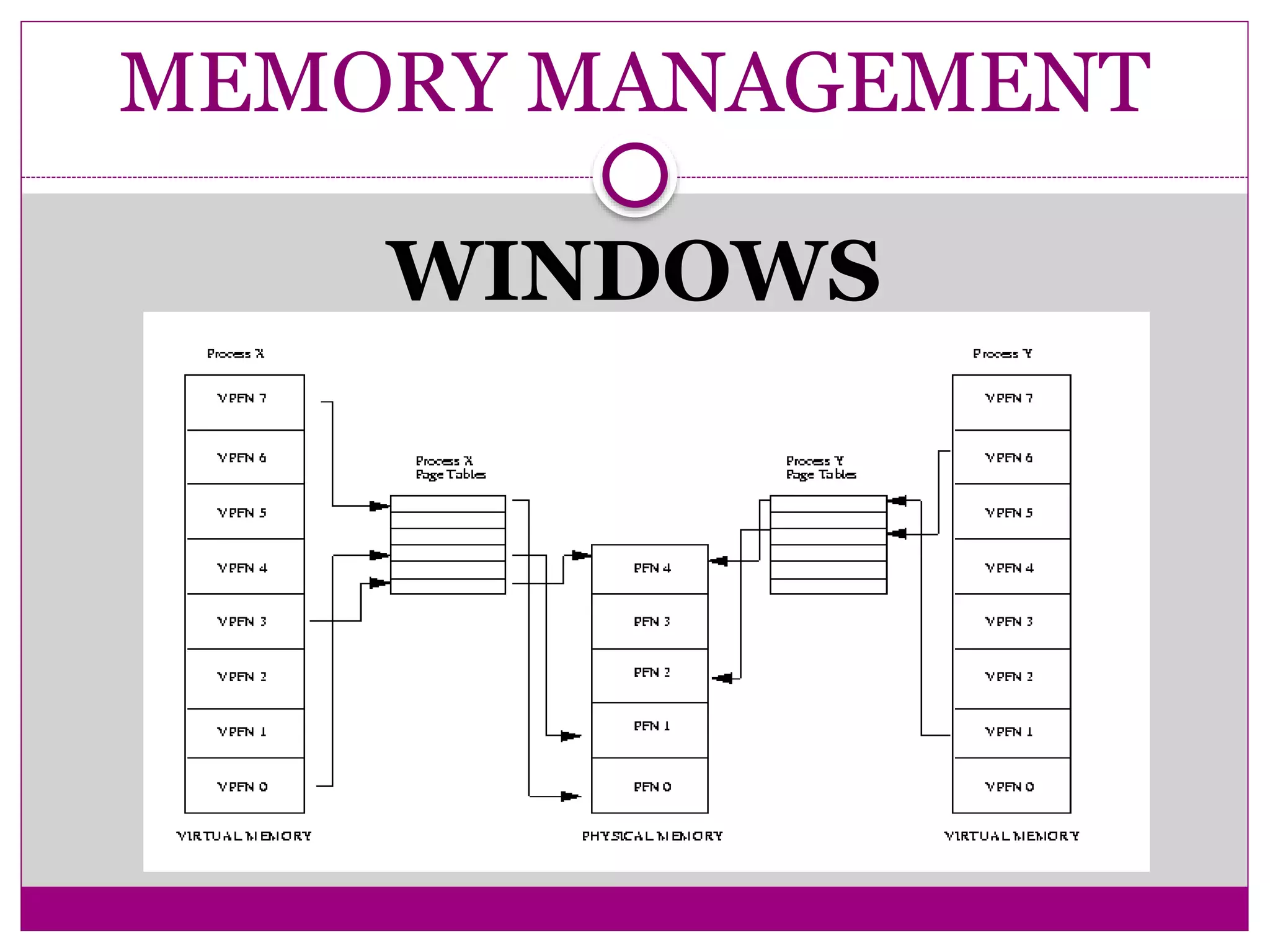
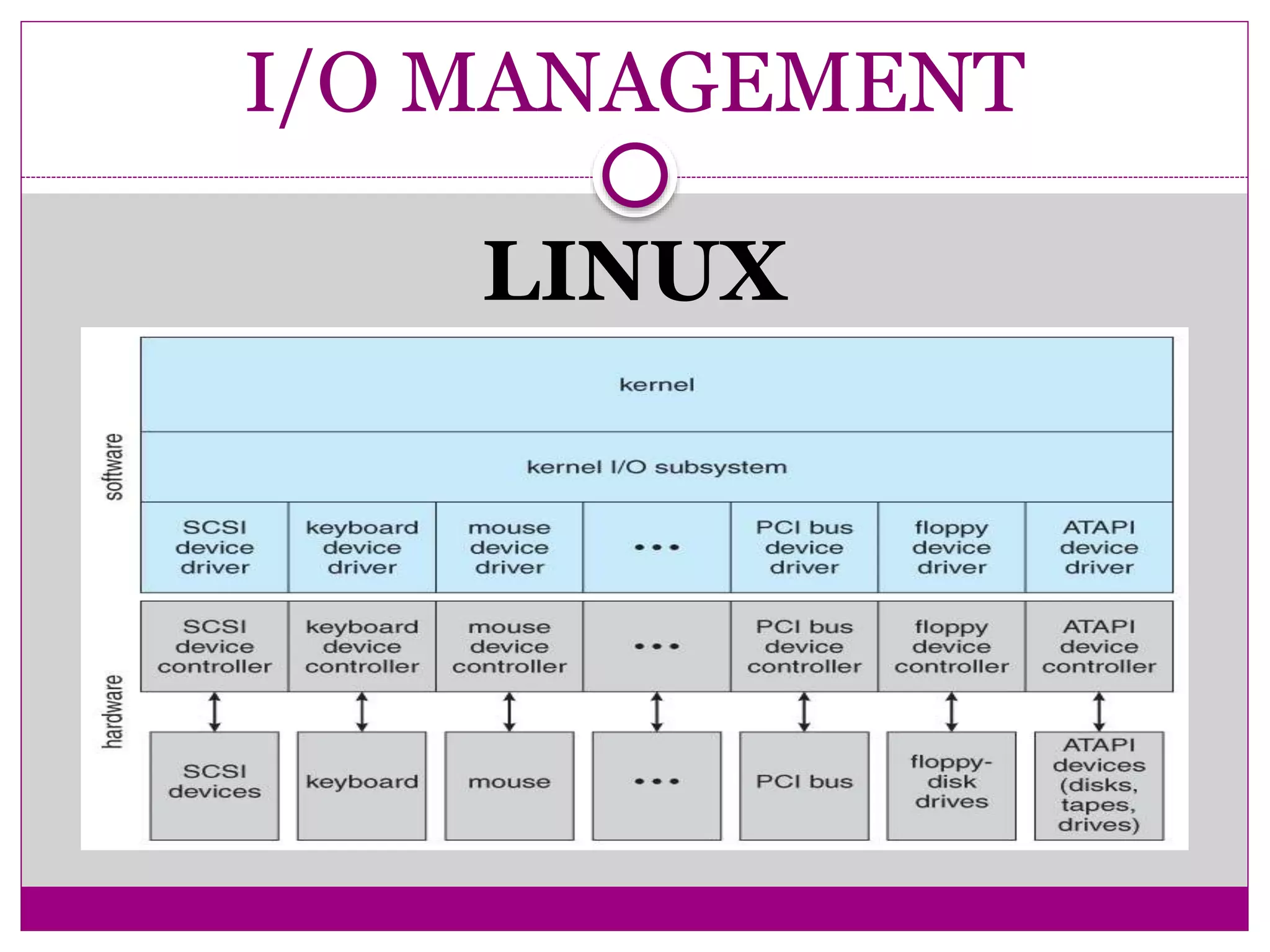
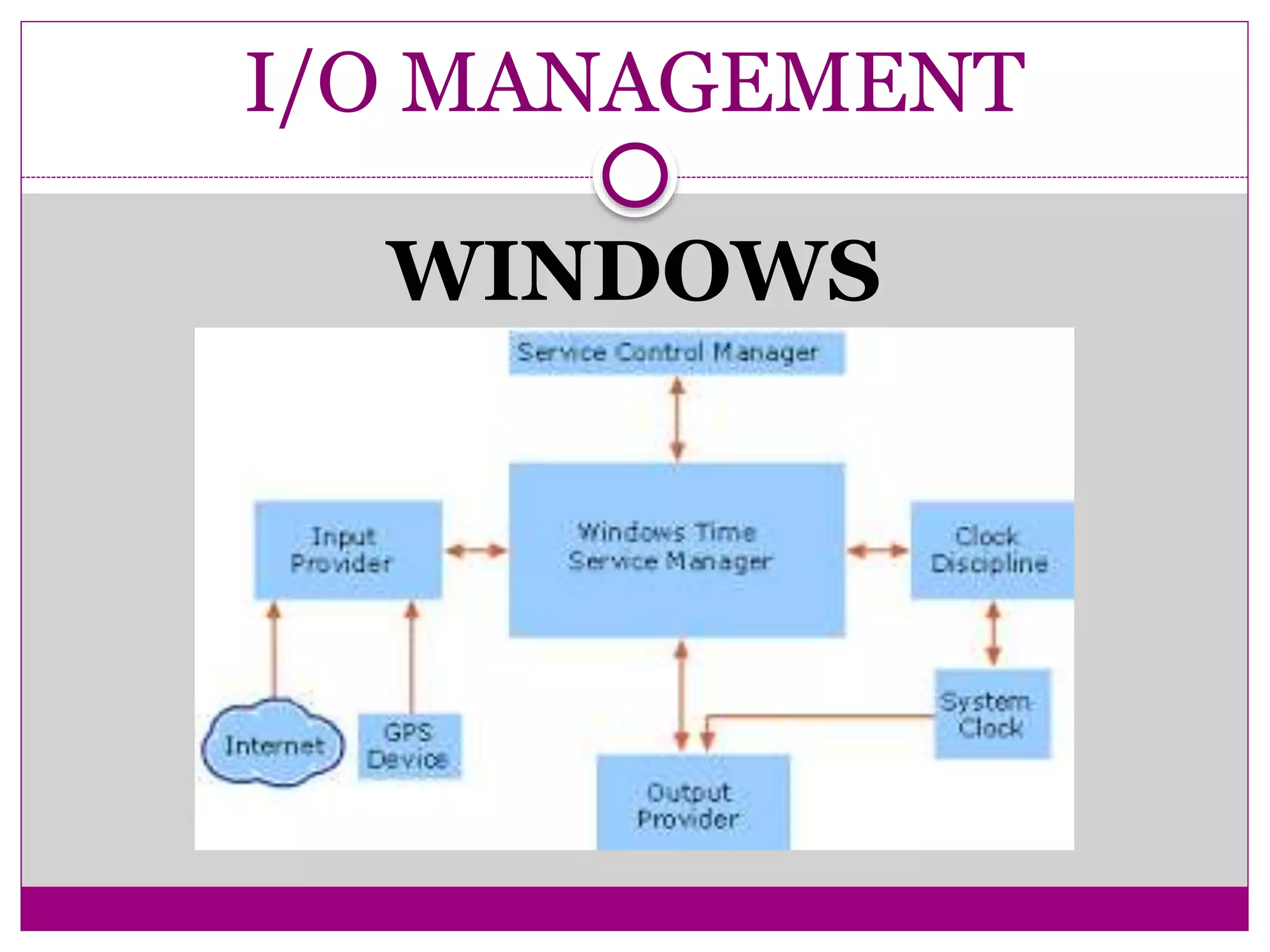
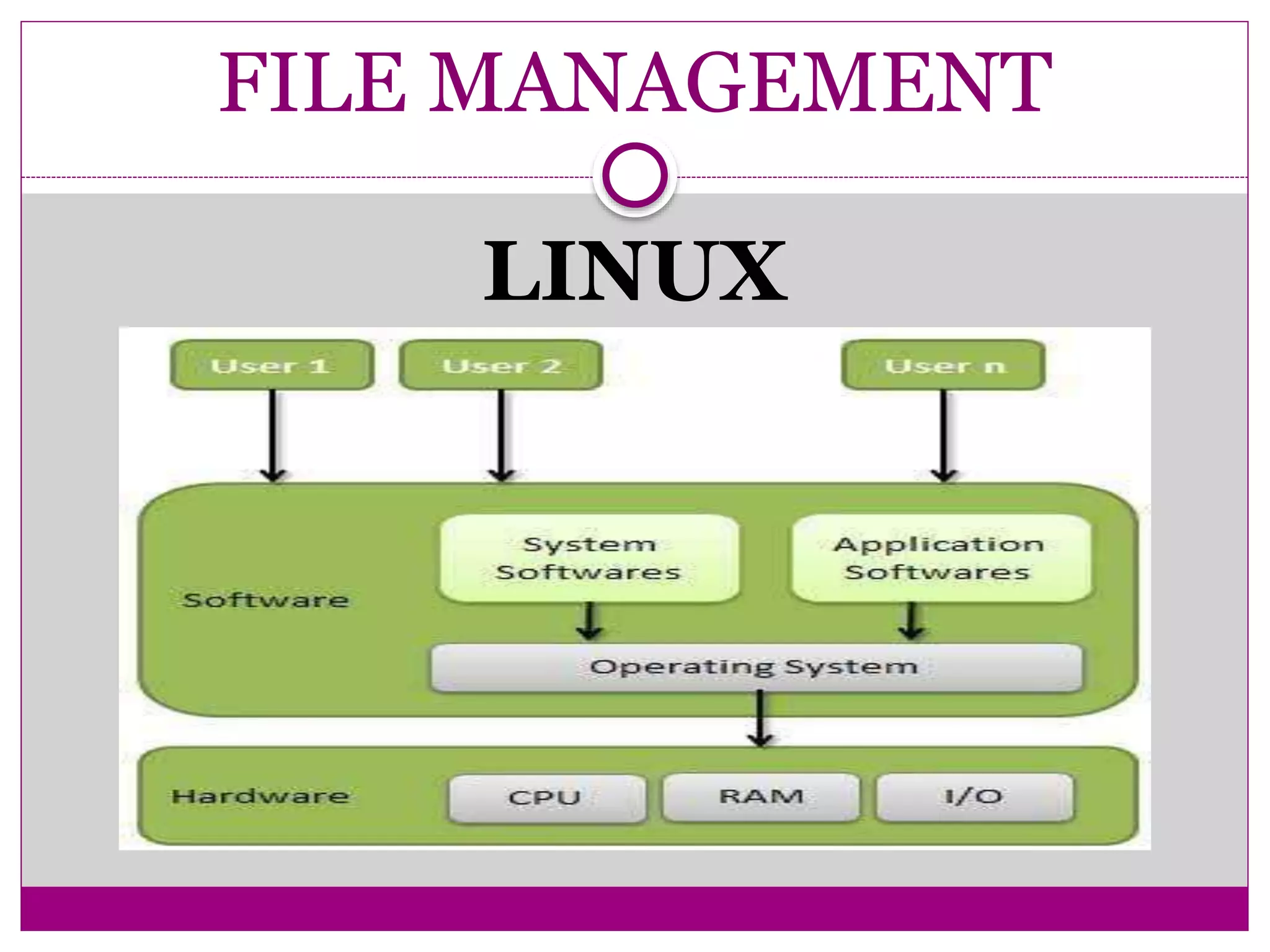
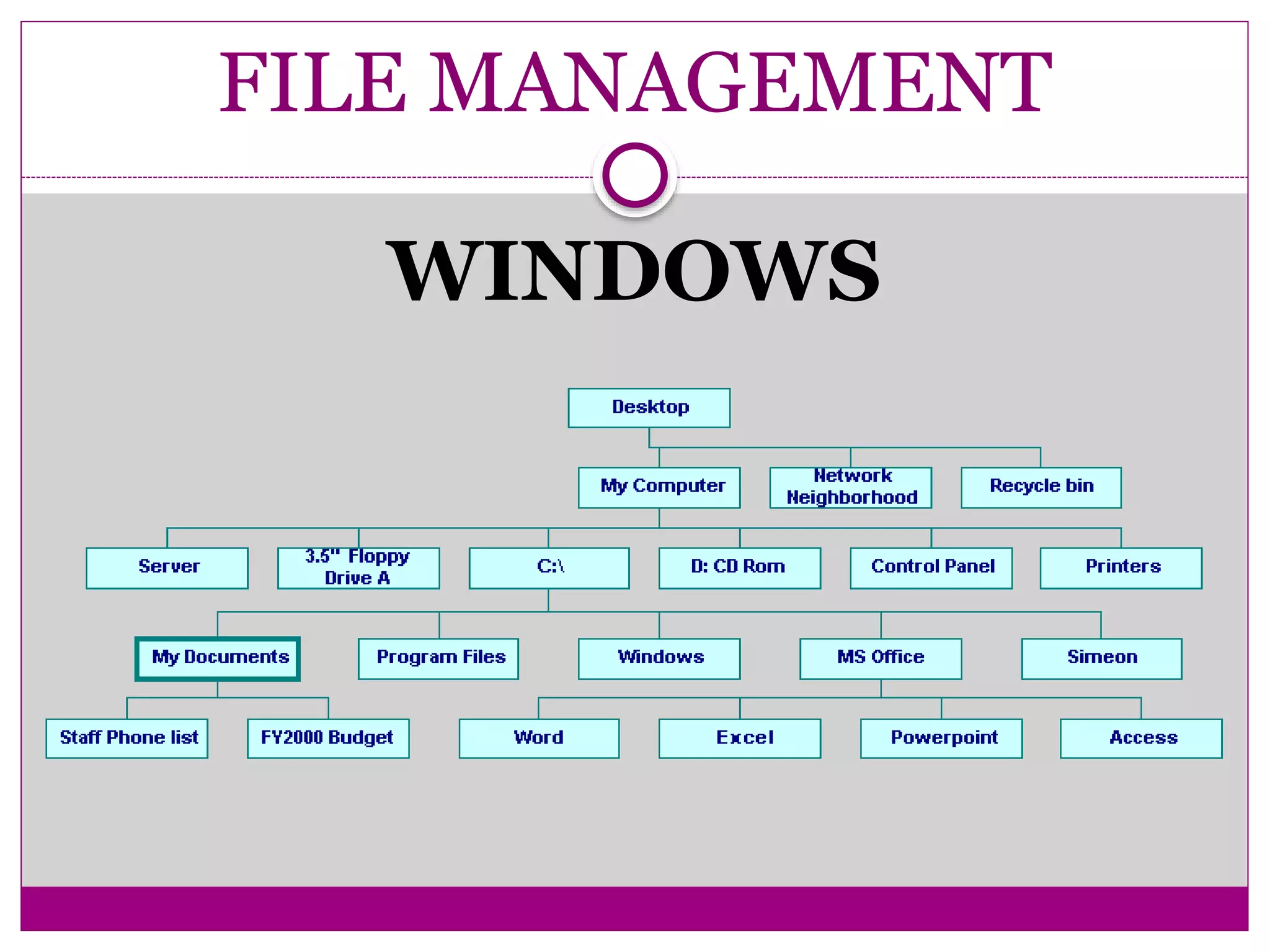
This document compares Linux and Windows operating systems. It provides histories of Linux, starting with the GNU project in 1984 and Linus Torvalds releasing the first Linux kernel in 1991. The evolution of Windows is also outlined from Windows 3.1 to Windows Me. The document then summarizes key differences between Linux and Windows in areas like process management, memory management, I/O management, and file management.