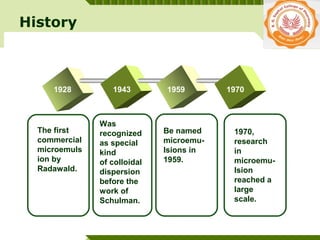
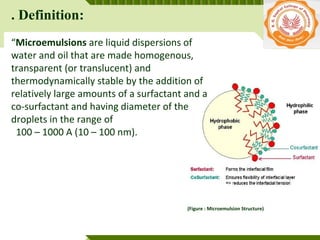
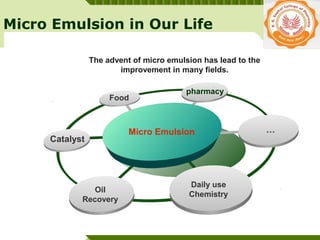
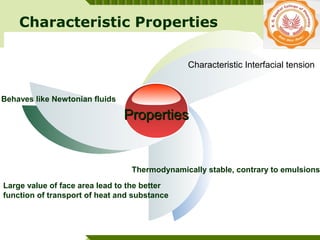
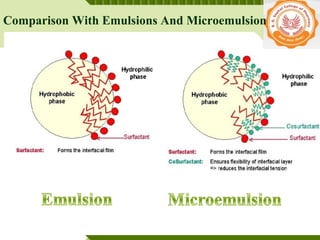
Microemulsions are thermodynamically stable transparent (or translucent) dispersions of oil, water, and surfactant, with droplet sizes typically between 10-100 nm. They form spontaneously due to the presence of surfactants and co-surfactants that lower the interfacial tension between oil and water. Microemulsions have advantages over emulsions such as improved drug solubilization, thermodynamic stability, and ease of manufacture. They are widely used in pharmaceuticals, personal care products, and enhanced oil recovery.