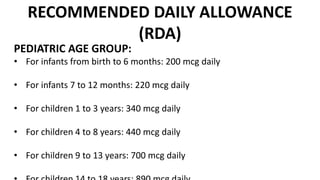
Copper is an essential trace element found in all human tissues. It plays an important role in many processes including iron transport, collagen formation, antioxidant activity and enzyme function. The average adult contains around 100-150mg of copper stored primarily in the muscles, bones and liver. Dietary sources include meat, shellfish, nuts and cereals. The recommended daily allowance is 900mcg for adults. Copper absorption requires special mechanisms and can be inhibited by other minerals or vitamins taken in excess. A copper deficiency can result in issues like anemia, bone disorders and grey hair.



![SOURCES
• Average diet provides 2 to 4 mg/day in the form of
meat, shellfish, legumes, nuts and cereals. Milk and
milk-products are poor sources.[1]
• oysters, liver, whole grain breads, dark green leafy
vegetables and chocolate are other sources.[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copper-170504082723/85/Copper-Nutrition-4-320.jpg)
![FUNCTIONS
• Copper is required in synthesis of hemoglobin, although it is not a
component of Hb.[1]
• Copper works together with iron to form RBCs. [2]
• Keeps nerve cells and immune system healthy.[2]
• It helps form collagen (key part of bones & connective tissue). [2]
• Acts as antioxidant. [2]
• Copper helps body absorb iron.[2]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copper-170504082723/85/Copper-Nutrition-5-320.jpg)
![FUNCTIONS[1]
• Role in enzyme action
• Helps in Fe++ metabolism
• Maturation of Elastin
• Formation of bones and maintenance of myelin sheath](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copper-170504082723/85/Copper-Nutrition-6-320.jpg)



![• If you take a copper supplement, you should
also take a zinc supplement (8 to 15 mg of zinc
for every 1 mg of copper), as an imbalance of
these two minerals can cause other health
problems.[3]
• For your body to use copper, you need to have a
balance of zinc and manganese.[3]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/copper-170504082723/85/Copper-Nutrition-11-320.jpg)





