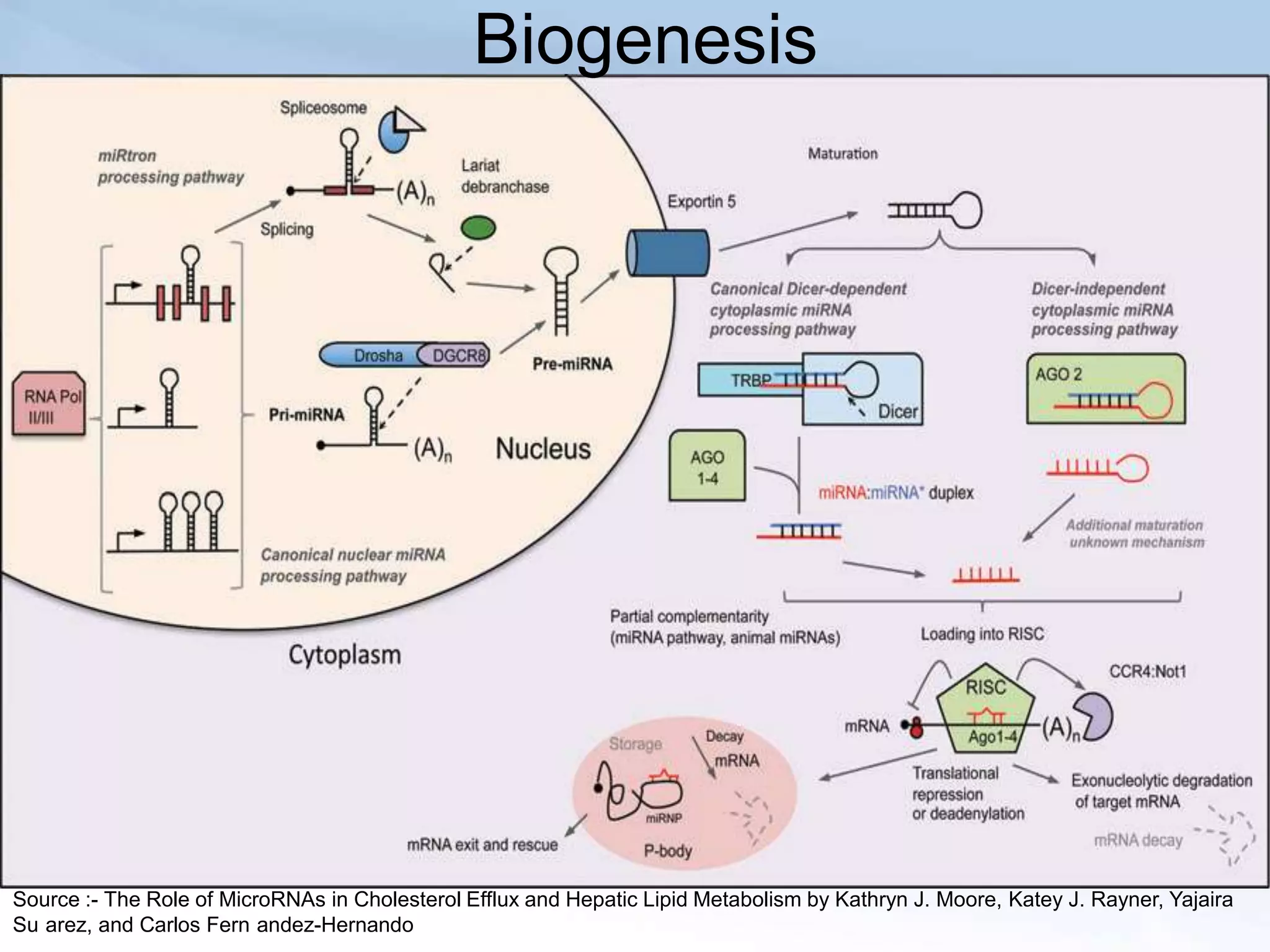
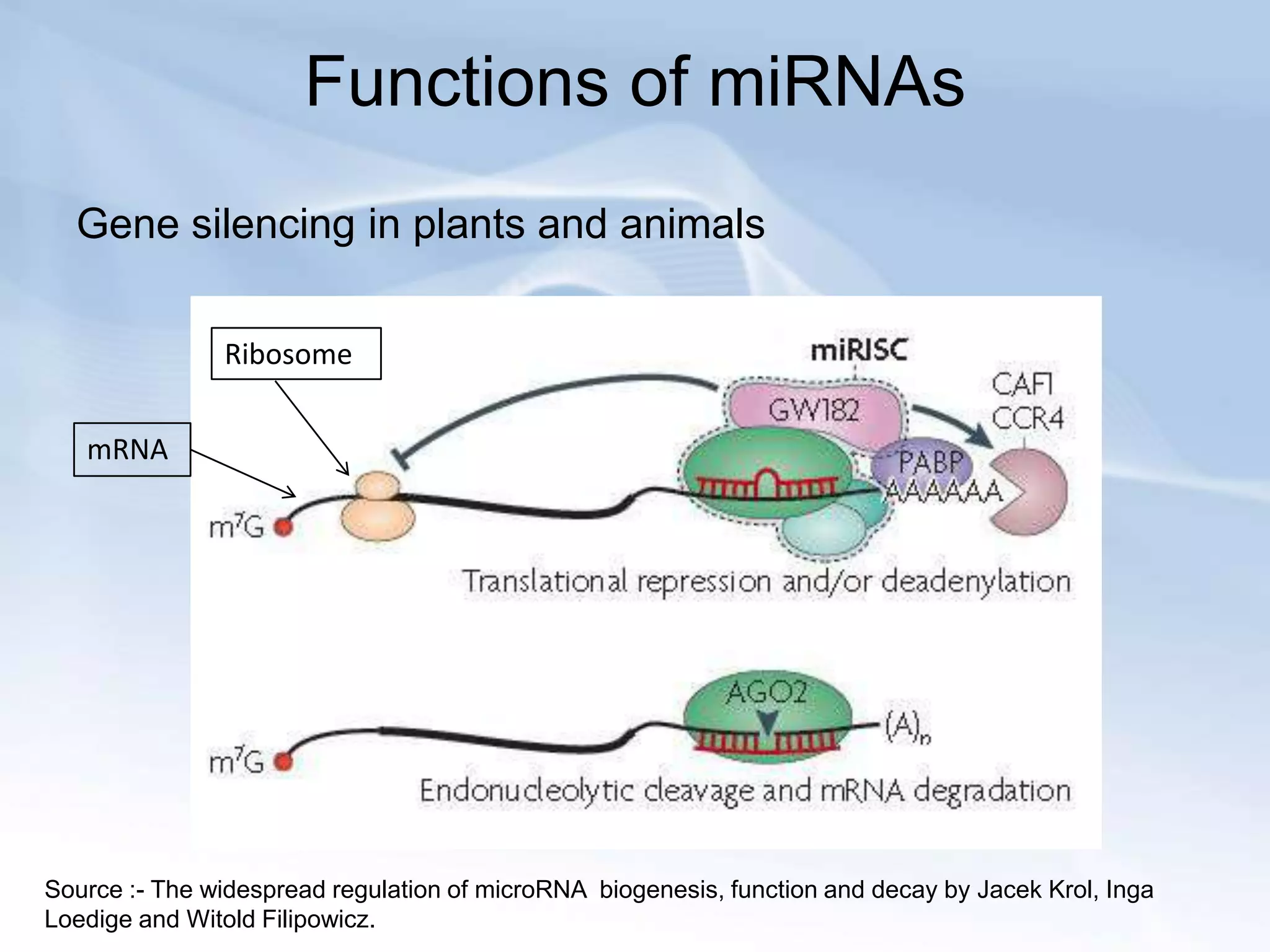
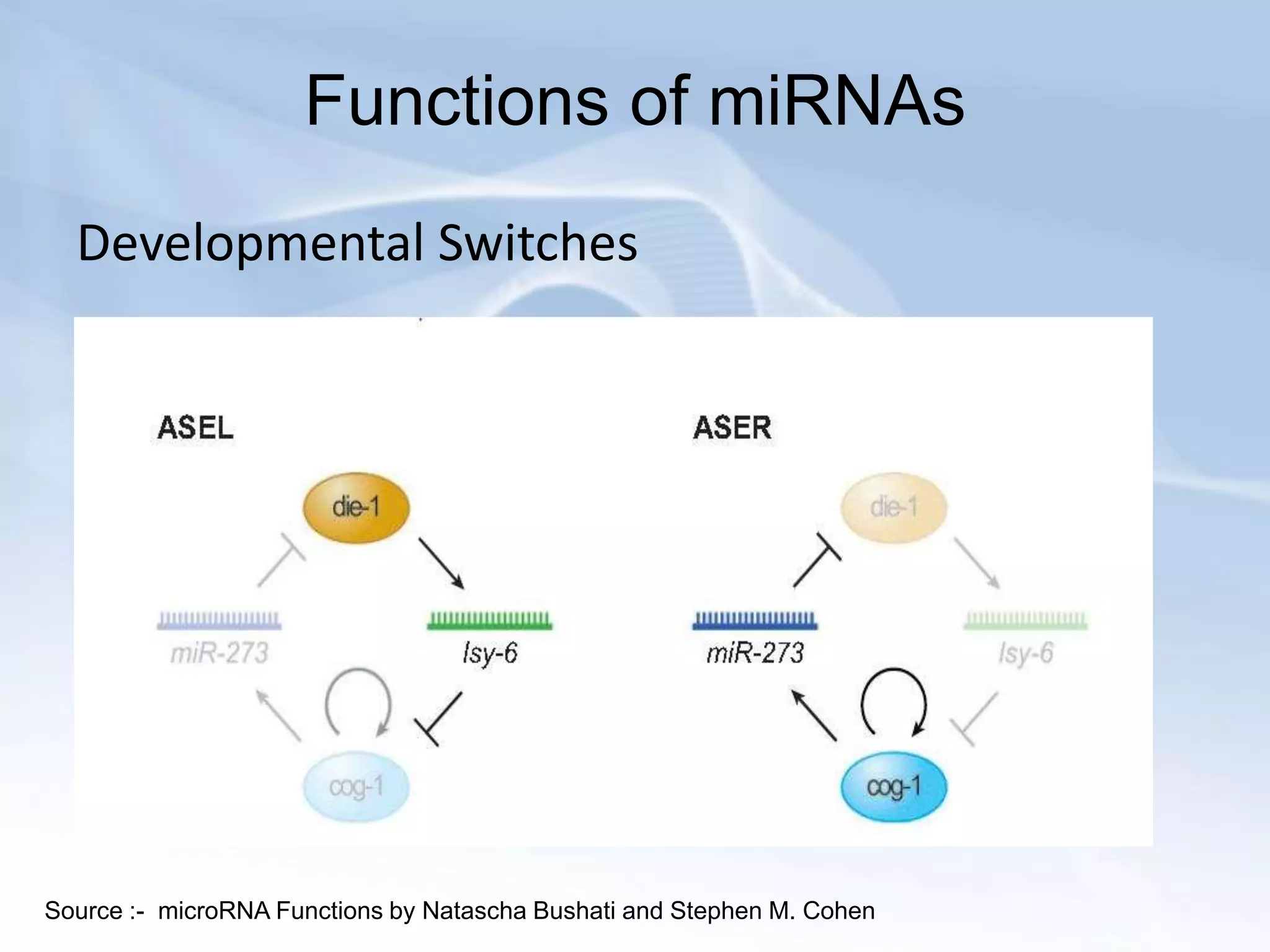
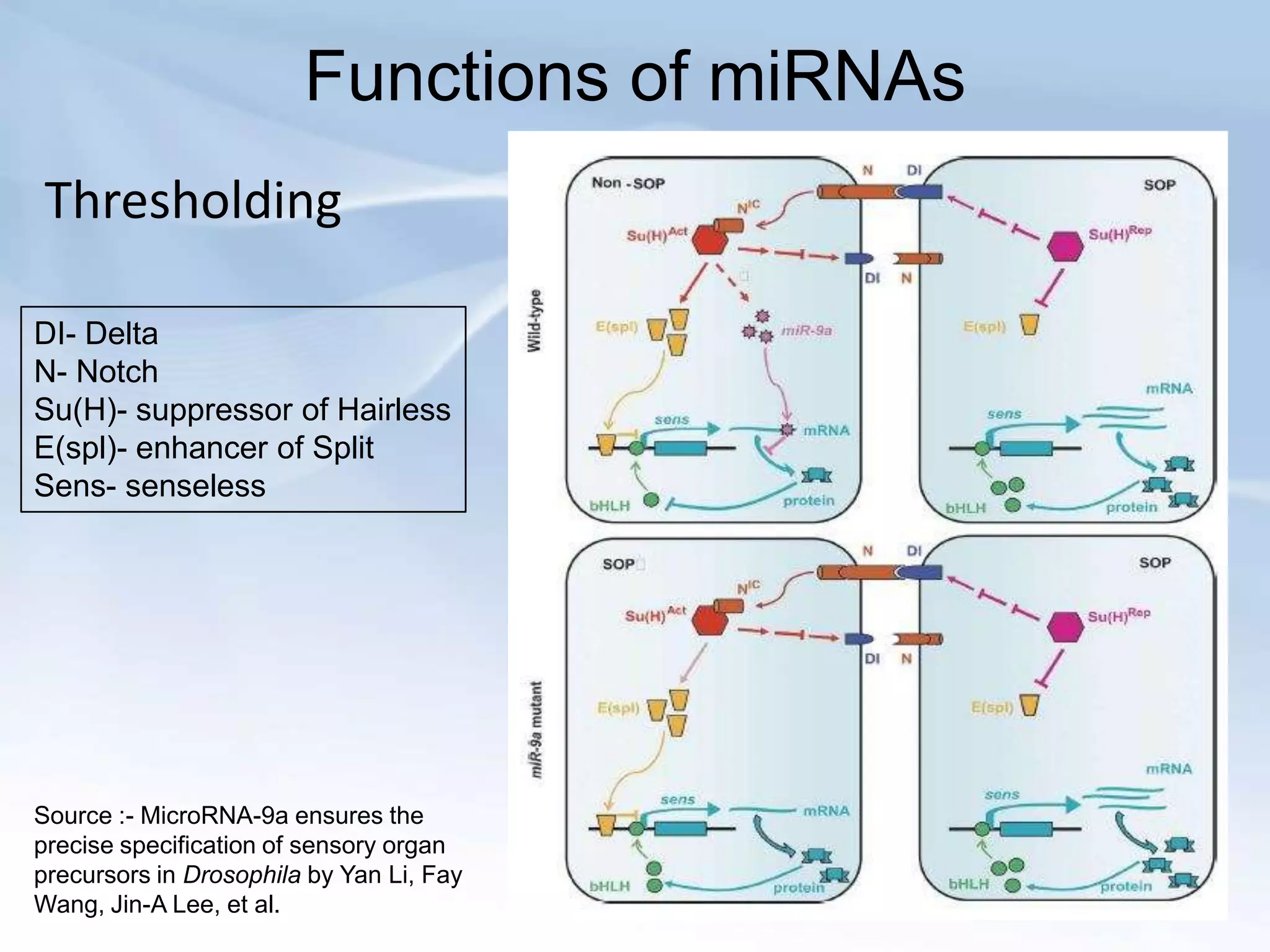
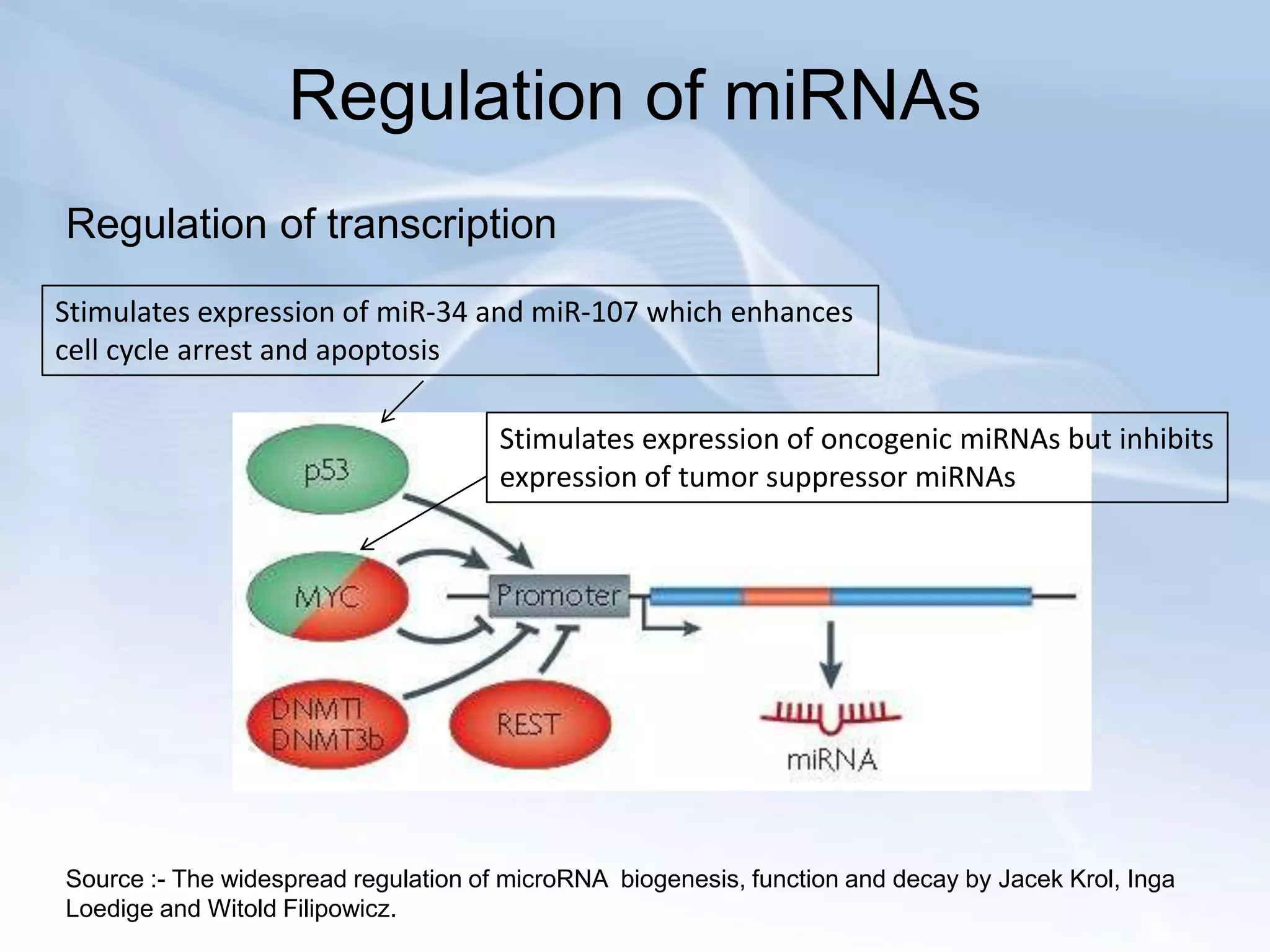
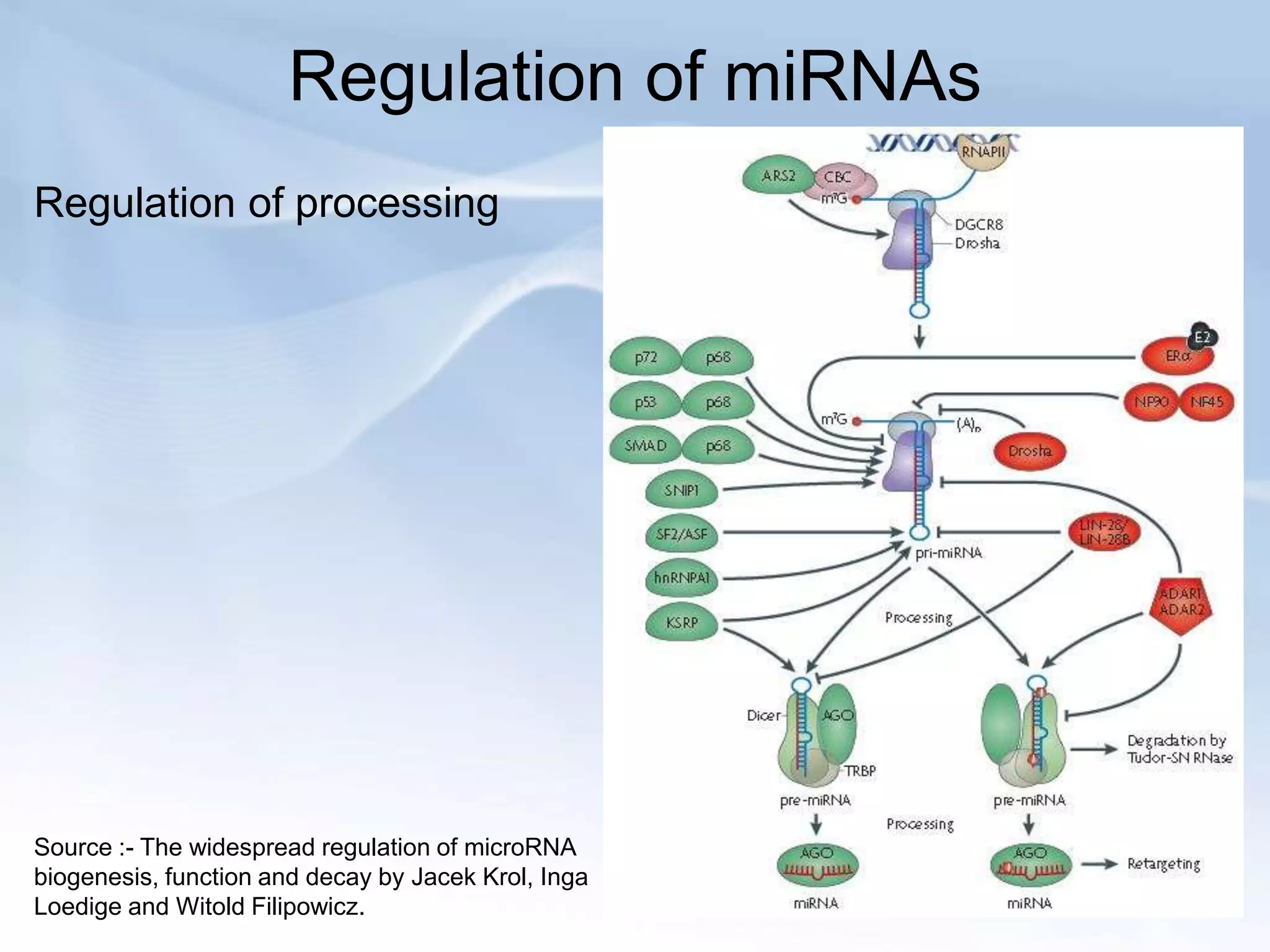
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs that play important gene regulatory roles in eukaryotic cells. They are approximately 22 nucleotides in length and are transcribed from independent genes or introns, then processed through a biogenesis pathway before targeting mRNAs for silencing or degradation. MiRNAs regulate genes involved in development, metabolism, and diseases like cancer. Their expression and function is tightly controlled through transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms in order to influence protein expression levels. While much progress has been made in understanding miRNAs, further study is still needed to elucidate their complex regulatory networks and roles in development and disease.