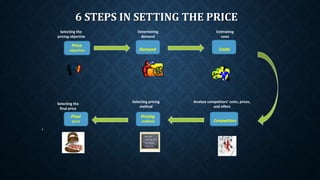
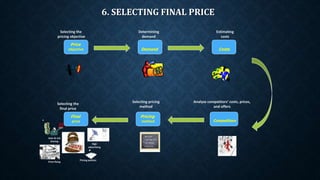
The document provides an overview of pricing strategies and concepts. It discusses factors that affect pricing decisions like costs, demand, competition and objectives. It also covers different pricing strategies such as market entry pricing, product-mix pricing, price adjustments and promotions. Specific strategies discussed include market skimming, bundling, discounts and odd/even pricing. The effects of the internet on pricing like transparency and weakened loyalty are also summarized.