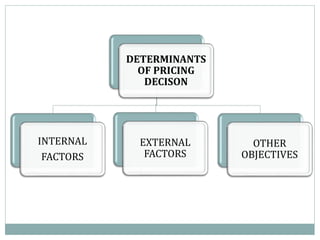
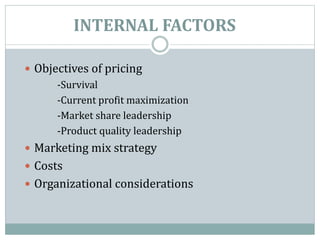
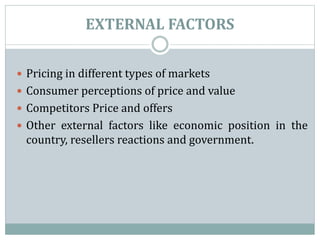
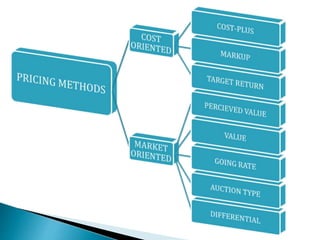
The document outlines pricing strategies and considerations for businesses, detailing both internal and external factors that influence pricing decisions. It covers various pricing methods such as cost-oriented and market-oriented pricing, including penetration and market skimming strategies. Ultimately, the guide serves as an educational resource for understanding how to effectively set prices in different market conditions.