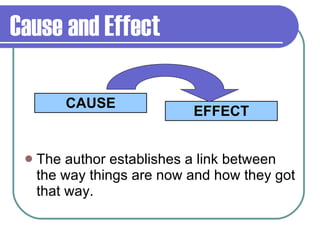
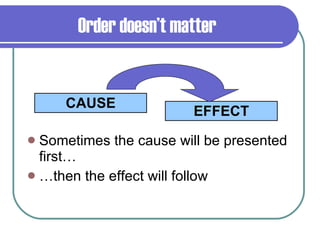
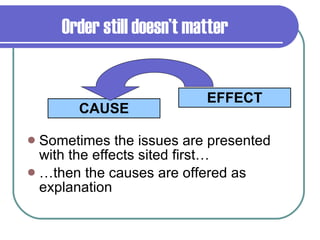
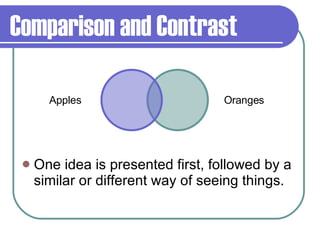
The document discusses different methods authors use to organize and present ideas in their writing, including chronological order, cause and effect, comparison and contrast, and main idea with supporting details. It provides examples to illustrate each organizational pattern and notes that authors choose patterns to support their purpose and make their ideas clear for readers.