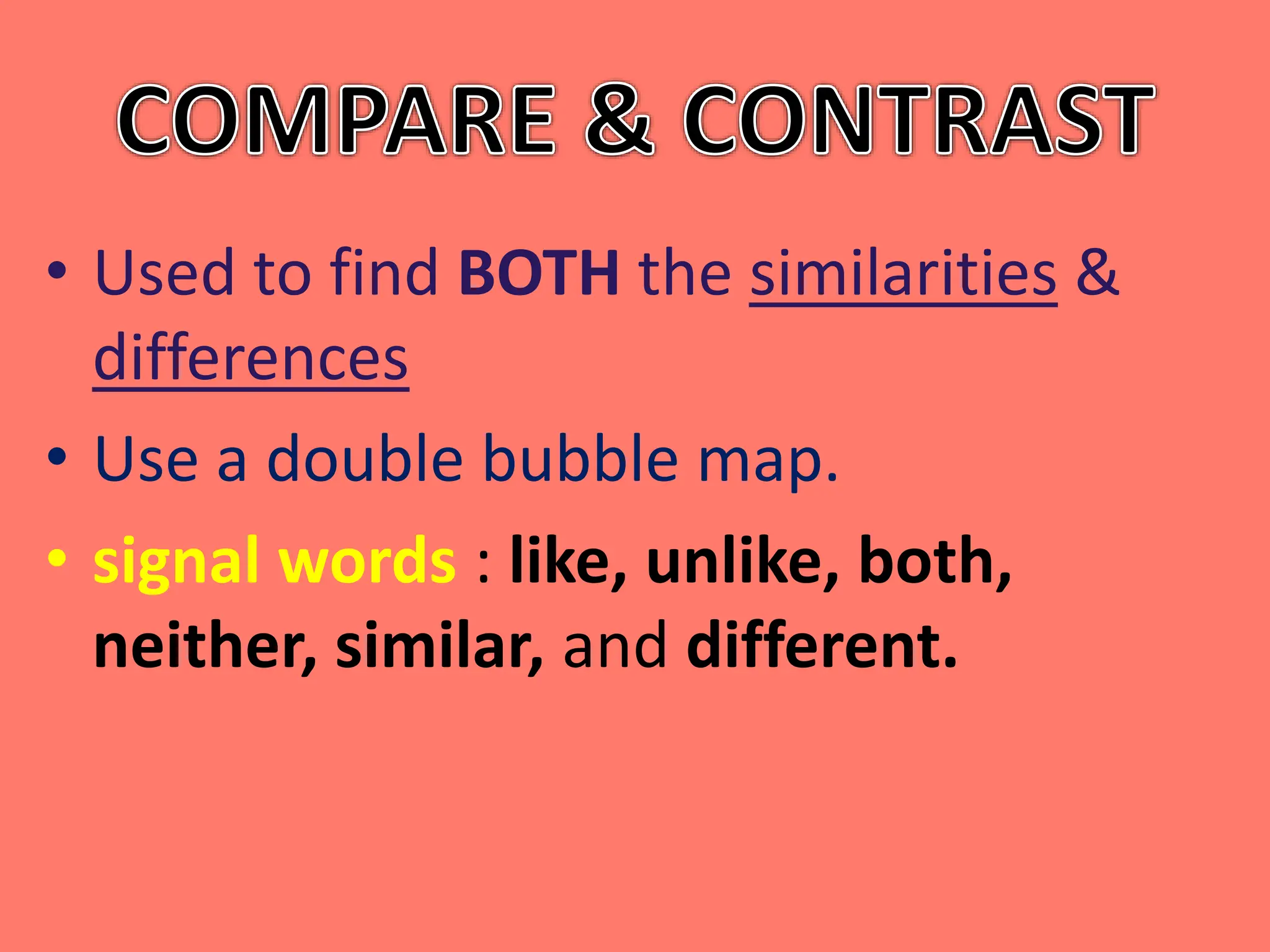
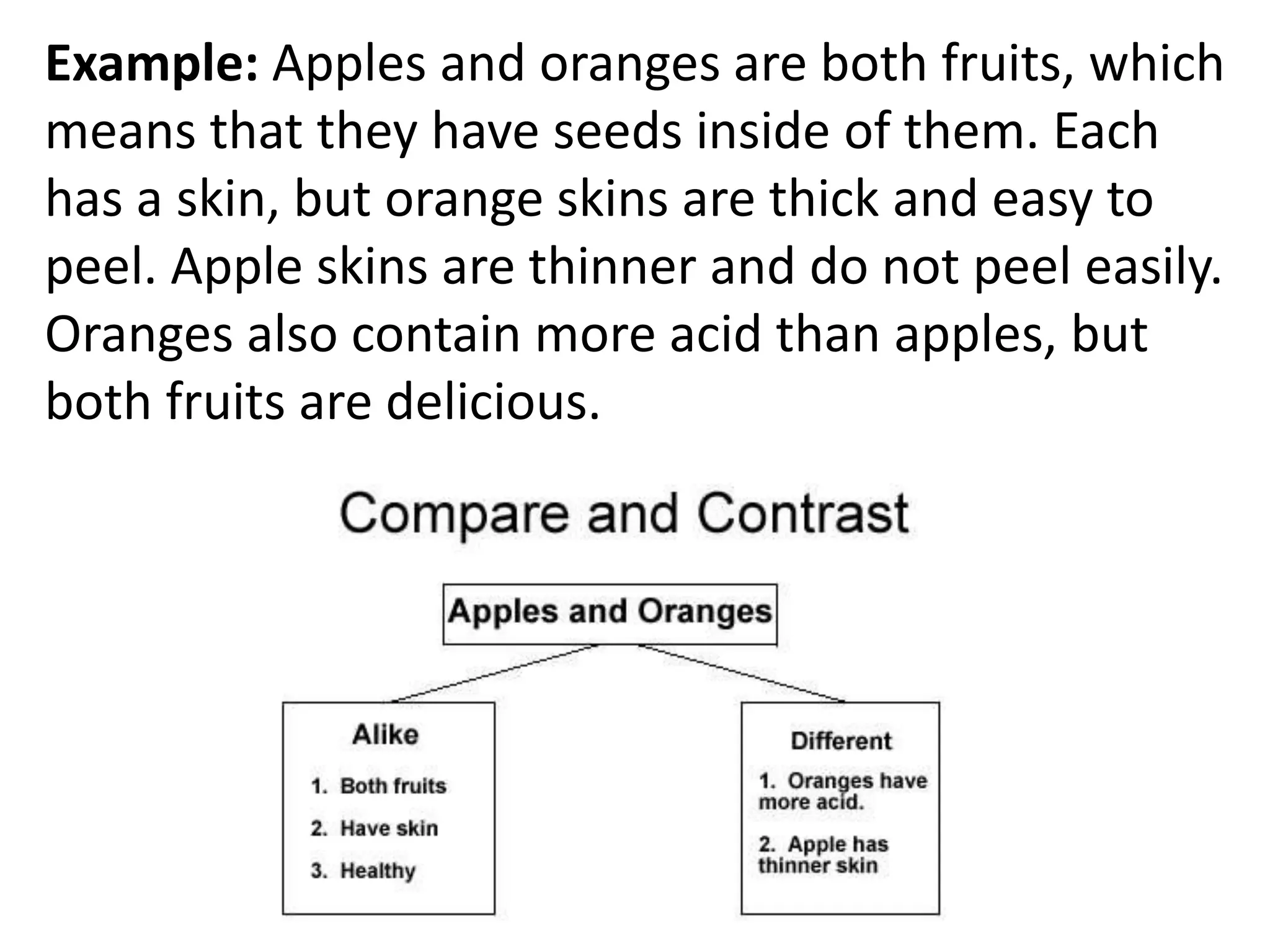
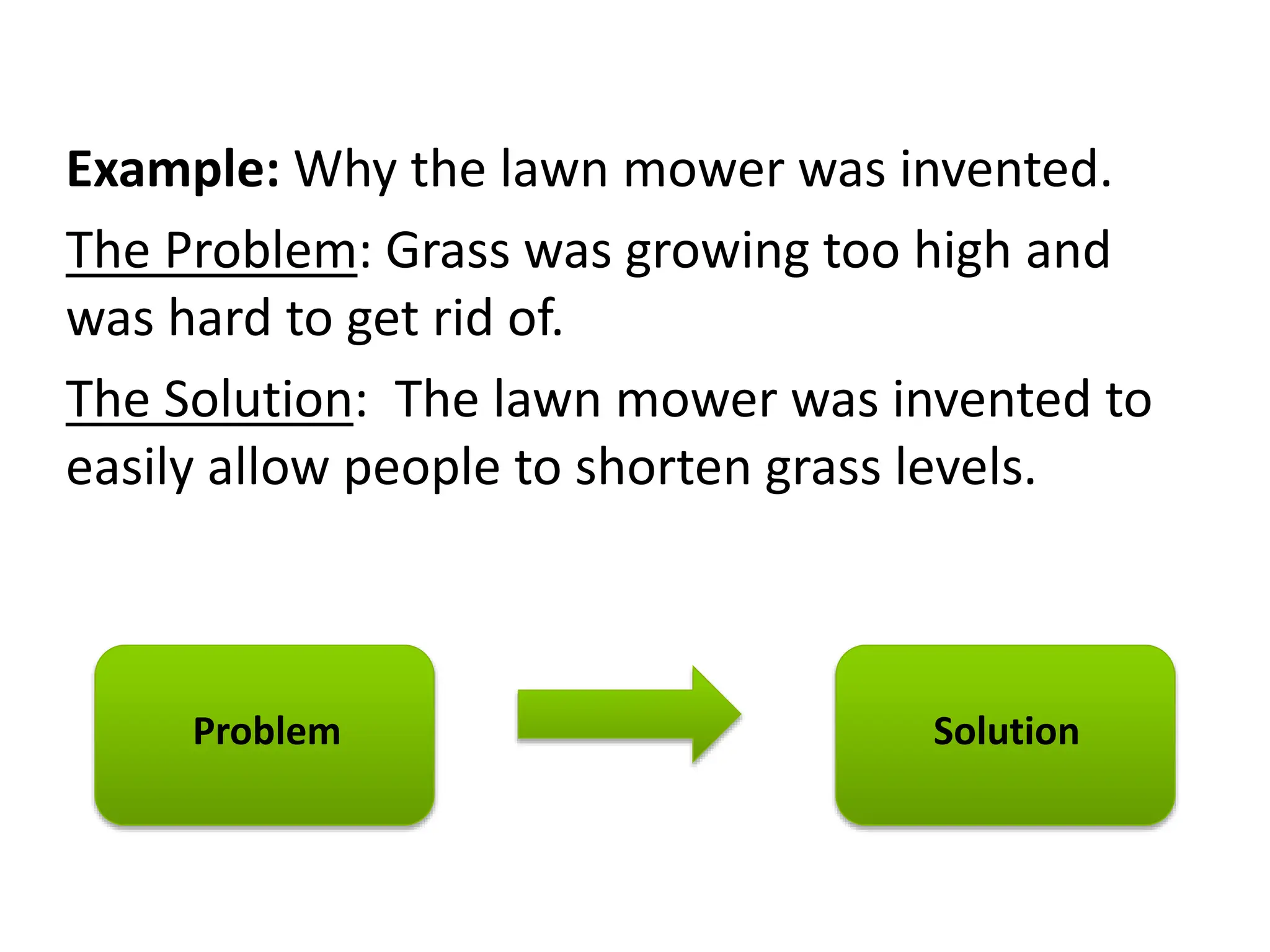
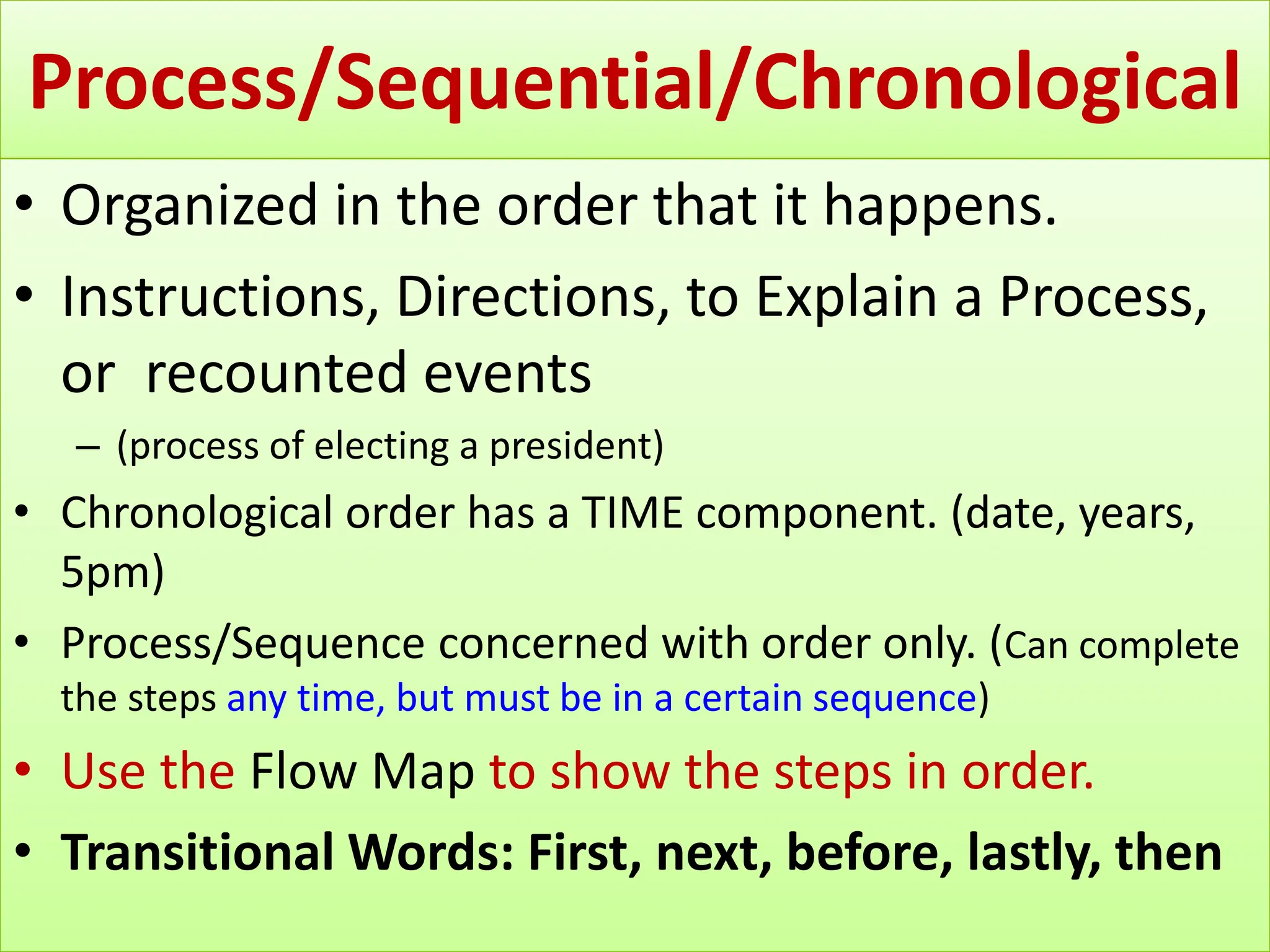
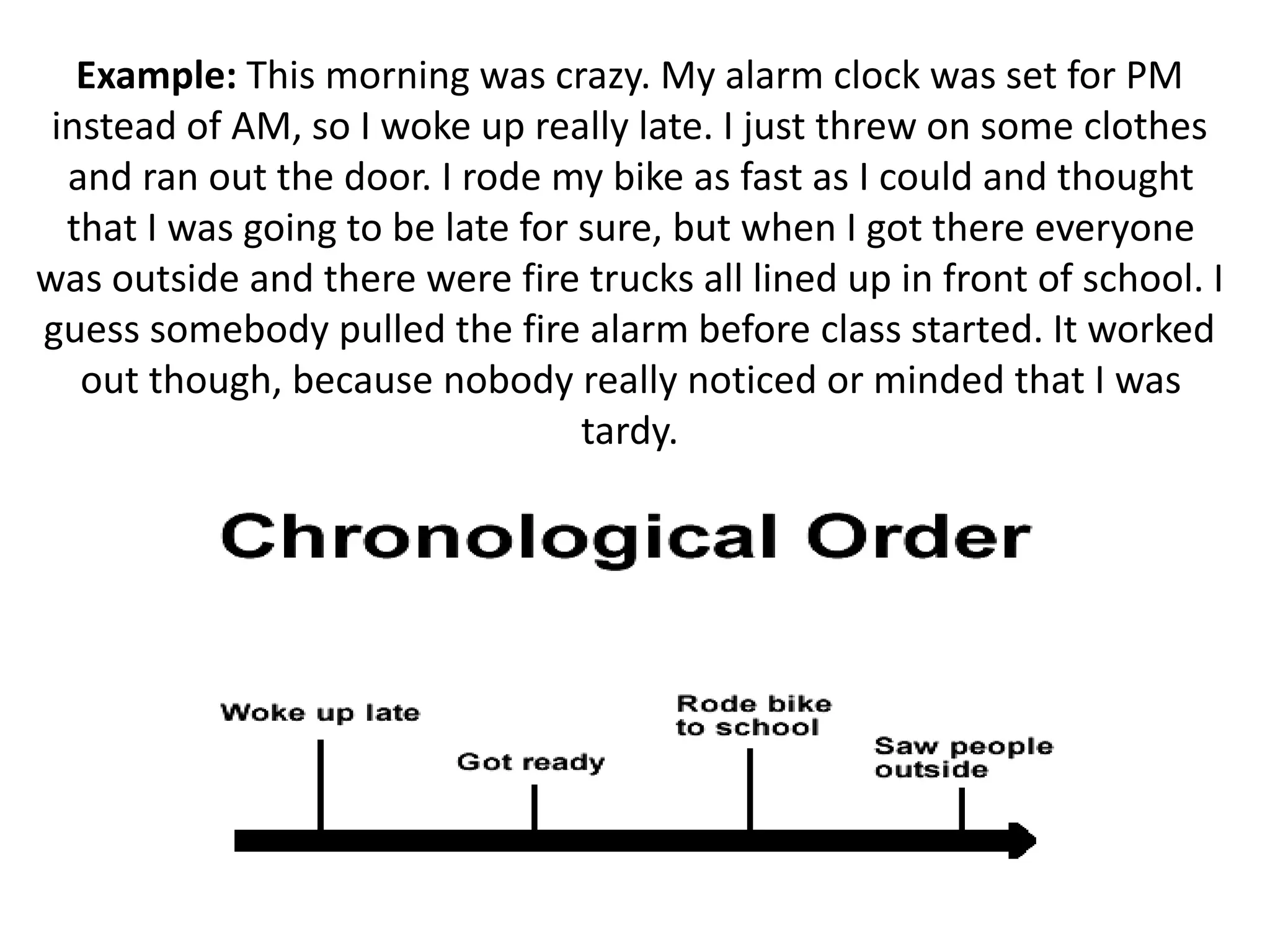
This document discusses the five most common organizational patterns for nonfiction writing: cause and effect, compare and contrast, problem and solution, process/chronological, and description. Each pattern is defined and examples are provided. Cause and effect explains reasons and consequences, compare and contrast finds similarities and differences, problem and solution presents an issue and solutions, process/chronological is ordered by steps or timeline, and description provides details about a topic.