Methodology Checklist : Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy
•Download as DOC, PDF•
1 like•127 views
This document presents a methodology checklist for studies of diagnostic accuracy based on the work of the QUADAS2 team at Bristol University. The checklist consists of 4 domains to assess risk of bias and applicability: 1) patient selection, 2) index test, 3) reference standard, and 4) flow and timing. Each domain contains criteria to determine if a study has introduced bias or is applicable to the diagnostic accuracy question. The overall quality of studies should be assessed as high, acceptable, or unacceptable based on how many criteria are met.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Critical appraisal of prognostic article

This document outlines key criteria for critically appraising the validity and usefulness of a study on prognosis. It discusses whether the study had a well-defined and representative patient sample, sufficiently long and complete follow-up, objective outcome criteria, adjustment for prognostic factors, and precise estimates of likelihood. It also addresses whether the study patients are similar to one's own, if the results can guide therapy decisions or patient counseling.
Appraisal of research v3

Dr. Kulkarni outlines 15 criteria for evaluating research papers, including the title, research questions, study population, sampling method, study design, bias, reporting standards, definitions, protocol deviations, tables/graphs, statistical analysis, discussion appropriateness, ethics, references, and overall impact. He provides examples and questions to consider for each criterion to thoroughly assess the strengths and limitations of a research article. The document serves to educate participants on properly analyzing journal articles through a systematic evaluation of their methodology and findings.
Critical appraisal diagnostic

This study evaluated the performance of rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) compared to ELISA for HIV screening. A total of 787 patient sera were tested using three different RDTs and ELISA, with western blot as the reference standard. The first RDT missed identifying 9 HIV-positive samples that ELISA correctly identified, giving the RDT a sensitivity of 77.5% compared to ELISA. The RDT also had 5 false positive results, giving it a specificity of 99.3% compared to ELISA. While the study provides the sensitivity and specificity of the RDT compared to ELISA, it does not provide confidence intervals for the results. The population studied represents asymptomatic individuals seeking HIV screening, so the results could likely be applied to screening
Levels of evidence, recommendations & phases of

This document discusses levels of evidence and phases of clinical trials. It defines evidence-based medicine as using current best evidence from systematic research to make decisions about patient care. Levels of evidence are ranked from 1A to 5 based on study design, with systematic reviews and randomized controlled trials ranked highest. Clinical trials progress through four phases to test safety, efficacy, and optimal use of new drugs or devices. Phase 1 assesses safety, phase 2 establishes efficacy, phase 3 confirms safety and efficacy in larger groups, and phase 4 studies monitor risks and benefits after marketing.
Dhiwahar ppt

This document provides an overview of critical appraisal of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). It defines critical appraisal as carefully examining research to assess its trustworthiness and relevance. RCTs are described as the gold standard for clinical trials, where participants are randomly allocated to groups that receive either a treatment or a control. Key factors to examine in appraising an RCT are described, including sample size, eligibility criteria, baseline characteristics, randomization, blinding, follow-up of participants, data collection, presentation of results, and applicability to local populations. Advantages of critical appraisal and RCTs include providing a systematic way to assess research validity and improving practice, while disadvantages include taking time and not always finding clear answers.
Assessment of Bias

This document discusses assessing risk of bias in studies included in systematic reviews. It defines bias as systematic error that can vary in direction and magnitude. The Cochrane Risk of Bias tool is recommended for assessing bias in domains such as selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, and reporting bias. Assessments involve describing the risk of bias and making a judgment of low, high, or unclear risk. Summary assessments of risk of bias are made within and across studies.
Critical appraisal guideline

This document provides an overview of evidence-based medicine and how to critically appraise clinical papers. It discusses how evidence-based medicine involves using both clinical expertise and the best available external evidence in decision making. The origins of evidence-based medicine in the 1970s and 1990s are also reviewed. The document then focuses on how to critically read clinical papers, including the key things to assess for diagnostic tests, clinical course/prognosis, causation, and therapy papers. It provides guidance on an appraisal format and emphasizes the need to both evaluate the study and summarize what it was about. Evidence-based medicine is positioned as an important guide but not a replacement for clinical expertise and judgment.
HLinc presentation: levels of evidence

What are hierarchies of evidence and why are they used? How are they different from grades of recommendation? HLinc presentation May 2014
Recommended
Critical appraisal of prognostic article

This document outlines key criteria for critically appraising the validity and usefulness of a study on prognosis. It discusses whether the study had a well-defined and representative patient sample, sufficiently long and complete follow-up, objective outcome criteria, adjustment for prognostic factors, and precise estimates of likelihood. It also addresses whether the study patients are similar to one's own, if the results can guide therapy decisions or patient counseling.
Appraisal of research v3

Dr. Kulkarni outlines 15 criteria for evaluating research papers, including the title, research questions, study population, sampling method, study design, bias, reporting standards, definitions, protocol deviations, tables/graphs, statistical analysis, discussion appropriateness, ethics, references, and overall impact. He provides examples and questions to consider for each criterion to thoroughly assess the strengths and limitations of a research article. The document serves to educate participants on properly analyzing journal articles through a systematic evaluation of their methodology and findings.
Critical appraisal diagnostic

This study evaluated the performance of rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) compared to ELISA for HIV screening. A total of 787 patient sera were tested using three different RDTs and ELISA, with western blot as the reference standard. The first RDT missed identifying 9 HIV-positive samples that ELISA correctly identified, giving the RDT a sensitivity of 77.5% compared to ELISA. The RDT also had 5 false positive results, giving it a specificity of 99.3% compared to ELISA. While the study provides the sensitivity and specificity of the RDT compared to ELISA, it does not provide confidence intervals for the results. The population studied represents asymptomatic individuals seeking HIV screening, so the results could likely be applied to screening
Levels of evidence, recommendations & phases of

This document discusses levels of evidence and phases of clinical trials. It defines evidence-based medicine as using current best evidence from systematic research to make decisions about patient care. Levels of evidence are ranked from 1A to 5 based on study design, with systematic reviews and randomized controlled trials ranked highest. Clinical trials progress through four phases to test safety, efficacy, and optimal use of new drugs or devices. Phase 1 assesses safety, phase 2 establishes efficacy, phase 3 confirms safety and efficacy in larger groups, and phase 4 studies monitor risks and benefits after marketing.
Dhiwahar ppt

This document provides an overview of critical appraisal of randomized controlled trials (RCTs). It defines critical appraisal as carefully examining research to assess its trustworthiness and relevance. RCTs are described as the gold standard for clinical trials, where participants are randomly allocated to groups that receive either a treatment or a control. Key factors to examine in appraising an RCT are described, including sample size, eligibility criteria, baseline characteristics, randomization, blinding, follow-up of participants, data collection, presentation of results, and applicability to local populations. Advantages of critical appraisal and RCTs include providing a systematic way to assess research validity and improving practice, while disadvantages include taking time and not always finding clear answers.
Assessment of Bias

This document discusses assessing risk of bias in studies included in systematic reviews. It defines bias as systematic error that can vary in direction and magnitude. The Cochrane Risk of Bias tool is recommended for assessing bias in domains such as selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, and reporting bias. Assessments involve describing the risk of bias and making a judgment of low, high, or unclear risk. Summary assessments of risk of bias are made within and across studies.
Critical appraisal guideline

This document provides an overview of evidence-based medicine and how to critically appraise clinical papers. It discusses how evidence-based medicine involves using both clinical expertise and the best available external evidence in decision making. The origins of evidence-based medicine in the 1970s and 1990s are also reviewed. The document then focuses on how to critically read clinical papers, including the key things to assess for diagnostic tests, clinical course/prognosis, causation, and therapy papers. It provides guidance on an appraisal format and emphasizes the need to both evaluate the study and summarize what it was about. Evidence-based medicine is positioned as an important guide but not a replacement for clinical expertise and judgment.
HLinc presentation: levels of evidence

What are hierarchies of evidence and why are they used? How are they different from grades of recommendation? HLinc presentation May 2014
Critically appraise evidence based findings

The document discusses critical appraisal of evidence-based findings. It defines critical appraisal as assessing the strength and quality of scientific evidence to evaluate its applicability to healthcare decision making. Strength of evidence depends on factors like quality, quantity, and consistency of research. Evidence is ranked in levels based on research design, with systematic reviews and randomized controlled trials having the highest levels of evidence. Evaluating the quality and applicability of evidence involves assessing the validity of results and whether results can be applied to target populations. Statistical evaluation through effect sizes can also aid in appraising evidence.
Critical appraisal of diagnostic article

This document provides guidance on critically appraising articles about diagnostic tests using the four steps of evidence-based medicine: ask, acquire, appraise, and apply. It discusses assessing whether diagnostic test results are valid by evaluating the study design, spectrum of patients, and blinding of test interpretation. Key results include likelihood ratios which indicate how much a test result changes the probability of disease. Application involves considering test reproducibility, applicability to practice, and whether test results will change management and improve patient outcomes with acceptable risks and available treatment.
4. level of evidence

The document discusses various frameworks for rating the level of evidence in studies, including the NHMRC, GRADE, Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, and Sackett scales. It outlines the different levels in each scale, with the highest levels reserved for systematic reviews and randomized controlled trials. The lowest levels include case series, case reports, and expert opinion without critical analysis. It also provides guidance on selecting the appropriate study design based on different types of clinical questions regarding therapy, diagnosis, etiology, prognosis, prevention, or costs.
Bias in clinical research 

This is an interesting ppt discussing in detail about bias in clinical research and how to overcome it...
Critical appraisal of published medical research (2)

This document outlines 8 steps for critically appraising published medical research: 1) consider the research hypothesis, 2) study design, 3) outcome variable, 4) predictor variables, 5) methods of analysis, 6) potential sources of bias, 7) interpretation of results, and 8) utility of results. For each step, it provides questions to consider when evaluating if a study has addressed that aspect appropriately and rigorously. The goal is to systematically evaluate the strengths and limitations of a published study.
Doug Altman - MedicReS World Congress 2012 

The document discusses tools for assessing risk of bias in systematic reviews. It outlines the development of the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool, which evaluates randomized controlled trials across 7 domains related to selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, and reporting bias. The tool aims to provide a standardized approach for assessing bias in a way that is transparent and focuses on biases rather than other quality issues. It has informed the risk of bias assessment approach used in Cochrane systematic reviews.
Research Design

The document discusses different types of research designs, including explanatory trials which aim to study efficacy under ideal conditions, pragmatic trials which aim to study effectiveness in regular clinical practice, and cost benefit studies which aim to study efficiency in relation to resources consumed. It also discusses analytical studies, experimental trials using control groups, randomized controlled trials including group comparative and cross-over designs, non-randomized controlled trials, uncontrolled clinical trials, cohort studies, cross-sectional studies, and case control studies. The key aspects of each design such as whether they are prospective or retrospective and examples are provided.
Randomised controlled trials

Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are considered the gold standard for clinical research. An RCT involves randomly assigning participants into experimental and control groups to receive different interventions. Randomization aims to make the groups comparable to limit bias. It reduces the influence of unknown factors and ensures the only difference between groups is the intervention being tested. RCTs can be single blind, double blind, or triple blind depending on who is aware of group assignments. They provide the most powerful and least biased assessments of clinical interventions.
Blinding in RCT the enigma unraveled

Randomized Control Trials
Enigma of Blinding Unraveled
Introduction
RCT
Steps in a RCT
Allocation Concealment
Bias in RCT
Phases in RCT
Types of RCT
Study Designs of RCT
Blinding
Methods of Blinding in different trials
Assessment of Blinding
Un-blinding
Current Scenario of Blinding
CONSORT
Conclusion
References
Critical appraisal of randomized clinical trials

The document discusses key concepts in randomized clinical trials (RCTs), including:
1) RCTs are considered the gold standard for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions due to their ability to minimize bias through randomization and blinding.
2) Proper randomization aims to create comparable treatment and control groups, conceal allocation to prevent bias, and may involve simple, stratified or blocked methods.
3) Blinding (masking) of participants, investigators and assessors can decrease observation bias and is important for RCT validity, though full blinding is not always possible.
4) Intention-to-treat analysis includes all randomized patients to preserve comparable groups and prevent bias from non-compliance.
5. experimental studies

This document provides an overview of experimental study design. It defines experimental studies as those where the investigator actively attempts to modify a dependent variable by introducing an intervention. It describes different types of experimental studies including clinical trials, field trials, and community trials. It then outlines the typical steps in a clinical trial, including deciding on the trial, forming research questions and hypotheses, defining and selecting the study population, determining inclusion/exclusion criteria, calculating sample size, enrolling and randomly allocating participants, implementing the regimen, measuring variables, following up on outcomes, analyzing results, and reporting findings. Finally, it briefly discusses phases of clinical trials and some variants like cross-over and factorial designs.
randomised controlled trial 

This document provides an overview of randomized controlled trials (RCTs), including their purpose and design. It discusses key aspects of RCTs such as randomization, blinding, and assessing outcomes. It provides examples of simple two-arm and cross-over RCT designs. The document also summarizes a specific cluster RCT that evaluated the effects of various child development and nutrition interventions on outcomes measured in children from birth to age 2 years.
Critical appraisal of published medical research

This document discusses critical appraisal of published medical research. It notes that thousands of new medical articles are published daily, making it difficult for clinicians to keep up-to-date. Critical appraisal involves assessing the validity, reliability, and applicability of a study rather than just dismissing it or looking only at the results. Key aspects of critical appraisal include describing the evidence, assessing internal validity by examining potential biases and confounding factors, evaluating external validity and whether results can apply to other populations, and comparing results to other evidence. The document provides guidance on how to critically appraise studies and lists resources for further information.
evidence based periodontics 

This document provides an overview of evidence-based periodontics. It discusses the need for evidence-based decision making to reduce variations in clinical practice. The advantages of an evidence-based approach are that it is objective, scientifically sound, patient-focused, and incorporates clinical expertise. The process of evidence-based decision making involves framing questions, searching for and appraising evidence from various sources and levels, evaluating outcomes, and implementing decisions. Key aspects include assessing evidence critically and avoiding changes to pre-established hypotheses.
Study design of Prof Zak

How to scientifically conduct a clinical professional research trial? In the current era of Collaborate or parish, we need to keep this design in our mind.
Enjoy
@copyLeft
Ebd jc part 5

This document summarizes a journal club presentation about critically appraising papers on dental therapy. It discusses key questions to consider when evaluating randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews relating to new therapeutic interventions. These include whether patient allocation was randomized, all patients were accounted for, blinding was used, groups were similar at outset, clinically important outcomes were assessed, and results can be applied to patients. It also reviews criteria for assessing systematic reviews, such as whether a clear question was asked, inclusion criteria were appropriate, search was comprehensive, study validity was evaluated, and findings were combined correctly.
Methodology Checklist: Cohort studies

The document provides a methodology checklist for cohort studies, outlining key criteria such as having a clearly focused question, comparable study groups, low dropout rates, blinding of outcome assessments, addressing potential confounders, and providing confidence intervals. The checklist is intended to help reviewers critically appraise cohort studies and identify potential sources of bias.
Ebm & critical appraisal

This document provides an introduction to evidence-based medicine (EBM) and principles of critical appraisal for first year psychiatry residents. It defines EBM as a systematic approach to obtaining clinically relevant information about treatment. Critical appraisal involves carefully examining research to assess validity, results, and relevance. The document outlines the five steps of EBM, different study designs commonly used in EBM like randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews, and factors to consider when critically appraising research like potential biases. Key aspects of randomized trials and systematic reviews are described, along with guidelines to standardize research reporting.
Critical appraisal of a journal article

1. This study was a cluster randomized controlled trial that assessed the effects of periodic vitamin A supplementation and deworming on child mortality in 1 million preschool children in North India.
2. The study had a 5-year study period from 1999-2004 and used a 2x2 factorial design to examine the effects of 6-monthly vitamin A supplementation, 6-monthly deworming with albendazole, and their combination on mortality in children aged 1-6 years.
3. The results found that vitamin A supplementation alone did not reduce child mortality as much as expected based on previous trials, reducing mortality by only 4%. However, meta-analysis of this study combined with previous trials still showed an average
3 cross sectional study

This document provides an overview of cross-sectional studies, including what they are, their uses, methodology, advantages, and disadvantages. A cross-sectional study involves observing a population at a single point in time to determine prevalence of disease. It is a quick and inexpensive way to describe characteristics of a population and identify associations between variables. However, it cannot determine causation due to its observational nature.
# 5th lect clinical trial process

This document outlines the key steps in conducting a clinical trial:
1. Drawing up a detailed research protocol that serves as the trial's operating manual.
2. Selecting and screening participants according to eligibility criteria to identify the study population. Sample size is also calculated.
3. Randomly allocating the study participants into experimental and control groups through a process like randomization to reduce bias.
bio equivalence studies

This document discusses bioequivalence studies. It defines bioequivalence as when two drug products reach systemic circulation to the same relative extent, with their plasma concentration-time profiles being identical without statistically significant differences. It describes the analytical methods, pharmacokinetic evaluation, and statistical evaluation used in bioequivalence studies. It also discusses study designs such as parallel designs, crossover designs, and fasting versus fed conditions that can be used in bioequivalence studies.
More Related Content
What's hot
Critically appraise evidence based findings

The document discusses critical appraisal of evidence-based findings. It defines critical appraisal as assessing the strength and quality of scientific evidence to evaluate its applicability to healthcare decision making. Strength of evidence depends on factors like quality, quantity, and consistency of research. Evidence is ranked in levels based on research design, with systematic reviews and randomized controlled trials having the highest levels of evidence. Evaluating the quality and applicability of evidence involves assessing the validity of results and whether results can be applied to target populations. Statistical evaluation through effect sizes can also aid in appraising evidence.
Critical appraisal of diagnostic article

This document provides guidance on critically appraising articles about diagnostic tests using the four steps of evidence-based medicine: ask, acquire, appraise, and apply. It discusses assessing whether diagnostic test results are valid by evaluating the study design, spectrum of patients, and blinding of test interpretation. Key results include likelihood ratios which indicate how much a test result changes the probability of disease. Application involves considering test reproducibility, applicability to practice, and whether test results will change management and improve patient outcomes with acceptable risks and available treatment.
4. level of evidence

The document discusses various frameworks for rating the level of evidence in studies, including the NHMRC, GRADE, Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine, and Sackett scales. It outlines the different levels in each scale, with the highest levels reserved for systematic reviews and randomized controlled trials. The lowest levels include case series, case reports, and expert opinion without critical analysis. It also provides guidance on selecting the appropriate study design based on different types of clinical questions regarding therapy, diagnosis, etiology, prognosis, prevention, or costs.
Bias in clinical research 

This is an interesting ppt discussing in detail about bias in clinical research and how to overcome it...
Critical appraisal of published medical research (2)

This document outlines 8 steps for critically appraising published medical research: 1) consider the research hypothesis, 2) study design, 3) outcome variable, 4) predictor variables, 5) methods of analysis, 6) potential sources of bias, 7) interpretation of results, and 8) utility of results. For each step, it provides questions to consider when evaluating if a study has addressed that aspect appropriately and rigorously. The goal is to systematically evaluate the strengths and limitations of a published study.
Doug Altman - MedicReS World Congress 2012 

The document discusses tools for assessing risk of bias in systematic reviews. It outlines the development of the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool, which evaluates randomized controlled trials across 7 domains related to selection bias, performance bias, detection bias, attrition bias, and reporting bias. The tool aims to provide a standardized approach for assessing bias in a way that is transparent and focuses on biases rather than other quality issues. It has informed the risk of bias assessment approach used in Cochrane systematic reviews.
Research Design

The document discusses different types of research designs, including explanatory trials which aim to study efficacy under ideal conditions, pragmatic trials which aim to study effectiveness in regular clinical practice, and cost benefit studies which aim to study efficiency in relation to resources consumed. It also discusses analytical studies, experimental trials using control groups, randomized controlled trials including group comparative and cross-over designs, non-randomized controlled trials, uncontrolled clinical trials, cohort studies, cross-sectional studies, and case control studies. The key aspects of each design such as whether they are prospective or retrospective and examples are provided.
Randomised controlled trials

Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are considered the gold standard for clinical research. An RCT involves randomly assigning participants into experimental and control groups to receive different interventions. Randomization aims to make the groups comparable to limit bias. It reduces the influence of unknown factors and ensures the only difference between groups is the intervention being tested. RCTs can be single blind, double blind, or triple blind depending on who is aware of group assignments. They provide the most powerful and least biased assessments of clinical interventions.
Blinding in RCT the enigma unraveled

Randomized Control Trials
Enigma of Blinding Unraveled
Introduction
RCT
Steps in a RCT
Allocation Concealment
Bias in RCT
Phases in RCT
Types of RCT
Study Designs of RCT
Blinding
Methods of Blinding in different trials
Assessment of Blinding
Un-blinding
Current Scenario of Blinding
CONSORT
Conclusion
References
Critical appraisal of randomized clinical trials

The document discusses key concepts in randomized clinical trials (RCTs), including:
1) RCTs are considered the gold standard for evaluating the effectiveness of interventions due to their ability to minimize bias through randomization and blinding.
2) Proper randomization aims to create comparable treatment and control groups, conceal allocation to prevent bias, and may involve simple, stratified or blocked methods.
3) Blinding (masking) of participants, investigators and assessors can decrease observation bias and is important for RCT validity, though full blinding is not always possible.
4) Intention-to-treat analysis includes all randomized patients to preserve comparable groups and prevent bias from non-compliance.
5. experimental studies

This document provides an overview of experimental study design. It defines experimental studies as those where the investigator actively attempts to modify a dependent variable by introducing an intervention. It describes different types of experimental studies including clinical trials, field trials, and community trials. It then outlines the typical steps in a clinical trial, including deciding on the trial, forming research questions and hypotheses, defining and selecting the study population, determining inclusion/exclusion criteria, calculating sample size, enrolling and randomly allocating participants, implementing the regimen, measuring variables, following up on outcomes, analyzing results, and reporting findings. Finally, it briefly discusses phases of clinical trials and some variants like cross-over and factorial designs.
randomised controlled trial 

This document provides an overview of randomized controlled trials (RCTs), including their purpose and design. It discusses key aspects of RCTs such as randomization, blinding, and assessing outcomes. It provides examples of simple two-arm and cross-over RCT designs. The document also summarizes a specific cluster RCT that evaluated the effects of various child development and nutrition interventions on outcomes measured in children from birth to age 2 years.
Critical appraisal of published medical research

This document discusses critical appraisal of published medical research. It notes that thousands of new medical articles are published daily, making it difficult for clinicians to keep up-to-date. Critical appraisal involves assessing the validity, reliability, and applicability of a study rather than just dismissing it or looking only at the results. Key aspects of critical appraisal include describing the evidence, assessing internal validity by examining potential biases and confounding factors, evaluating external validity and whether results can apply to other populations, and comparing results to other evidence. The document provides guidance on how to critically appraise studies and lists resources for further information.
evidence based periodontics 

This document provides an overview of evidence-based periodontics. It discusses the need for evidence-based decision making to reduce variations in clinical practice. The advantages of an evidence-based approach are that it is objective, scientifically sound, patient-focused, and incorporates clinical expertise. The process of evidence-based decision making involves framing questions, searching for and appraising evidence from various sources and levels, evaluating outcomes, and implementing decisions. Key aspects include assessing evidence critically and avoiding changes to pre-established hypotheses.
Study design of Prof Zak

How to scientifically conduct a clinical professional research trial? In the current era of Collaborate or parish, we need to keep this design in our mind.
Enjoy
@copyLeft
Ebd jc part 5

This document summarizes a journal club presentation about critically appraising papers on dental therapy. It discusses key questions to consider when evaluating randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews relating to new therapeutic interventions. These include whether patient allocation was randomized, all patients were accounted for, blinding was used, groups were similar at outset, clinically important outcomes were assessed, and results can be applied to patients. It also reviews criteria for assessing systematic reviews, such as whether a clear question was asked, inclusion criteria were appropriate, search was comprehensive, study validity was evaluated, and findings were combined correctly.
Methodology Checklist: Cohort studies

The document provides a methodology checklist for cohort studies, outlining key criteria such as having a clearly focused question, comparable study groups, low dropout rates, blinding of outcome assessments, addressing potential confounders, and providing confidence intervals. The checklist is intended to help reviewers critically appraise cohort studies and identify potential sources of bias.
Ebm & critical appraisal

This document provides an introduction to evidence-based medicine (EBM) and principles of critical appraisal for first year psychiatry residents. It defines EBM as a systematic approach to obtaining clinically relevant information about treatment. Critical appraisal involves carefully examining research to assess validity, results, and relevance. The document outlines the five steps of EBM, different study designs commonly used in EBM like randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews, and factors to consider when critically appraising research like potential biases. Key aspects of randomized trials and systematic reviews are described, along with guidelines to standardize research reporting.
Critical appraisal of a journal article

1. This study was a cluster randomized controlled trial that assessed the effects of periodic vitamin A supplementation and deworming on child mortality in 1 million preschool children in North India.
2. The study had a 5-year study period from 1999-2004 and used a 2x2 factorial design to examine the effects of 6-monthly vitamin A supplementation, 6-monthly deworming with albendazole, and their combination on mortality in children aged 1-6 years.
3. The results found that vitamin A supplementation alone did not reduce child mortality as much as expected based on previous trials, reducing mortality by only 4%. However, meta-analysis of this study combined with previous trials still showed an average
3 cross sectional study

This document provides an overview of cross-sectional studies, including what they are, their uses, methodology, advantages, and disadvantages. A cross-sectional study involves observing a population at a single point in time to determine prevalence of disease. It is a quick and inexpensive way to describe characteristics of a population and identify associations between variables. However, it cannot determine causation due to its observational nature.
What's hot (20)
Critical appraisal of published medical research (2)

Critical appraisal of published medical research (2)
Similar to Methodology Checklist : Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy
# 5th lect clinical trial process

This document outlines the key steps in conducting a clinical trial:
1. Drawing up a detailed research protocol that serves as the trial's operating manual.
2. Selecting and screening participants according to eligibility criteria to identify the study population. Sample size is also calculated.
3. Randomly allocating the study participants into experimental and control groups through a process like randomization to reduce bias.
bio equivalence studies

This document discusses bioequivalence studies. It defines bioequivalence as when two drug products reach systemic circulation to the same relative extent, with their plasma concentration-time profiles being identical without statistically significant differences. It describes the analytical methods, pharmacokinetic evaluation, and statistical evaluation used in bioequivalence studies. It also discusses study designs such as parallel designs, crossover designs, and fasting versus fed conditions that can be used in bioequivalence studies.
3 Methodology.pptx

This document discusses various study designs and methods in epidemiological research. It describes key components of methods sections, including study setting, population, design, sampling, data collection and analysis. Some main study designs covered are descriptive studies like case reports, cross-sectional and ecological studies; and analytical studies such as cohort, case-control and experimental/intervention studies. The advantages and disadvantages of different designs are also reviewed. The document emphasizes that choice of design depends on research questions, goals, available time and resources.
Evidence based decision making

Evidence- based periodontology is a bridge from all the available literature to clinical practice. It is a tool which can be used for decision making from available evidence during clinical practice.It should be scientifically sound and patient focussed.
L4. case control study design

This document discusses case-control study design. It begins by outlining the learning objectives, which are to discuss traditional and modern views of case-control studies, describe the steps of case control study design, and identify biases. It then provides details on selecting cases and controls, including sources of each. Methods for ascertaining exposure are also reviewed, noting the importance of using similar procedures for both cases and controls. Finally, variants of case-control studies like cumulative, nested, and case-cohort designs are mentioned.
Surgical_audit_&_research_iagsisbbbuikbb

This document discusses surgical audit and research. It defines audit as the systematic analysis of surgical care quality, including procedures, treatments, complications, outcomes and resource use. Research is defined as investigations that aim to increase medical knowledge. The document outlines different types of studies including observational, case-control, cross-sectional, longitudinal, experimental and randomized controlled trials. It discusses important aspects of research like sample size calculations, eliminating bias, confidence intervals, p-values and levels of evidence. The importance of evidence-based surgery and organizations like the Cochrane Collaboration are also mentioned.
Research methodology

1. The document discusses various types of medical research designs including observational and experimental studies.
2. Observational studies are divided into descriptive studies which aim to describe health problems without comparisons, and analytical studies which aim to identify associations between exposures and outcomes.
3. Experimental research designs involve assigning subjects to treatment or control groups randomly to evaluate new interventions while controlling for confounding factors. Randomized controlled trials are considered the gold standard for evaluating new treatments.
Surgical_audit_&_research_mm (1).ppt

This document discusses surgical audit and research. It defines audit as the systematic analysis of surgical care quality including procedures, treatments, complications, and patient outcomes and quality of life. Research is defined as determining the safety and effectiveness of medical treatments and technologies. The key differences between audit and research are that research can involve experiments while audit only reviews existing care, and research aims to increase medical knowledge while audit aims to identify opportunities to improve care quality. The document also outlines types of studies, sample sizes, biases, statistical analysis methods, levels of evidence, and the Cochrane Collaboration.
Evidence based medicine in clinical Practice

The document discusses evidence-based medicine (EBM) and summarizes its key principles. EBM involves integrating the best research evidence with a clinician's expertise and the patient's values and circumstances. It describes the 5 steps of EBM: 1) framing a clinical question based on a patient encounter, 2) finding relevant evidence, 3) critically appraising the evidence for validity and applicability, 4) applying relevant evidence to the patient, and 5) evaluating outcomes. EBM aims to formalize using literature to guide decisions by focusing on strong evidence from well-designed studies.
1 Quantitative Synopsis and Appraisal Studentf

1
Quantitative Synopsis and Appraisal
Studentfirstname Studentlastname
College of Nursing, Resurrection University
NUR4440: Research in Nursing
Professor Carina Piccinini
February 14, 2020
2
Quantitative Appraisal and Synopsis
The purpose of this paper is to summarize and appraise a research study testing the use of
disinfectant caps on intravenous (IV lines) to reduce the rate of hospital associated bloodstream
infections (BSI). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, 2019) reports that
central line associated bloodstream infections (CLABSI) remain a major concern in hospital
settings causing fatalities, increased length of stay, and increased costs. The CDC (2019)
recommends proper maintenance of intravenous lines to reduce the risk of infection. Current
research is still looking to define what proper maintenance should be, including whether
disinfectant caps influence rates of infection for intravenous (IV) lines.
Summary of the Study
The CDC recommends that healthcare workers disinfect all needleless connectors for
peripheral and central IVs prior to connection to reduce the risk of CLABSIs without further
recommendation on the type or length of disinfections. The authors of this study note other
studies have tested disinfecting caps and sought to confirm those results.
Merrill et al. (2014) conducted a quasi-experimental study to identify if disinfectant caps
reduce CLABSI incidence and the relationship between nursing compliance with the caps and
CLABSI rates. This study was held in a single Trauma 1 hospital with 430 beds in the United
States.
The researchers obtained their sample through nonrandom convenience sampling by
including all patients meeting inclusion criteria at the hospital starting January 2012. Participants
were included if they had a central or peripheral intravenous line, of any age, and were admitted
to 13 specific hospital floors. Subjects were excluded if they were on the following floors:
emergency department; labor, delivery or post-partum; ambulatory care, surgical services; and
Commented [CP1]: This answers “Why is this important
to study?” It’s not just ensuring our patients do not get
CLABSIs…it goes beyond that to fatalities, length of stay in
hospitals, and healthcare costs.
The CDC and other healthcare related organizations are great
sources of information on the importance of topics.
Commented [CP2]: What is known (recommendation to
disinfect ports), not known (what specifically should be
used), and gap in knowledge (confirmation of other study
results).
This information is found in the introduction to every
research article. DO NOT use the discussion/conclusions
section of an article for this information! It will be
WRONG.
Commented [CP3]: Study being summarized/appraised is
correctly cited.
Specific research design stated.
Setting of study stated.
3
well-baby nursery. The study did ...
1 Quantitative Synopsis and Appraisal Studentf

1
Quantitative Synopsis and Appraisal
Studentfirstname Studentlastname
College of Nursing, Resurrection University
NUR4440: Research in Nursing
Professor Carina Piccinini
February 14, 2020
2
Quantitative Appraisal and Synopsis
The purpose of this paper is to summarize and appraise a research study testing the use of
disinfectant caps on intravenous (IV lines) to reduce the rate of hospital associated bloodstream
infections (BSI). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, 2019) reports that
central line associated bloodstream infections (CLABSI) remain a major concern in hospital
settings causing fatalities, increased length of stay, and increased costs. The CDC (2019)
recommends proper maintenance of intravenous lines to reduce the risk of infection. Current
research is still looking to define what proper maintenance should be, including whether
disinfectant caps influence rates of infection for intravenous (IV) lines.
Summary of the Study
The CDC recommends that healthcare workers disinfect all needleless connectors for
peripheral and central IVs prior to connection to reduce the risk of CLABSIs without further
recommendation on the type or length of disinfections. The authors of this study note other
studies have tested disinfecting caps and sought to confirm those results.
Merrill et al. (2014) conducted a quasi-experimental study to identify if disinfectant caps
reduce CLABSI incidence and the relationship between nursing compliance with the caps and
CLABSI rates. This study was held in a single Trauma 1 hospital with 430 beds in the United
States.
The researchers obtained their sample through nonrandom convenience sampling by
including all patients meeting inclusion criteria at the hospital starting January 2012. Participants
were included if they had a central or peripheral intravenous line, of any age, and were admitted
to 13 specific hospital floors. Subjects were excluded if they were on the following floors:
emergency department; labor, delivery or post-partum; ambulatory care, surgical services; and
Commented [CP1]: This answers “Why is this important
to study?” It’s not just ensuring our patients do not get
CLABSIs…it goes beyond that to fatalities, length of stay in
hospitals, and healthcare costs.
The CDC and other healthcare related organizations are great
sources of information on the importance of topics.
Commented [CP2]: What is known (recommendation to
disinfect ports), not known (what specifically should be
used), and gap in knowledge (confirmation of other study
results).
This information is found in the introduction to every
research article. DO NOT use the discussion/conclusions
section of an article for this information! It will be
WRONG.
Commented [CP3]: Study being summarized/appraised is
correctly cited.
Specific research design stated.
Setting of study stated.
3
well-baby nursery. The study did ...
Rerearch design

This document discusses research design. It defines research design as the specific plan for conducting a study to translate a conceptual hypothesis into an operational one. Research design helps make decisions about how to complete the entire research process validly, objectively, accurately, and economically. The document then discusses classifications of study designs based on number of contacts with participants, reference period, and nature of investigation. It provides examples and advantages and disadvantages of descriptive studies like case reports, case series, and ecological studies as well as analytical studies like case-control and cohort studies. It also discusses experimental design, blind studies, and double-blind studies.
Evidence-based medicine

Evidence-based medicine involves integrating clinical expertise, patient values, and the best research evidence in clinical decision making. The best evidence comes from sound clinical studies. The steps of evidence-based practice are constructing a clear question, finding relevant evidence, appraising the evidence quality, applying the evidence to the individual patient, and evaluating performance. Different types and levels of evidence are used to rank the strength and applicability of clinical research findings.
HLT 362 V GCU Quiz 11. When a researcher uses a random sam

HLT 362 V GCU
Quiz 1
1. When a researcher uses a random sample of 400 to make conclusions about a larger population, this is an example of:
· Descriptive statistics
· Demographics
· Inferential statistics
· Dependent variables
2. If a study is comparing number of falls by age, age is considered what type of variable?
· Interval
· Ordinal
· Ratio
· Nominal
3. Validity is:
· A data item, such as characteristics, numbers, properties, or quantities, that can be measured or counted.
· The extent to which an idea or measurement is well-founded and an accurate representation of the real world.
· A measurement level with equal distances between the points and a zero-starting point.
· Raw unorganized information from which conclusions can be made.
4. Data is defined as:
· A data item, such as characteristics, numbers, properties, or quantities, that can be measured or counted.
· The extent to which an idea or measurement is well-founded and an accurate representation of the real world.
· A measurement level with equal distances between the points and a zero-starting point.
· Raw unorganized information from which conclusions can be made.
5. The average of the collected data is known as:
· Mean
· Median
· Variance
· Range
6. The experimental or predictor variable is an example of:
· Extraneous variable
· Dependent variable
· Independent variable
· Nominal data
7. Level of measurement that defines the relationship between things and assigns an order or ranking to each thing is known as:
· Interval
· Ordinal
· Ratio
· Nominal
8. A variable is considered:
· A data item, such as characteristics, numbers, properties, or quantities, that can be measured or counted.
· A component of mathematics that looks at gathered data.
· Statistics designed to allow the researcher to infer characteristics regarding a population from sample population.
· External and internal influences within a study that can affect the validity and reliability of the outcomes.
9. External and internal influences within a study that can affect the validity and reliability of outcomes is called:
· Continuous variables
· Demographics
· Bias
· Standard deviation
10. The subset of the population to be studied is called:
· Sample
· Variable
· Population
· Demographic
Put the below in your own words into 1-2 paragraphs for the main conclusion and 1-2 paragraphs for the clinical application
Main conclusion:
The following is one example of a main conclusion and clinical applicability to assist you in formulating your take home message for the dissemination assignment. The details in these descriptions are intentionally detailed for your consideration. Do not include this level of detail in the dissemination assignment.
HPV study:
The Healthy People 2020 HPV vaccination goal of 80% of all United States adolescents[KG1] is not being met with current practices (citation). With insufficient vaccination, reduction in HPV-related disease ...
Critical appraisal.docx IMPORTAN TO HEALTH SCIENCE STUDENTS

Critical appraisal is the process of systematically examining evidence to assess its validity, results, and relevance before using it to inform decisions. This document discusses tools for critically appraising different types of studies, including systematic reviews, guidelines, and primary studies. It provides examples of appraising systematic reviews using the AMSTAR tool and appraising randomized controlled trials using the JBI critical appraisal checklist. The document concludes that plastic wraps effectively prevent hypothermia in preterm and low birth weight infants compared to standard care, as shown in multiple systematic reviews and randomized trials.
Recall bais

Irrespective of study design, the first step in the process of avoiding any type of bias is the proper definition and articulation of the research question.
Consequently, this step will lead to a number of questions that need to be adequately addressed by the investigator during the planning stage of research:
what kind of information are required to answer this question in the study in terms of exposure, outcome, and possible confounders?
what is the most appropriate method to collect these information?
how to achieve comparable accuracy of data collection between the study groups?
1_Intro to Research.pdf

This document provides an overview of different research methods and designs used in health research. It begins with an introduction to research and outlines quantitative and qualitative research designs. Quantitative designs discussed include descriptive, correlational, causal-comparative, experimental, and cross-sectional studies. Qualitative designs explored are case studies and qualitative methods. Other study types covered are cohort and case-control studies. Randomized controlled trials are also summarized, outlining key aspects like random assignment, control and experimental groups, and blinding. The document provides examples and explanations of each research method and design.
Five steps to conducting a systematic review

Five steps to conducting a systematic review outlines a 5-step process for conducting systematic reviews: 1) Framing questions, 2) Identifying relevant publications, 3) Assessing study quality, 4) Summarizing evidence, and 5) Interpreting findings. The document uses the example of a review on water fluoridation safety to illustrate these steps. It describes framing a clear structured question, extensively searching for studies, selecting 254 studies that compared fluoridated to non-fluoridated areas, assessing study quality considering biases, and summarizing evidence on cancer outcomes from 26 studies to determine the safety of water fluoridation.
Biostatistics made easy comprehensive.pptx

This document provides an overview of different types of epidemiological study designs, including descriptive and analytical studies. Descriptive studies observe characteristics of a population or phenomenon without making comparisons. Common descriptive study designs discussed include case reports, case series, ecological studies, and cross-sectional studies. Analytical studies seek to identify associations between exposures and outcomes. Major analytical study designs covered are observational studies like cohort and case-control studies, as well as intervention studies like randomized controlled trials. The key aspects, strengths, and limitations of each study design are described.
Articulo 1

1) The study examined the experiences of practice staff conducting diabetes screening in six general practices as part of a clinical trial.
2) Each practice implemented screening differently depending on staffing levels, workload, and practice size but all emphasized the importance of administrative support.
3) Staff found that screening involved more work than expected and extended beyond just testing to providing health information and advice to patients.
Similar to Methodology Checklist : Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy (20)
HLT 362 V GCU Quiz 11. When a researcher uses a random sam

HLT 362 V GCU Quiz 11. When a researcher uses a random sam
Critical appraisal.docx IMPORTAN TO HEALTH SCIENCE STUDENTS

Critical appraisal.docx IMPORTAN TO HEALTH SCIENCE STUDENTS
More from QURATULAIN MUGHAL
Patient management process

This document outlines the process of patient management in physical therapy. It discusses the key components of examination, evaluation, diagnosis, prognosis and care planning, intervention, and outcomes. The examination involves obtaining a health history, systems review, and specific tests to evaluate the patient's impairments, functional limitations, and disabilities. In the evaluation, the therapist analyzes and interprets the examination data. They then make a diagnosis, which can be a label or the diagnostic process. The prognosis predicts the patient's expected functional outcomes and time to achieve them. The care plan establishes goals and the interventions needed. The interventions directly work with the patient, and outcomes measure the results including the patient's function and satisfaction.
Reading comprehension

Sally loves to bake cakes, especially chocolate ones. Her mother helps Sally by mixing the batter and putting the finished cake in the oven. Sally lets the cooled cake sit before baking for her family.
Islamiat

This document contains questions about various topics in Islam including the books of Allah, the pillars of Islam, cleanliness and purity, prayers, getting up early, eating manners, greeting manners, good deeds, and Prophet Adam (peace be upon him). It asks about the number of books revealed by Allah, their purpose, the number of sections in the Quran, virtues for reciting letters, the meaning of religion, pillars of Islam, why Muslims go to the mosque, the month of fasting, giving charity, people Allah likes, necessity of clean clothes, cleaning before prayers, using a toothbrush, importance of cleanliness, a hadith about cleanliness, worshipping Allah, who taught prayers, number of daily prayers,
Comparative words

This document contains a list of adjectives that can be used to describe words in a comparative sense, with some adjectives implying comparison by size, quantity, or intensity and others not clearly comparative but simply descriptive. The list includes both one- and two-syllable adjectives from across the spectrum of meaning.
KNOW YOUR KEYBOARD

This document provides information about computer keyboards. It asks questions to test understanding of keyboard parts like the spacebar, backspace, delete keys, and alphabet and number keys. It also defines the cursor and differentiates the backspace and delete keys. Students are asked to identify keys on a diagram, fill in blanks about keyboard features, and determine whether statements are true or false. The keyboard has 104 keys in total, including 26 alphabet keys and 10 number keys. The spacebar is the longest key.
Uses of computer

This document contains questions and answers about the uses of computers. It asks about uses of computers in school, things that can be done on computers, why teachers use computers, entertainment uses of computers, and the differences between playing cricket on a field versus on a computer. It also includes puzzles to unjumble letters into words related to computer uses, identify games on computer monitors, fill in blanks about computer uses, and identify true and false statements regarding computers.
Parts of computer

This document provides an overview of the main parts of a computer and questions to test understanding. It begins by listing 5 common computer parts: monitor, CPU, keyboard, mouse, and speaker. It then describes the functions of these parts. The remaining questions and answers cover topics like what CPU stands for, how components connect, starting and shutting down a computer, and differences between monitors and televisions. Fill-in-the-blank and unscrambling questions are also included to reinforce key computer terminology.
A computer

This document provides questions and answers about machines and computers. It asks the reader to define a machine, provide examples of machines inside and outside the home, and explain what a computer is and what it can do. It also asks the reader to compare humans and computers and complete other activities like unjumbling letters, identifying machines in pictures, and filling in blanks. The answers key defines a machine, provides examples of indoor and outdoor machines, and lists differences between humans and computers such as the ability to store and process large amounts of information quickly.
Patient management and clinical decision

This document discusses clinical decision making and patient management in physical therapy. It outlines:
1. The requirements for skilled clinical decision making, including knowledge, experience, critical thinking, and evidence-based practice.
2. The steps of evidence-based practice, which involves forming a question, searching literature, analyzing evidence, and integrating findings into patient care.
3. A patient management model to help patients achieve their highest level of function through a process that includes examination, evaluation, diagnosis, prognosis, treatment plan, and intervention.
Process and models of disablement

The document discusses disablement, its process, and common models used to describe it. It defines disablement and outlines Nagi, ICIDH, and ICF models of the disablement process. These models progress from pathology and impairment at the tissue/organ level to functional limitation and disability at the personal level to participation restrictions at the societal level. The document also discusses how therapeutic exercise can impact different levels of the disablement process by reducing impairments and improving function. Common physical therapy impairments, limitations, activity categories, and risk factors are also outlined.
Therapeutic exercise foundation concepts

This document outlines foundational concepts of therapeutic exercise, including definitions, types of exercises, and safety considerations. It defines therapeutic exercise as planned bodily movements intended to remediate or prevent impairments, improve function, reduce health risks, and optimize health. The document discusses key aspects of physical function such as balance, flexibility, mobility and muscle performance. It also describes different types of therapeutic exercises and emphasizes patient and therapist safety.
WORD OPPOSITE

The document lists pairs of words that are opposites of each other, such as "asleep" and "awake", "attack" and "ahead", "safe" and "buy". It contains over 50 pairs of opposite words in two columns without any other context or explanation.
Feminine masculine

This document lists masculine and feminine terms for various animals and roles. It pairs male and female terms such as bull and cow, king and queen, husband and wife, brother and sister, as well as terms for family members, jobs, and animals to illustrate linguistic differences between genders.
Addition worksheet

The document contains a series of number additions without explanations or context. It includes adding single digit and double digit numbers together in a seemingly random order across multiple lines.
More from QURATULAIN MUGHAL (20)
Recently uploaded
Pharmacology of Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes and Leukotrienes

This presentation gives information on the pharmacology of Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes and Leukotrienes i.e. Eicosanoids. Eicosanoids are signaling molecules derived from polyunsaturated fatty acids like arachidonic acid. They are involved in complex control over inflammation, immunity, and the central nervous system. Eicosanoids are synthesized through the enzymatic oxidation of fatty acids by cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase enzymes. They have short half-lives and act locally through autocrine and paracrine signaling.
“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Mo...

“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Mo...Université de Montréal
“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Montreal Expanding the medical model to embrace the humanities. Link: https://www.psychiatrictimes.com/view/-psychiatry-and-the-humanities-an-innovative-course-at-the-university-of-montreal5 Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Irregular Periods

Discover the benefits of homeopathic medicine for irregular periods with our guide on 5 common remedies. Learn how these natural treatments can help regulate menstrual cycles and improve overall menstrual health.
Visit Us: https://drdeepikashomeopathy.com/service/irregular-periods-treatment/
Pollen and Fungal allergy: aeroallergy.pdf

Pollen and Fungal allergy: aeroallergy.pdfChulalongkorn Allergy and Clinical Immunology Research Group
Pollen and Fungal allergy
Presented by Chaloemchai Chumsaengchotsakul, MD.
June 14, 2024Foundation of Yoga, YCB Level-3, Unit-1 

Unit -1 of Yoga certification board, level 3, all topics covered. An exam conducted by ministry of Ayush for yoga enthusiastic students.
Computer in pharmaceutical research and development-Mpharm(Pharmaceutics)

Statistics- Statistics is the science of collecting, organizing, presenting, analyzing and interpreting numerical data to assist in making more effective decisions.
A statistics is a measure which is used to estimate the population parameter
Parameters-It is used to describe the properties of an entire population.
Examples-Measures of central tendency Dispersion, Variance, Standard Deviation (SD), Absolute Error, Mean Absolute Error (MAE), Eigen Value
Travel Clinic Cardiff: Health Advice for International Travelers

Travel Clinic Cardiff offers comprehensive travel health services, including vaccinations, travel advice, and preventive care for international travelers. Our expert team ensures you are well-prepared and protected for your journey, providing personalized consultations tailored to your destination. Conveniently located in Cardiff, we help you travel with confidence and peace of mind. Visit us: www.nxhealthcare.co.uk
Helminthiasis or Worm infestation in Children for Nursing students

Brief description worm infestation/Helminthiasis for Basic B.Sc Nursing students
Gene Expression System-viral gene delivery Mpharm(Pharamaceutics)

Gene therapy can be broadly defined as the transfer of genetic material to cure a disease or at least to improve the clinical status of a patient.
One of the basic concepts of gene therapy is to transform viruses into genetic shuttles, which will deliver the gene of interest into the target cells.
Safe methods have been devised to do this, using several viral and non-viral vectors.
In the future, this technique may allow doctors to treat a disorder by inserting a gene into a patient's cells instead of using drugs or surgery.
The biggest hurdle faced by medical research in gene therapy is the availability of effective gene-carrying vectors that meet all of the following criteria:
Protection of transgene or genetic cargo from degradative action of systemic and endonucleases,
Delivery of genetic material to the target site, i.e., either cell cytoplasm or nucleus,
Low potential of triggering unwanted immune responses or genotoxicity,
Economical and feasible availability for patients .
Viruses are naturally evolved vehicles that efficiently transfer their genes into host cells.
Choice of viral vector is dependent on gene transfer efficiency, capacity to carry foreign genes, toxicity, stability, immune responses towards viral antigens and potential viral recombination.
There are a wide variety of vectors used to deliver DNA or oligo nucleotides into mammalian cells, either in vitro or in vivo.
The most common vector system based on retroviruses, adenoviruses, herpes simplex viruses, adeno associated viruses.
Giloy in Ayurveda - Classical Categorization and Synonyms

Giloy, also known as Guduchi or Amrita in classical Ayurvedic texts, is a revered herb renowned for its myriad health benefits. It is categorized as a Rasayana, meaning it has rejuvenating properties that enhance vitality and longevity. Giloy is celebrated for its ability to boost the immune system, detoxify the body, and promote overall wellness. Its anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and antioxidant properties make it a staple in managing conditions like fever, diabetes, and stress. The versatility and efficacy of Giloy in supporting health naturally highlight its importance in Ayurveda. At Planet Ayurveda, we provide a comprehensive range of health services and 100% herbal supplements that harness the power of natural ingredients like Giloy. Our products are globally available and affordable, ensuring that everyone can benefit from the ancient wisdom of Ayurveda. If you or your loved ones are dealing with health issues, contact Planet Ayurveda at 01725214040 to book an online video consultation with our professional doctors. Let us help you achieve optimal health and wellness naturally.
Call Girls In Mumbai +91-7426014248 High Profile Call Girl Mumbai

Call Girls In Mumbai +91-7426014248 High Profile Call Girl Mumbai
Demystifying Fallopian Tube Blockage- Grading the Differences and Implication...

Fallopian tube blockage may cause female infertility. For treatment, herbal medicine Fuyan Pill can be a solution.
District Residency Programme (DRP) for PGs in India.pptx

District Residency Programme (DRP) for PG in India
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis - Pathogenesis , Clinical Features & Manage...

In this presentation , SBP ( spontaneous bacterial peritonitis ) , which is a common complication in patients with cirrhosis and ascites is described in detail.
The reference for this presentation is Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease Textbook ( 11th edition ).
Ageing, the Elderly, Gerontology and Public Health

Challenges associated with ageing from a public health perspective
Pharmacology of 5-hydroxytryptamine and Antagonist

5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT or Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that serves a range of roles in the human body. It is sometimes referred to as the happy chemical since it promotes overall well-being and happiness.
It is mostly found in the brain, intestines, and blood platelets.
5-HT is utilised to transport messages between nerve cells, is known to be involved in smooth muscle contraction, and adds to overall well-being and pleasure, among other benefits. 5-HT regulates the body's sleep-wake cycles and internal clock by acting as a precursor to melatonin.
It is hypothesised to regulate hunger, emotions, motor, cognitive, and autonomic processes.
Recently uploaded (20)
Pharmacology of Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes and Leukotrienes

Pharmacology of Prostaglandins, Thromboxanes and Leukotrienes
“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Mo...

“Psychiatry and the Humanities”: An Innovative Course at the University of Mo...
pharmacy exam preparation for undergradute students.pptx

pharmacy exam preparation for undergradute students.pptx
5 Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Irregular Periods

5 Effective Homeopathic Medicines for Irregular Periods
Computer in pharmaceutical research and development-Mpharm(Pharmaceutics)

Computer in pharmaceutical research and development-Mpharm(Pharmaceutics)
Travel Clinic Cardiff: Health Advice for International Travelers

Travel Clinic Cardiff: Health Advice for International Travelers
Helminthiasis or Worm infestation in Children for Nursing students

Helminthiasis or Worm infestation in Children for Nursing students
Gene Expression System-viral gene delivery Mpharm(Pharamaceutics)

Gene Expression System-viral gene delivery Mpharm(Pharamaceutics)
Giloy in Ayurveda - Classical Categorization and Synonyms

Giloy in Ayurveda - Classical Categorization and Synonyms
Call Girls In Mumbai +91-7426014248 High Profile Call Girl Mumbai

Call Girls In Mumbai +91-7426014248 High Profile Call Girl Mumbai
Demystifying Fallopian Tube Blockage- Grading the Differences and Implication...

Demystifying Fallopian Tube Blockage- Grading the Differences and Implication...
District Residency Programme (DRP) for PGs in India.pptx

District Residency Programme (DRP) for PGs in India.pptx
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis - Pathogenesis , Clinical Features & Manage...

Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis - Pathogenesis , Clinical Features & Manage...
Ageing, the Elderly, Gerontology and Public Health

Ageing, the Elderly, Gerontology and Public Health
Pharmacology of 5-hydroxytryptamine and Antagonist

Pharmacology of 5-hydroxytryptamine and Antagonist
Methodology Checklist : Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy
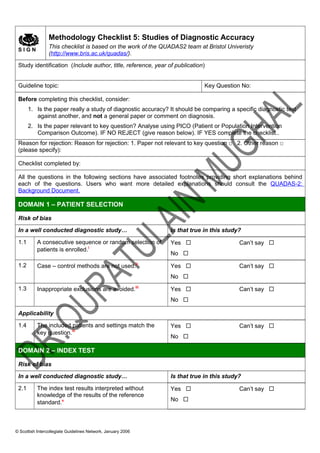
- 1. S I G N Methodology Checklist 5: Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy This checklist is based on the work of the QUADAS2 team at Bristol Univeristy (http://www.bris.ac.uk/quadas/). Study identification (Include author, title, reference, year of publication) Guideline topic: Key Question No: Before completing this checklist, consider: 1. Is the paper really a study of diagnostic accuracy? It should be comparing a specific diagnostic test against another, and not a general paper or comment on diagnosis. 2. Is the paper relevant to key question? Analyse using PICO (Patient or Population Intervention Comparison Outcome). IF NO REJECT (give reason below). IF YES complete the checklist.. Reason for rejection: Reason for rejection: 1. Paper not relevant to key question □ 2. Other reason □ (please specify): Checklist completed by: All the questions in the following sections have associated footnotes providing short explanations behind each of the questions. Users who want more detailed explanations should consult the QUADAS-2: Background Document. DOMAIN 1 – PATIENT SELECTION Risk of bias In a well conducted diagnostic study… Is that true in this study? 1.1 A consecutive sequence or random selection of patients is enrolled.i Yes No Can’t say 1.2 Case – control methods are not used.ii Yes No Can’t say 1.3 Inappropriate exclusions are avoided.iii Yes No Can’t say Applicability 1.4 The included patients and settings match the key question.iv Yes No Can’t say DOMAIN 2 – INDEX TEST Risk of bias In a well conducted diagnostic study… Is that true in this study? 2.1 The index test results interpreted without knowledge of the results of the reference standard.v Yes No Can’t say © Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, January 2006
- 2. 2.2 If a threshold is used, it is pre-specified.vi Yes No Can’t say © Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, January 2006
- 3. Applicability 2.3 The index test, its conduct, and its interpretation is similar to that used in practice with the target population of the guideline.vii Yes No Can’t say DOMAIN 3 – REFERENCE STANDARD Risk of bias In a well conducted diagnostic study… Is that true in this study? 3.1 The reference standard is likely to correctly identify the target condition.viii Yes No Can’t say 3.2 Reference standard results are interpreted without knowledge of the results of the index test.ix Yes No Can’t say Applicability 3.3 The target condition as defined by the reference standard matches that found in the target population of the guideline.x Yes No Can’t say DOMAIN 4 – FLOW AND TIMING Risk of bias In a well conducted diagnostic study… Is that true in this study? 4.1 There is an appropriate interval between the index test and reference standard.xi Yes No Can’t say 4.2 All patients receive the same reference standard.xii Yes No Can’t say 4.3 All patients recruited into the study are included in the analysis.xiii Yes No Can’t say SECTION 5: OVERALL ASSESSMENT OF THE STUDY 5.1 How well was the study done to minimise bias? Code as follows:xiv High quality (++) Acceptable (+) Unacceptable – reject 0 5.2 What is your assessment of the applicability of this study to our target population? Directly applicable Some indirectness (Please explain in the following section for Notes) 5.2 Notes. Summarise the authors conclusions. Add any comments on your own assessment of the study, and the extent to which it answers your question. © Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, January 2006
- 4. i Studies should enrol either all eligible patients suspected of having the target condition during a specified period, or a random sample of those patients. The essential point is that investigators should have no freedom of choice as to which individual patients are or are not included. ii There is evidence that studies comparing patients with known disease with a control group without the condition tend to exaggerate diagnostic accuracy. iii Inappropriate exclusions may result in either overestimates (eg by excluding ‘difficult to diagnose’ patients) or underestimates (eg by excluding patients with ‘red flags’ suggesting presence of disease) of the degree of diagnostic accuracy. iv Patients included in the study should match the target population of the guideline in terms of severity of the target condition, demographic features, presence of differential diagnosis or co-morbidity, setting of the study and previous testing protocols. v This is similar to the question of ‘blinding’ in intervention studies. The index test should always been done first, or by a separate investigator with no knowledge of the outcome of the reference test. vi Bias can be introduced if a threshold level is set after data has been collected. Any minimum threshold should be specified at the start of the trial. vii Variations in test technology, execution, or interpretation (eg use of a higher ultrasound transducer frequency) may affect estimates of diagnostic accuracy. viii Estimates of test accuracy are based on the assumption that the reference standard is 100% sensitive (=accurately diagnoses the target condition). ix This is the similar to question 2.1, but in this case relates to making sure the reference standard is applied without any prior knowledge of the outcome of previous tests. x The definition of the target condition used when testing the reference standard may differ from that used by the NHS in Scotland. eg threshold levels used in laboratory cultures may differ. xi The index test and reference standard should be performed as close together in time as possible, otherwise changes in the patients condition is likely to invalidate the results. xii In some cases the choice of reference standard may be influenced by the outcome of the index test or the urgency of the need for diagnosis. Use of different reference standards is likely to lead to overestimates of both sensitivity and specificity. xiii Not including all patients in the analysis may lead to bias as there may be some systematic difference between those lost to follow-up and those analysed. xiv Rate the overall methodological quality of the study, using the following as a guide: High quality (++): Majority of criteria met. Little or no risk of bias. Results unlikely to be changed by further research. Acceptable (+): Most criteria met. Some flaws in the study with an associated risk of bias, Conclusions may change in the light of further studies. Low quality (0): Either most criteria not met, or significant flaws relating to key aspects of study design. Conclusions likely to change in the light of further studies.
