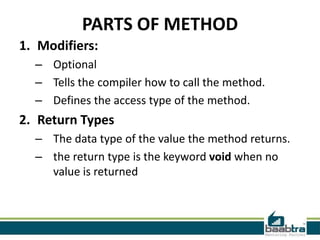
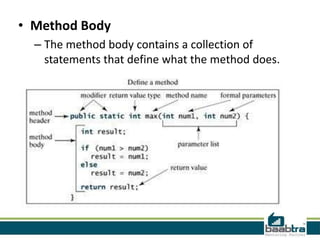
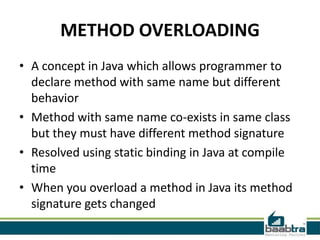
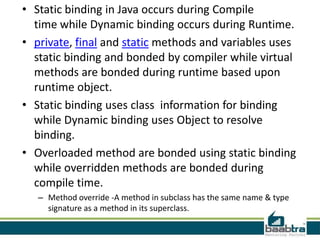
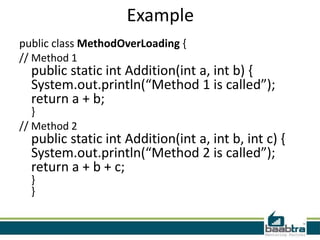
This document discusses method overloading in Java. It defines a method as a collection of statements that perform an operation. A method has a header specifying its modifiers, return type, name, and parameters. The body contains the statements. Method overloading allows multiple methods with the same name but different signatures. Signatures can vary by parameter types, numbers, or orders. Overloaded methods use static binding at compile time. The example shows two Addition methods differentiated by an extra parameter, with the correct one called based on arguments.







![public static void main(String[] args) {
int Answer1 = Addition(5, 6); // In this case
Method 1 will be called
System.out.println(“Answer 1 = ” + Answer1);
System.out.println(“----------------------------”);
int Answer2 = Addition(5, 6, 7); // In this case
Method 2 will be called
System.out.println(“Answer 2 = ” + Answer2);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/methodoverloading-121126075120-phpapp01/85/Method-overloading-13-320.jpg)




