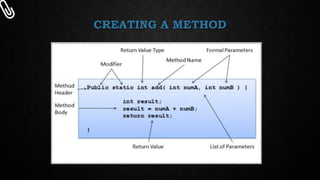
This document discusses method overloading in Java. Method overloading allows multiple methods to have the same name but different parameters. It demonstrates polymorphism. Methods can be overloaded by changing the number of arguments, data types of arguments, or return types. An example shows a class with multiple check methods that vary the parameters. The rules for overloading require changing the method signature by altering the number, type, or order of arguments but keeping the name the same. Advantages of overloading include cleaner code, increased readability, and flexibility to call similar methods for different data types.





![EXAMPLE
//method overloading.
class Ovrld
{
void check()
{
System.out.println("No parameters");
}
// Overload check for single integer parameter
void check(int a)
{
System.out.println("a: " + a);
}
// Overload check for two integer parameters.
void check(int a, int b)
{
System.out.println("a and b: " + a + " " + b);
}
// overload check for a double parameter
double check(double a)
{
System.out.println("double a: " + a);
return a*a;
}
}
//Now we create a main class Overload,
which prints all overloaded methods.
class Overload
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Ovrld ob = new Ovrld();
double result;
// call all versions of check()
ob.check();
ob.check(10);
ob.check(10, 20);
result = ob.check(123.2);
System.out.println("Result of ob.check(123.2): " + result);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/methodoverloading-190416163754/85/Method-overloading-7-320.jpg)



