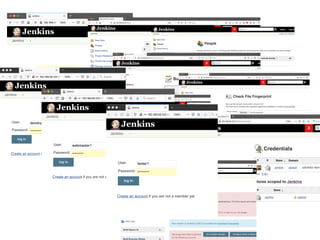
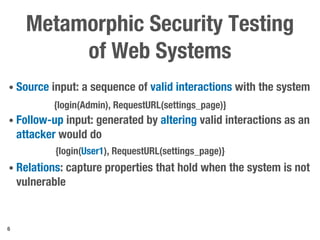
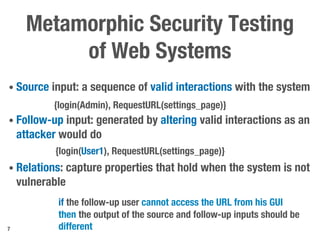
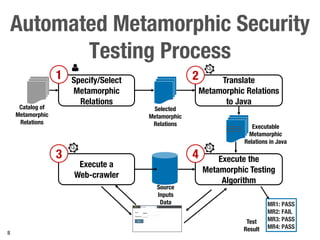
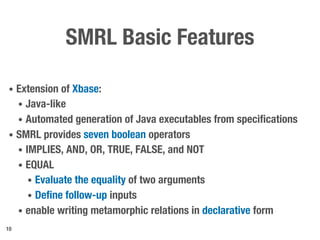
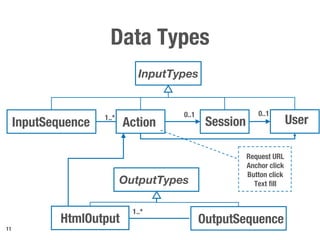
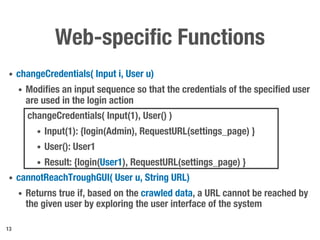
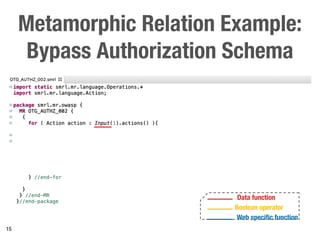
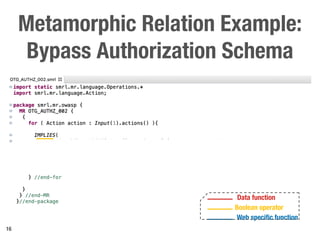
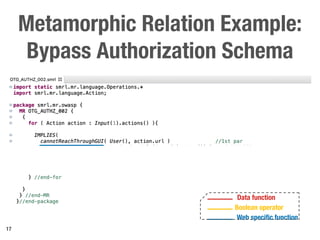
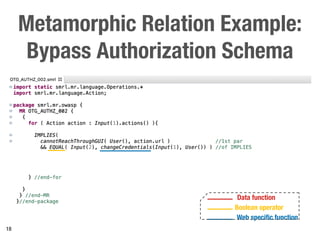
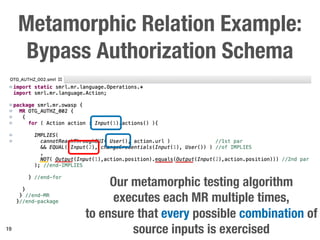
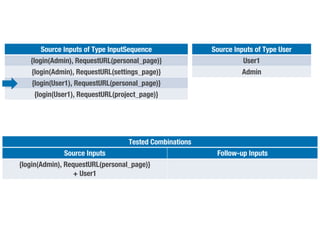
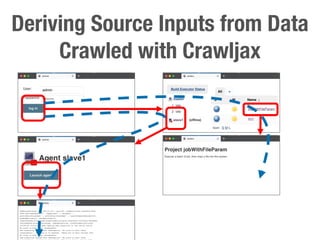
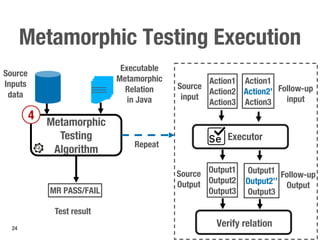
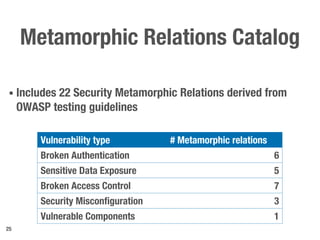
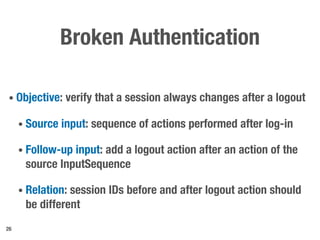
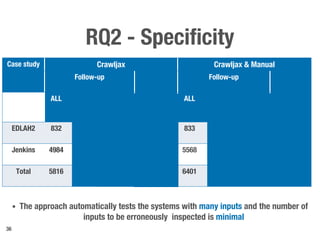
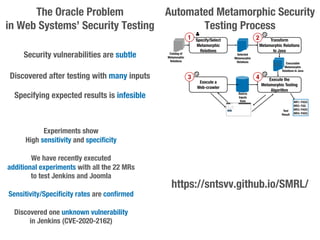
Metamorphic testing is proposed to address the oracle problem in web security testing. Relations capture necessary properties between multiple inputs and outputs that must hold when a system is not vulnerable. Experiments on commercial and open source systems show the approach has high sensitivity (58.33-83.33%) and specificity (99.43-99.50%), detecting vulnerabilities without many false alarms. Extensive experiments with 22 relations achieved similar results for Jenkins and Joomla.