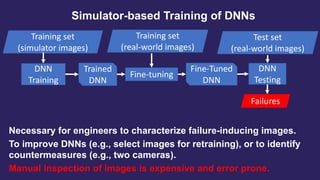
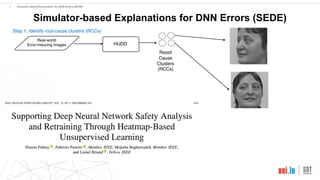
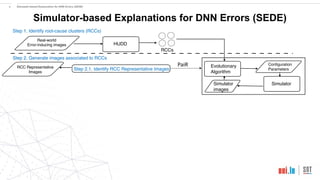
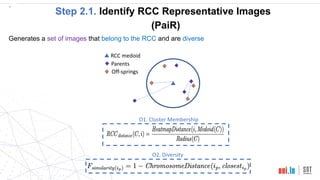
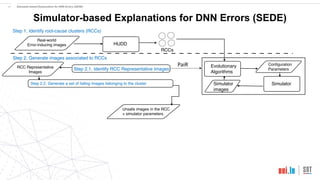
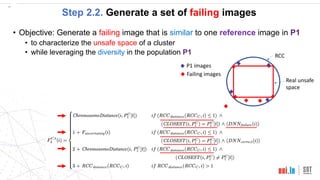
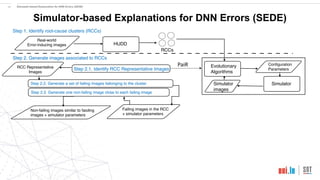
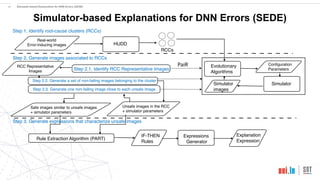
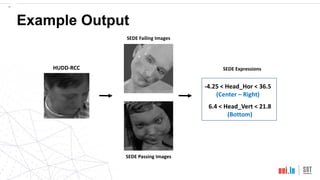
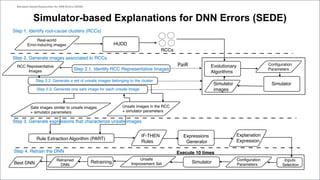
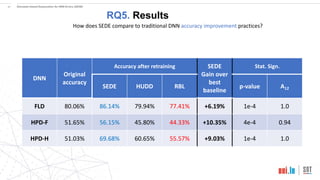
This document proposes a method called SEDE (Simulator-based Explanations for DNN Errors) to automatically generate explanations for errors in DNN-based safety-critical systems by constraining simulator parameters. SEDE first identifies clusters of error-inducing images, then uses an evolutionary algorithm to generate simulator images within each cluster, including failing, passing, and representative images. SEDE extracts rules characterizing the unsafe parameter space and uses the generated images to retrain DNNs, improving accuracy compared to alternative methods. The paper evaluates SEDE on head pose and face landmark detection DNNs in terms of generating diverse cluster images, delimiting unsafe spaces, and enhancing DNN performance.