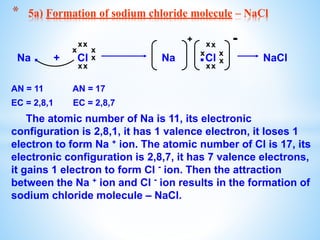
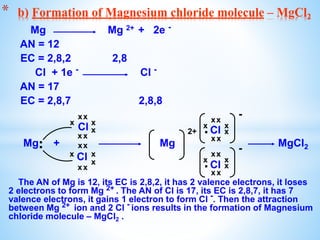
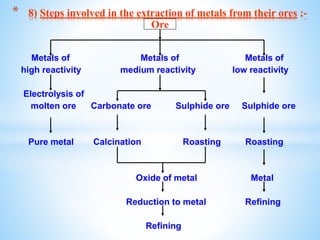
The document outlines the physical and chemical properties of metals and non-metals, emphasizing reactions with oxygen, water, and acids, along with the reactivity series of metals. It details how metals are extracted from their ores through processes such as roasting, calcination, and electrolytic reduction. Additionally, it discusses the prevention of corrosion and the formation and properties of alloys.