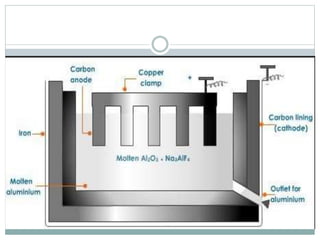
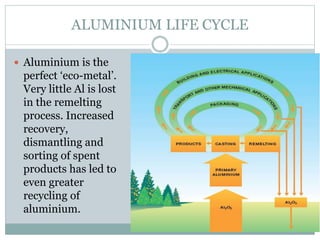
Aluminum is the third most abundant element in the Earth's crust. It is a soft, lightweight, corrosion-resistant metal that is highly conductive of heat and electricity. Aluminum occurs naturally as bauxite ore and is extracted through the Bayer process to produce alumina, which is then smelted using the Hall-Héroult process to produce aluminum metal. Aluminum and its alloys have a variety of applications due to their properties, including in transportation, packaging, construction, and electrical sectors. Aluminum is fully recyclable without loss of quality and recycling it requires much less energy than producing it from ore.