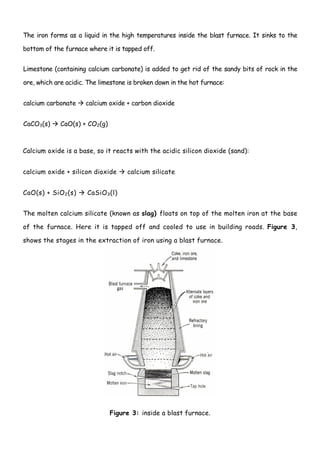
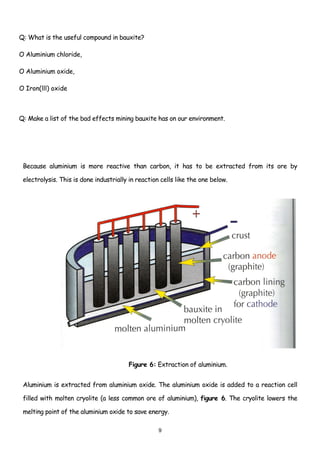
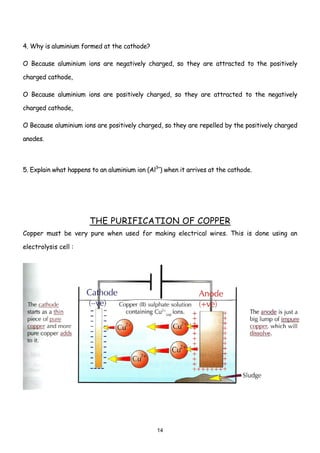
Iron is extracted from its main ore, haematite, in a blast furnace. Haematite, coke, and limestone are fed into the top of the blast furnace where temperatures reach 1500°C. The main reducing agent, carbon monoxide, reduces the iron(III) oxide to iron. The molten iron collects at the bottom and is tapped off, while the limestone removes sandy impurities to form a slag.