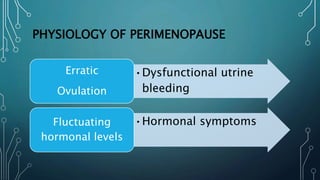
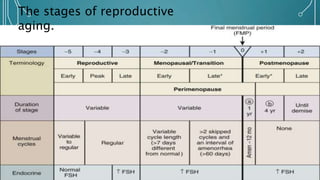
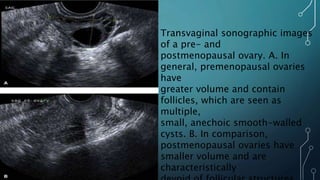
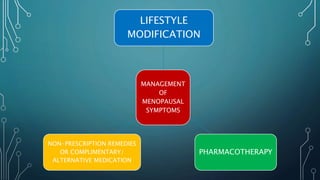
Menopause is a natural process marking the end of a woman's reproductive years, occurring typically between ages 45 and 55, characterized by the cessation of menstruation and hormonal changes. Symptoms include menstrual irregularities, vasomotor issues like hot flashes, psychological effects, and various physiological changes due to decreased estrogen and progesterone. Treatment options range from lifestyle modifications and non-hormonal therapies to hormone replacement therapy (HRT), which can alleviate symptoms and maintain quality of life, albeit with some associated risks.