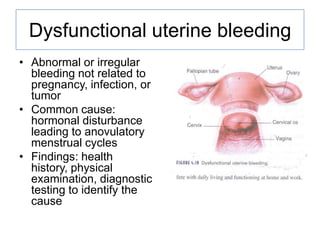
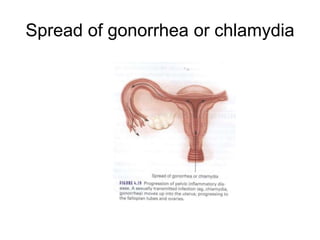
This document discusses various menstrual disorders including amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, dysfunctional bleeding, premenstrual syndrome, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, pelvic relaxation disorders, cystitis, urinary incontinence, and perimenopause. It defines each condition, discusses etiology and pathophysiology, assessment findings, diagnosis, and treatment. Nursing considerations are provided for educating women on prevention and management of these common gynecological issues.