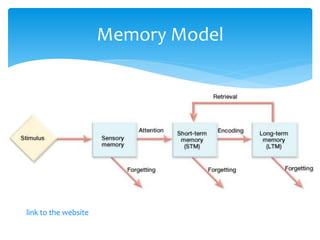
The document discusses memory and its role in second language acquisition. It describes the different types of memory, including sensory memory, working memory, and long-term memory. Sensory memory is very brief, while working memory holds information for short periods of time and plays an important role in language learning. Information is transferred from working memory to long-term memory for permanent storage. Memorization and repetition are important for maintaining information in long-term memory.