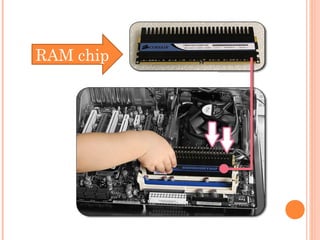
RAM is the primary memory of a computer that stores programs and data being currently processed. It allows direct access to stored data in any order. RAM is made up of small chips on the motherboard, and programs load from the hard drive into RAM to run without lag time. More RAM can speed up a computer. ROM contains permanent, built-in instructions to boot the computer. PROM and EPROM can be programmed once but retain data when powered off, while EEPROM can be repeatedly erased and reprogrammed electrically without removal.