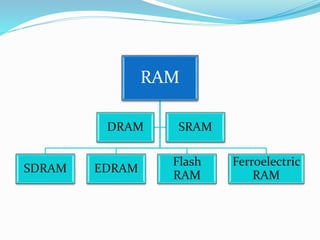
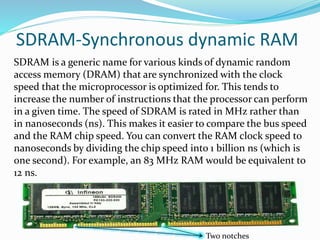
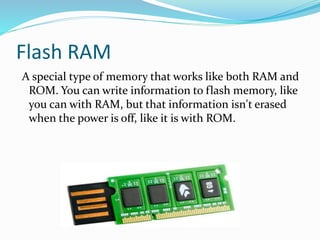
RAM is a type of volatile memory that can be written and accessed randomly. It is used to store frequently used instructions to speed up a computer. Data in RAM is lost when power is turned off. ROM is non-volatile memory whose contents cannot be changed. It is used to store low-level startup instructions and cannot be erased like RAM.