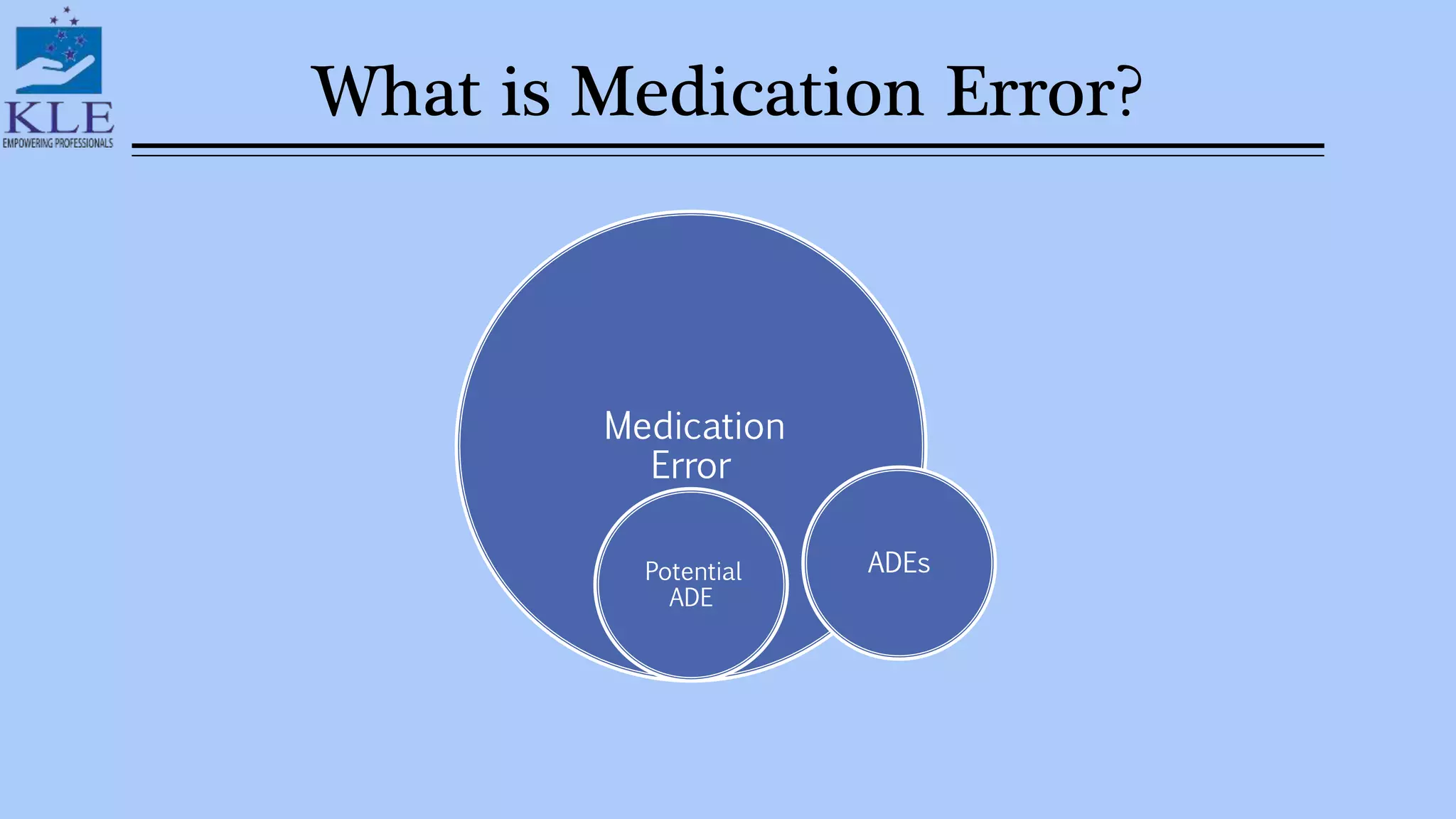
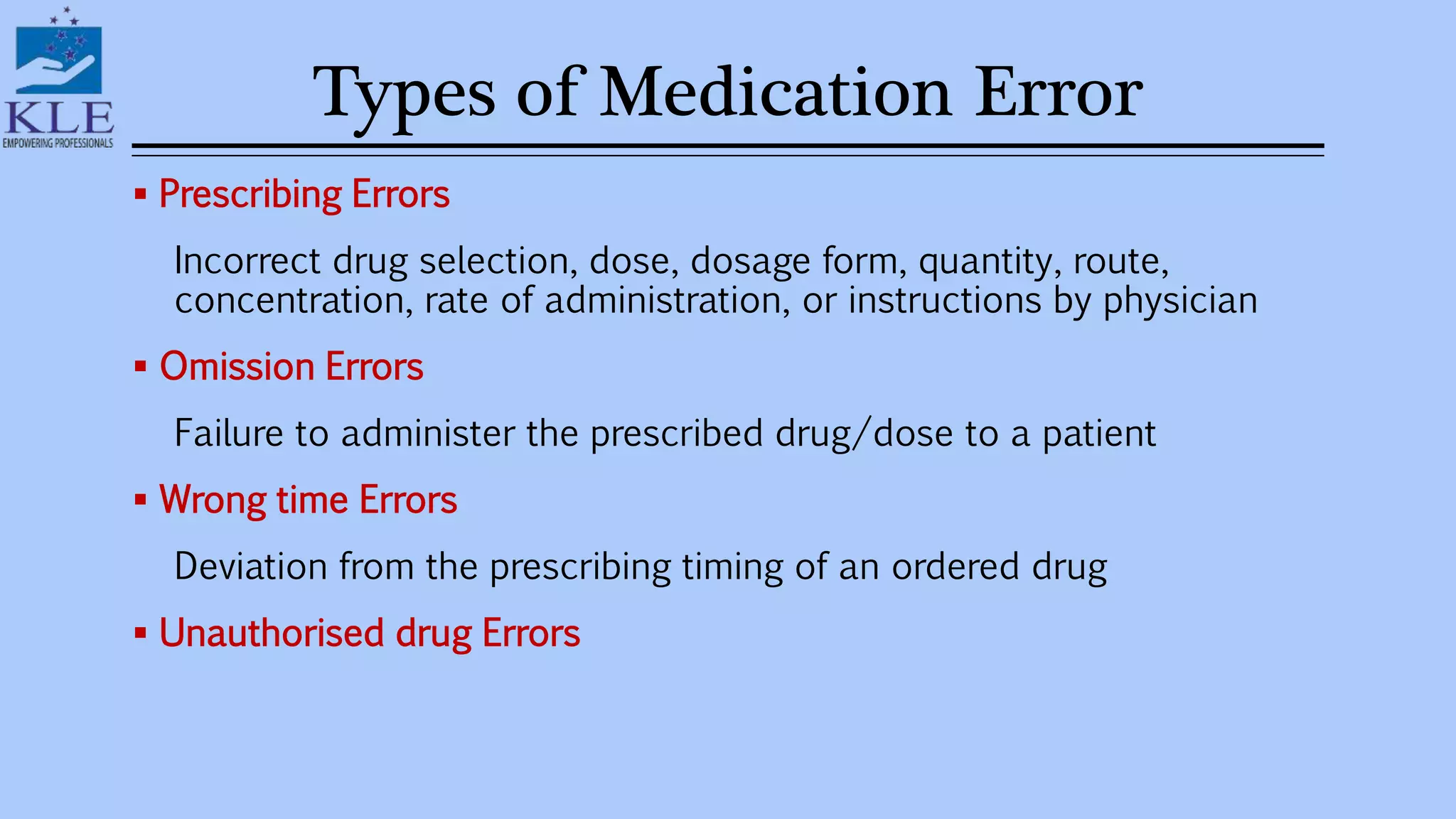
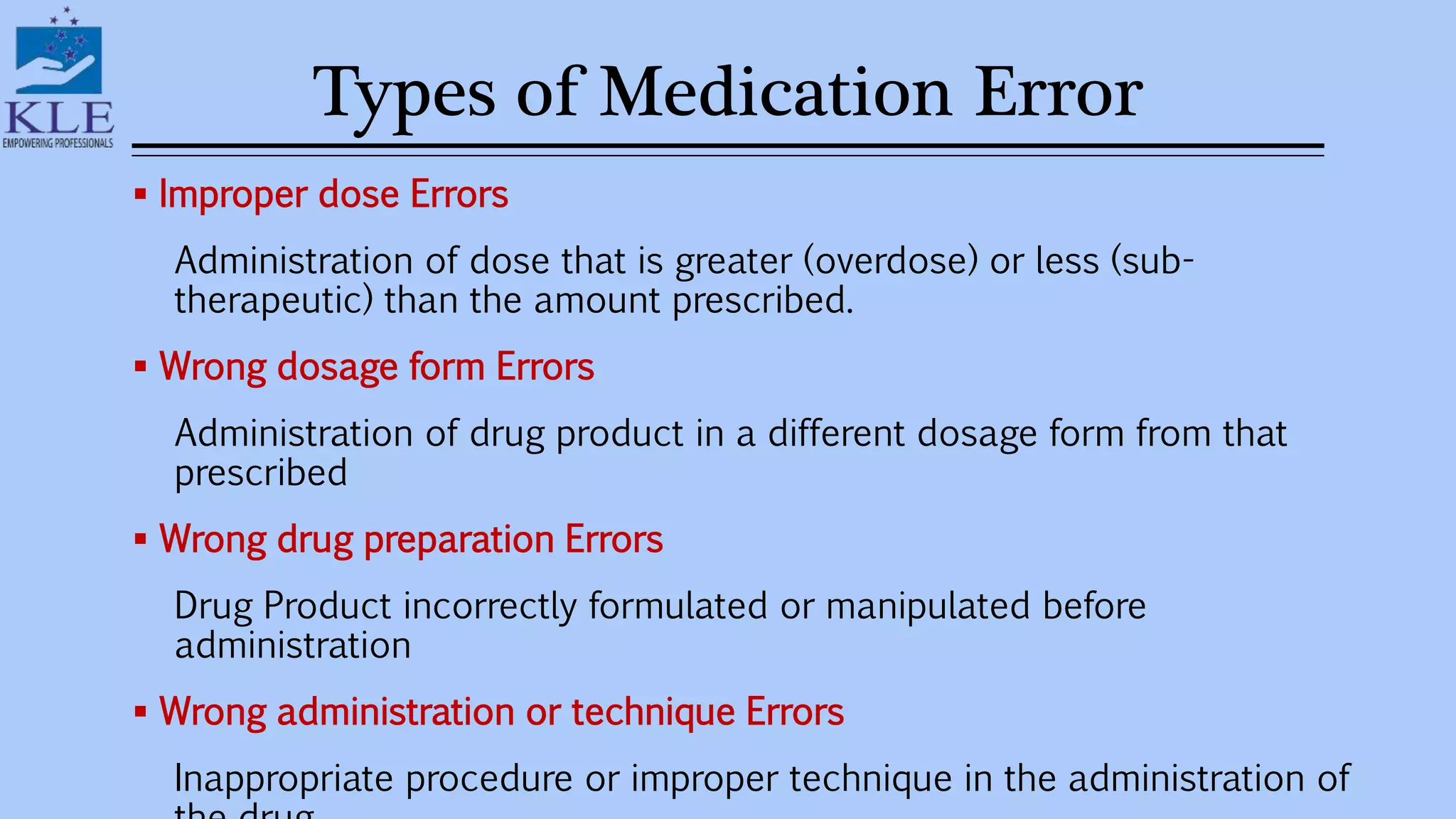
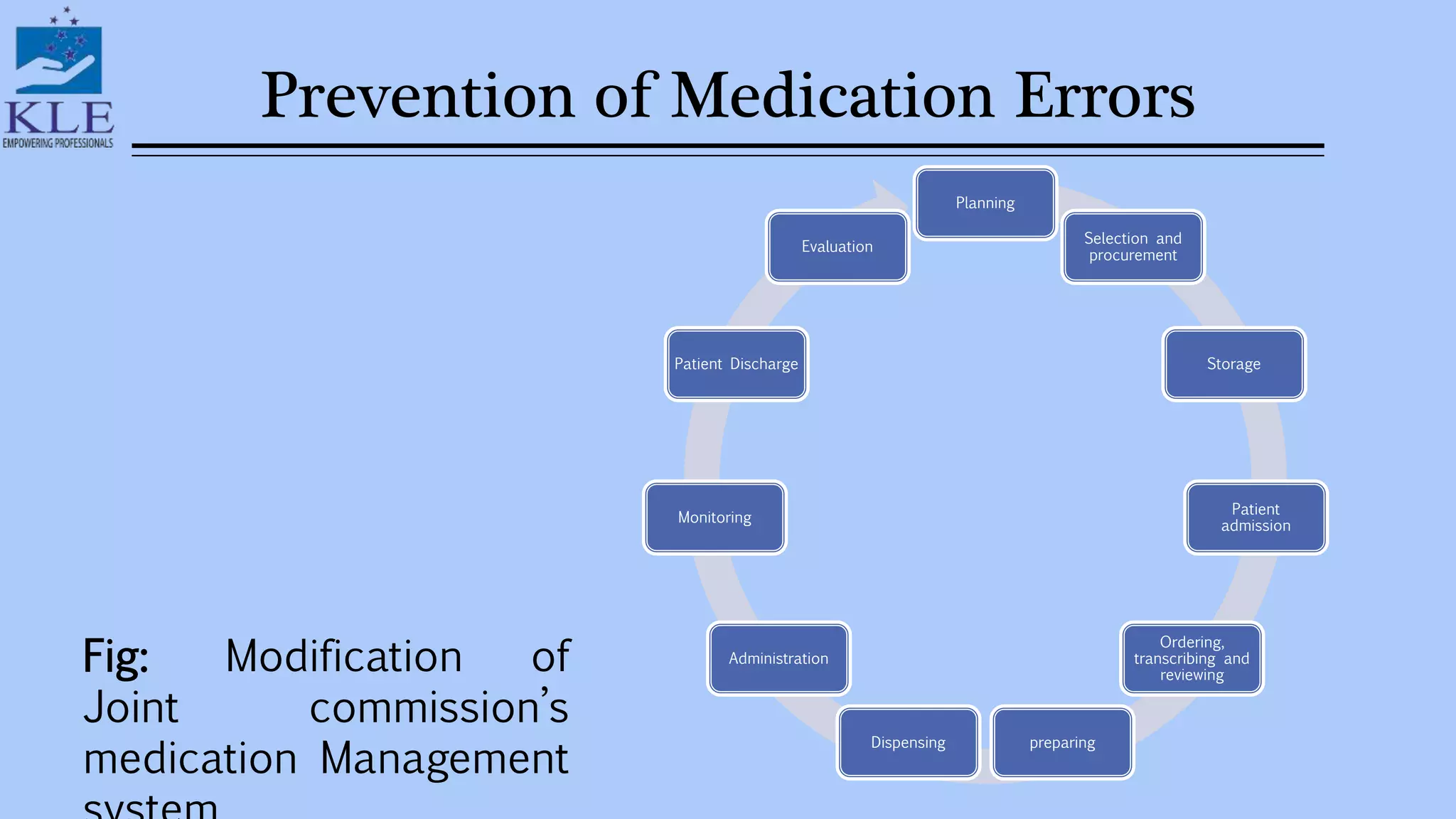
This document discusses medication errors, which are preventable events that can cause inappropriate medication use or harm to a patient. It defines medication errors based on definitions from the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists and the National Coordinating Committee on Medication Error Reporting and Prevention. Common types of medication errors include prescribing errors, dispensing errors, administration errors, and compliance errors. The document also discusses causes of medication errors and strategies to prevent errors, including standardized ordering processes, double checks, limiting abbreviations, and use of computerized prescriber order entry systems.