This document discusses medication errors, including definitions, types, contributing factors, detection, reporting processes, and prevention. The key points are:
- Medication errors are preventable events that may harm patients and are caused by mistakes in prescribing, dispensing, or administering drugs.
- Common types of errors include prescription errors, dispensing errors, administration errors, and transcription errors.
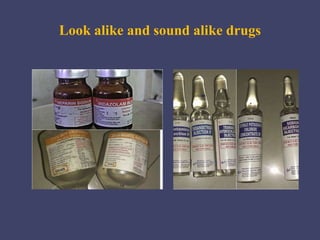
- Factors like look-alike drug names, poor communication, and environmental distractions contribute to errors.
- Errors can be detected through methods like medical rounds, medication administration records, and analyzing returned doses.
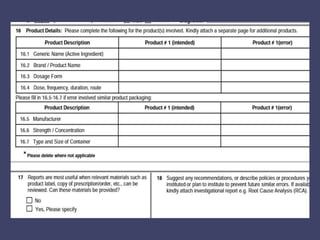
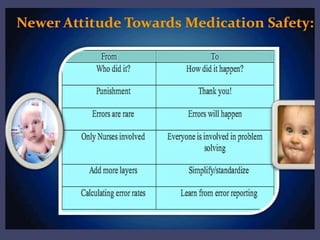
- Reporting helps identify root causes and improve safety, but relies on voluntary participation and protecting confidentiality