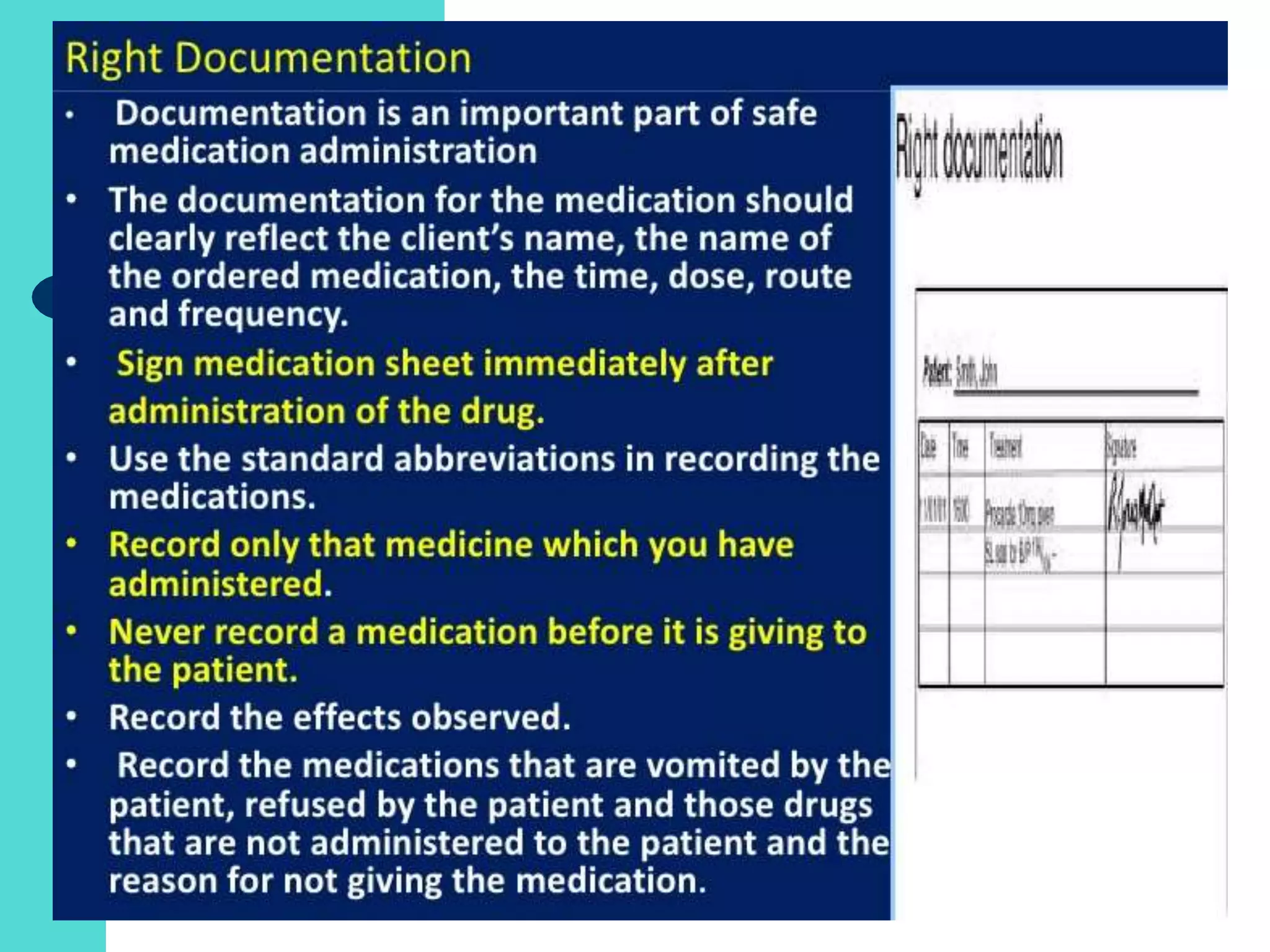
This document discusses key concepts related to safe medication administration in nursing. It defines key terms and outlines learning objectives. The document covers medication names, classifications, routes of administration, principles of drug action, and factors affecting drug safety. It also discusses medication orders, prescriptions, calculations, and legal aspects of medication administration. The goal is to develop knowledge around safe and effective medication practices in nursing.