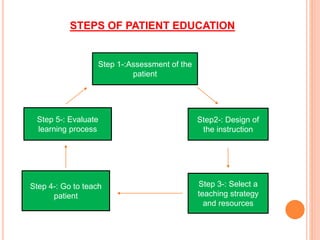
This document discusses patient education, including its definition, types, goals, objectives, steps, outcomes, and the nurse's role. Patient education aims to influence patient behavior and health by imparting knowledge and skills. It can be clinical education tailored for individual patients or broader health education. The goals are to help patients adapt, cooperate with treatment, and solve problems. Nurses play a key role in assessing patients, designing and delivering education, and evaluating outcomes. Effective patient education requires understanding barriers and tailoring the approach to each patient.