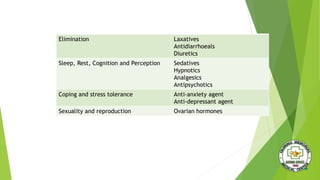
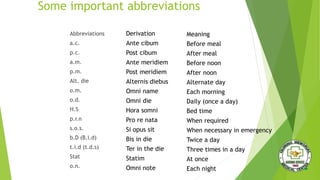
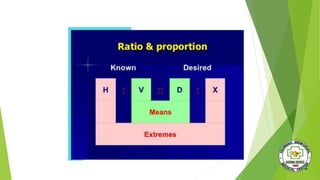
The document discusses safe medication administration. It defines key terms and outlines objectives related to administering medication properly. It discusses factors that affect drug action, legal implications, common abbreviations, and calculating dosages. The document also covers medication assessment, types of medication orders, routes of administration, and safety measures like the "five rights" to prevent errors.