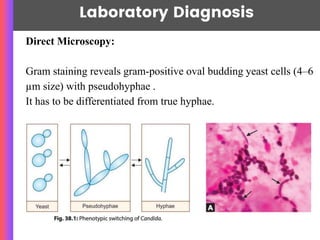
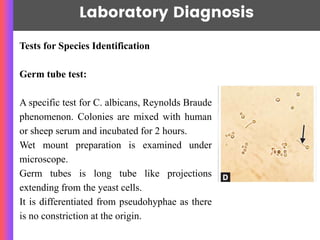
Candida albicans is a major pathogenic yeast that commonly causes opportunistic infections in immunocompromised individuals and forms part of the normal flora in various mucosal surfaces. The organism can lead to various clinical manifestations, including oral, genital, and invasive candidiasis, with diagnosis typically achieved through microscopy and culture methods. Treatment options include antifungal medications like amphotericin B, azoles, and echinocandins, though resistance is an emerging concern.