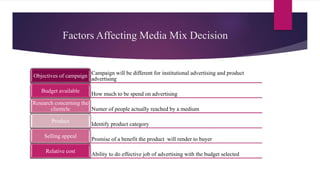
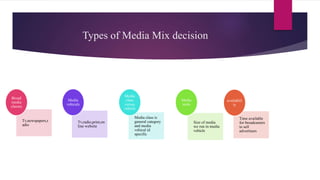
The document discusses various aspects of media planning and management. It covers topics like media mix, factors affecting media choices, different types of media like print, television, radio, out of home, and emerging digital media. It also discusses media strategy formulation including defining the target group, market prioritization, determining media weights and scheduling.